Abstract
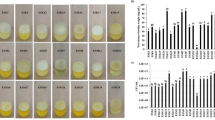
Salinity has a significant impact on the water quality and crop yield. Physical desalination techniques were once thought to be expensive and time-consuming. Among biological techniques, halotolerant bacteria were thought to be the fastest and most effective way to reduce the salt content in brackish saltwater water. In the current study, halotolerant bacterial biofilms were used to desalinate saline water on abiotic substrates (such as sand, pebbles, glass beads, and plastic beads), and studied subsequently for the effects on Zea mays germination. Briefly, salt samples (SLT7 and SLT8) from the Khewra site in Punjab, Pakistan, as well as seawater and sea sand samples (USW1, USW3, USW6, DSW1, DSW4, SS1, and SS3) from Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan’s Arabian Sea, were collected. Halotolerant bacteria were isolated and characterized. Crystal violet ring assays and capsule staining were used to estimate extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) and biofilm development, respectively. All halotolerant bacterial strains were spore formers and produced EPS and formed biofilms well. 16S rRNA gene sequencing of the best halotolerant bacteria, USW6, showed the closest (100%) similarity to Bacillus aerius strain G-07 (a novel species) (accession number ON202984). A pilot-scale experiment for desalinating the artificial water (supplemented with 1 M NaCl) using biofilm adhered abiotic beads showed declined level of NaCl from 1 M to 0.00003 M after 15 days in treated water. Also, Zea mays germination was observed in the plants using treated water compared to no growth in the non-treated saline water. Estimations of chlorophyll, total soluble sugar, and protein revealed that plants cultivated using elute collected from a desalinated pilot scale setup contained less chlorophyll (i.e., 5.994 and 116.76). Likewise, plants grown with elute had a total soluble protein and sugar content of 1.45 mg/ml and 1.3 mg/ml, respectively. Overall, in treated water plants, a minor drop in chlorophyll content, a slight increase in total soluble sugar content, and a slight increase in protein content were noted. The study concluded that biofilm-treated desalt water has the potential to significantly reduce the effects of droughts, soil salinization, and economic and environmental issues associated with agricultural drainage. The results specified the application of halotolerant bacteria biofilms (Bacillus aerius, a novel species, USW6) for water desalination to overcome the problem of water scarcity caused by global warming and the increased salinity.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data related to article is available in manuscript.
References
Ajibade FO, Adelodun B, Lasisi KH, Fadare OO, Ajibade TF, Nwogwu NA, Sulaymon ID, Ugya AY, Wang HC, Wang A (2021) Environmental pollution and their socioeconomic impacts. In Microbe mediated remediation of environmental contaminants (pp. 321–354). Woodhead Publishing
de Lourdes MM, Pérez D, García MT, Mellado E (2013) Halophilic bacteria as a source of novel hydrolytic enzymes. Life 3(1):38–51
Donkadokula NY, Naz I, Kola AK, Saroj D (2020) Assessment of the aerobic glass beads fixed biofilm reactor (GBs-FBR) for the treatment of simulated methylene blue wastewater. Sci Rep 10(1):1–14
Farooq F, Rashid N, Ibrar D, Hasnain Z, Ullah R, Nawaz M, Irshad S, Basra SM, Alwahibi MS, Elshikh MS, Dvorackova H (2022) Impact of varying levels of soil salinity on emergence, growth and biochemical attributes of four Moringa oleifera landraces. PLoS One 17(2):e0263978
Haque M, Biswas M, Mosharaf MK, Islam M, Nahar K, Shozib HB (2022) Halotolerant biofilm-producing rhizobacteria mitigate seawater-induced salt stress and promote growth of tomato. Sci Rep 12(1):1–22
Hong BH, Joe MM, Selvakumar G, Kim KY, Choi JH, Sa TM (2017) Influence of salinity variations on exocellular polysaccharide production, biofilm formation and flocculation in halotolerant bacteria. J Environ Biol 38(4):657
Hussain S, Shaukat M, Ashraf M, Zhu C, ** Q, Zhang J (2019) Salinity stress in arid and semi-arid climates: effects and management in field crops. Clim Change Agric 13
Jha S, Singh AA, Thakur N (2022) Role of exopolysaccharide and biofilms in microorganisms for alleviating salt stress. In Mitigation of Plant Abiotic Stress by Microorganisms (pp. 205–230). Academic Press
Li Y, He N, Hou J, Xu L, Liu C, Zhang J, Wang Q, Zhang X, Wu X (2018) Factors influencing leaf chlorophyll content in natural forests at the biome scale. Front Ecol Evol 6:64
Liaqat I, Bachmann RT, Edyvean RG (2014) Type 2 quorum sensing monitoring, inhibition and biofilm formation in marine microrganisms. Curr Microbiol 68(3):342–351
Liaqat I, Bachmann RT, NasimSabri A, Edyvean RG, Biggs CA (2008) Investigating the effect of patulin, penicillic acid and EDTA on biofilm formation of isolates from dental unit water lines. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:349–358
Liaqat I, Bachmann RT, Sabri AN, Edyvean RG (2010) Isolate-specific effects of patulin, penicillic Acid and EDTA on biofilm formation and growth of dental unit water line biofilm isolates. Curr Microbial 61(2):148–156
Liaqat I, Liaqat M, Tahir HM, Ali NM, Arshad M, Arshad N (2019) Motility effects biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter cloacae. Pak J Pharm Sci 1:32(3)
Liaqat I, Sabri AN (2009) Isolation and characterization of biocides resistant bacteria from dental unit water line biofilms. J Basic Microbiol 49(3):275–284
Liaqat I, Sumbal F, Sabri AN (2009) Tetracycline and chloramphenicol efficiency against selected biofilm forming bacteria. Curr Microbiol 59(2):212–220
Ling T (2022) A global study about water crisis. In 2021 International Conference on Social Development and Media Communication (SDMC 2021) (pp. 809–814). Atlantis Press
Locher K, Belanger CR, Eckbo E, Caza M, Velapatino B, Charles MK (2022) Automated 16S sequencing using an R-based analysis module for bacterial identification. Microbiol Spectr 10(2):e00408-e422
Mahdi I, Fahsi N, Hafidi M, Allaoui A, Biskri L (2020) Plant growth enhancement using rhizospheric halotolerant phosphate solubilizing bacterium Bacillus licheniformis QA1 and Enterobacter asburiae QF11 isolated from Chenopodium quinoa willd. Microorganisms 8(6):948
Nagaraju Y, Gundappagol RC (2020) Mining saline soils to manifest plant stress-alleviating halophilic bacteria. Curr Microbiol 77:2265–2278
Panagopoulos A, Giannika V (2022) Decarbonized and circular brine management/valorization for water & valuable resource recovery via minimal/zero liquid discharge (MLD/ZLD) strategies. J Environ Manage 324:116239
Panagopoulos A (2022) Process simulation and analysis of high-pressure reverse osmosis (HPRO) in the treatment and utilization of desalination brine (saline wastewater). Int J Energy Res
Panagopoulos A (2021) Water-energy nexus: desalination technologies and renewable energy sources. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(17):21009–21022
Qadeer A, Wakeel A, Cheema SA, Sanaullah M (2022) Interactive effects of salinity and drought stresses on soil respiration and microbial activities. Pak J Agric Sci 59(1):35–42
Qurashi AW, Sabri AN (2012) Biofilm formation in moderately halotolerant bacteria is influenced by varying salinity levels. J Basic Microbiol 52(5):566–572
Rafay M, Madnee M, Ashraf MI, Abid M, Ghaffar MU, Malik Z, Basit H, Hassan SU (2022) Phytoremediation capabilities and antioxidant enzymes’ activities of two halophytic shrubs Capparis Decidua and Haloxylon Salicornicum from Cholistan Desert, Pakistan Under Salinity Stress. Pak J Bot 54(4):1231–1236
Rathakrishnan D, Gopalan AK (2022) Isolation and characterization of halophilic isolates from Indian salterns and their screening for production of hydrolytic enzymes. Environ Chall 6:100426
Raval VH, Bhatt HB, Singh SP (2018) Adaptation strategies in halophilic bacteria. In Extremophiles (pp. 137–164). CRC Press
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425
Sehar S, Naz I (2016) Role of the biofilms in wastewater treatment. Microbial biofilms-importance and applications 121–144
Selvarajan R, Sibanda T, Tekere M, Nyoni H, Meddows-Taylor S (2017) Diversity analysis and bioresource characterization of halophilic bacteria isolated from a South African saltpan. Molecules 22(4):657
Subramanian SB, Yan S, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) producing bacterial strains of municipal wastewater sludge: isolation, molecular identification, EPS characterization and performance for sludge settling and dewatering. Water Res 44(7):2253–2266
Turan MA, Elkarim AH, Taban N, Taban S (2009) Effect of salt stress on growth, stomatal resistance, proline and chlorophyll concentrations on maize plant. Afr J Agric 4(9):893–897
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: IL and AWQ; methodology: SJG; formal analysis and investigation: SJG, AWQ, IL, UZ, MAV; writing — original draft preparation: SJG, AWQ, IL; writing — review and editing: SJG, IL, AWQ, UZ, CA, MF, MM; supervision: AWQ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gerald Thouand
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gauhar, S.J., Qurashi, A.W., Liaqat, I. et al. Halotolerant bacterial biofilms for desalination and water treatment: a pilot study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 72563–72574 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27411-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27411-5