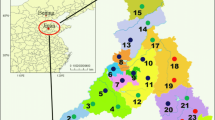
Abstract
Concern over the influences of constant addition of emerging anthropogenic chemicals to the environment has become a public issue during the rapid urbanization. Here, we investigated the occurrence of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in soil and corresponding tree bark in a megacity, Western China. Our results showed levels of OPEs in tree bark (1250 ± 573 ng/g dry weight (dw)) were 1–2 orders of magnitude higher than those in soil (40.4 ± 30.8 ng/g dw). Rooster Mountain is a background mountain area, exhibiting significantly lower concentrations of OPEs in soil and tree bark than those in other sites with relatively high population density. This result highlights the effect of human activities on the distribution of OPEs in environmental matrices. Alkyl-OPEs were predominant compounds in soil, whereas halogenated- (Cl-) OPEs were characterized in tree bark. Furthermore, tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate (TCEP) positively correlated with tris(2-chloroisopropyl) phosphate (TCIPP) in soil (r2 = 0.43, P < 0.05) while negatively correlated with TCIPP in tree bark (r2 = 0.31, P < 0.05). The ratios of logarithm concentrations of OPEs in tree bark to those in soil correlated well with logKOA values of OPEs from 6 to 10, indicating the equilibrium status was achieved between OPE partitioning in soil and in tree bark. Nevertheless, tris (2-butoxyethyl) phosphate (TBEP) and tris(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate (TEHP) with high values of logKOA deviated from this linear tendency, which was possibly due to the fact that they were subjected to the particle-bound deposition process, leading to partition into the soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript and published article.
References
Abdollahi A, Eng A, Jantunen LM, Ahrens L, Shoeib M, Parnis JM et al (2017) Characterization of polyurethane foam (PUF) and sorbent impregnated PUF (SIP) disk passive air samplers for measuring organophosphate flame retardants. Chemosphere 167:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.111
Aston LS, Seiber JN (1996) Methods for the comparative analysis of organophosphate residues in four compartments of needles of Pinus ponderosa. J Agric Food Chem 44:2728–2735. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf950197s
Blum A, Behl M, Birnbaum LS, Diamond ML, Phillips A, Singla V et al (2019) Organophosphate ester flame retardants: are they a regrettable substitution for polybrominated diphenyl ethers? Environ Sci Technol Lett 6:638–649. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.9b00582
Collins C, Fryer M, Grosso A (2006) Plant uptake of non-ionic organic chemicals. Environ Sci Technol 40:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0508166
Cui K, Wen J, Zeng F, Li S, Zhou X, Zeng Z (2017) Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate esters in urban soils of the subtropical city, Guangzhou, China. Chemosphere 175:514–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.070
Ding J, Xu Z, Huang W, Feng L, Yang F (2016) Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in human placenta in Eastern China. Sci Total Environ 554:211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.171
European Commission (2009) European Union risk assessment report: tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate, TCEP.
Fu X, Wang J, Zhou X, Deng J, Liu Y, Zhang W et al (2014) Tree bark as a passive air sampler to indicate atmospheric polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in southeastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7668–7677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2650-0
Ge X, Ma S, Zhang X, Yang Y, Li G, Yu Y (2020) Halogenated and organophosphorous flame retardants in surface soils from an e-waste dismantling park and its surrounding area: distributions, sources, and human health risks. Environ Int 139:105741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105741
Guéguen F, Stille P, Millet M (2011) Air quality assessment by tree bark biomonitoring in urban, industrial and rural environments of the Rhine Valley: PCDD/Fs, PCBs and trace metal evidence. Chemosphere 85:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.032
He C, ** J, Li G, Wang Y (2016) Exchange of organohalogen compounds between air and tree bark in the Yellow River region. Chemosphere 153:478–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.089
He MJ, Yang T, Yang ZH, Zhou H, Wei SQ (2018) Current state, distribution, and sources of phthalate esters and organophosphate esters in soils of the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 74(3):502–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0469-7
He J, Li J, Ma L, Wu N, Zhang Y, Niu Z (2019) Large-scale distribution of organophosphate esters (flame retardants and plasticizers) in soil from residential area across China: implications for current level. Sci Total Environ 697:133997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133997
Hermanson MH, Hites RA (1990) Polychlorinated biphenyls in tree bark. Environ Sci Technol 24:666–671. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00075a008
Hu JC, ** J, Wang Y, Ma Z, Zheng W (2011) Levels of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and hexabromocyclododecane in the atmosphere and tree bark from Bei**g, China. Chemosphere 84:355–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.04.002
Kim UJ, Kannan K (2018) Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate flameretardants/plasticizers in surface waters, tap water, and rainwater: implications for human exposure. Environ Sci Technol 52:5625–5633
Kipopoulou AM, Manoli E, Samara C (1999) Bioconcentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in vegetables grown in an industrial area. Environ Pollut 106:369–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00107-4
Kurt-Karakus P, Alegria H, Birgul A, Gungormus E, Jantunen L (2018) Organophosphate ester (OPEs) flame retardants and plasticizers in air and soil from a highly industrialized city in Turkey. Sci Total Environ 625:555–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.307
Krivoshiev BV, Beemster GTS, Sprangers K, Blust R, Husson SJ (2018) A toxicogenomics approach to screen chlorinated flame retardants tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate and tris(2-chloroisopropyl) phosphate for potential health effects. J Appl Toxicol 38:459–470. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3553
Li Q, Lu Y, ** J, Li G, Li P, He C et al (2016) Comparison of using polyurethane foam passive samplers and tree bark samples from Western China to determine atmospheric organochlorine pesticide. J Environ Sci 41:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.05.022
Li WH, Wang Y, Kannan K (2019) Occurrence, distribution and human exposure to 20 organophosphate esters in air, soil, pine needles, river water, and dust samples collected around an airport in New York state, United States. Environ Int 131:105054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105054
Liao C, Kim UJ, Kannan K (2020) Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate esters in sediment from northern Chinese coastal waters. Sci Total Environ 704:135328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135328
Liu R, Lin Y, Liu R, Hu F, Ruan T, Jiang G (2016) Evaluation of two passive samplers for the analysis of organophosphate esters in the ambient air. Talanta 147:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.09.034
Luo Q, Wang S, Sun LN, Wang H (2018) Simultaneous accelerated solvent extraction and purification for the determination of 13 organophosphate esters in soils by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:19546–19554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2047-6
Ma Y, **e Z, Lohmann R, Mi W, Gao G (2017) Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in ocean sediments from the north pacific to the arctic ocean. Environ Sci Technol 51(7):3809–3815. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00755
Marklund A, Andersson B, Haglund P (2003) Screening of organophosphorus compounds and their distribution in various indoor environments. Chemosphere 53:1137–1146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00666-0
Marklund A, Andersson B, Haglund P (2005) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in Swedish sewage treatment plants. Environ Sci Technol 39:7423–7429. https://doi.org/10.1021/es051013l
McDonough CA., De Silva AO, Sun C, Cabrerizo A, Adelman D, Soltwedel T, Bauerfeind E, Muir DCG, Lohmann R (2018) Dissolved organophosphate esters and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in remote marine environments: Arctic Surface water distributions and net transport through fram strait. Environ Sci Technol 52(11):6208–6216. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01127
Meredith ML, Hites RA (1987) Polychlorinated biphenyl accumulation in tree bark and wood growth rings. Environ Sci Technol 21:709–712. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00161a013
Mihajlovic I, Miloradov MV, Fries E (2011) Application of twisselmann extraction, SPME, and GC-MS to assess input sources for organophosphate esters into soil. Environ Sci Technol 45:2264–2269. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103870f
Möller A, **e Z, Caba A, Sturm R, Ebinghaus R (2011) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in the atmosphere of the North Sea. Environ Pollut 159(12):3660–3665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.07.022
Möller A, Sturm R, **e Z, Cai M, He J, Ebinghaus R (2012) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in airborne particles over the northern Pacific and Indian Ocean toward the polar regions: evidence for global occurrence. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3127–3134. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204272v
Odabasi M, Falay EO, Tuna G, Altiok H, Kara M, Dumanoglu Y et al (2015) Biomonitoring the spatial and historical variations of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in an industrial region. Environ Sci Technol 49:2105–2114. https://doi.org/10.1021/es506316t
Peverly AA, Salamova A, Hites RA (2014) Air is still contaminated 40 years after the Michigan chemical plant disaster in St. Louis, Michigan. Environ Sci Technol 48:11154–11160. https://doi.org/10.1021/es502809f
Peverly AA, Salamova A, Hites RA (2015) Locating POPs sources with tree bark. Environ Sci Technol 49:13743–13748. https://doi.org/10.1021/es505394y
Pier MD, Zeeb BA, Reimer KJ (2002) Patterns of contamination among vascular plants exposed to local sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in the Canadian Arctic and Subarctic. Sci Total Environ 297:215–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00134-1
Poma G, Glynn A, Malarvannan G, Covaci A, Darnerud PO (2017) Dietary intake of phosphorus flame retardants (PFRs) using Swedish food market basket estimations. Food Chem Toxicol 100:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.12.011
Ren G, Chen Z, Feng J, Ji W, Zhang J, Zheng K et al (2016) Organophosphate esters in total suspended particulates of an urban city in East China. Chemosphere 164:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.090
Ren GF, Chu XD, Zhang J, Zheng KW, Zhou XY, Zeng XY et al (2019) Organophosphate esters in the water, sediments, surface soils, and tree bark surrounding a manufacturing plant in north China. Environ Pollut 246:374–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.12.020
Salamova A, Hites RA (2010) Evaluation of tree bark as a passive atmospheric sampler for flame retardants, PCBs, and organochlorine pesticides. Environ Sci Technol 44:6196–6201. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101599h
Salamova A, Ma Y, Venie M, Hites RA (2014) High levels of organophosphate flame retardants in the Great Lakes Atmosphere. Environ Sci Technol Lett 1:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1021/ez400034n
Schulz H, Popp P, Huhn G, Stark HJ, Schuurmann G (1999) Biomonitoring of airborne inorganic and organic pollutants by means of pine tree barks. I. Temporal and spatial variations. Sci Total Environ 232:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00109-6
Schmidt N, Castro-Jimenez J, Fauvelle V, Ourgaud M, Sempere R (2020) Occurrence of organic plastic additives in surface waters of the Rhone River (France). Environ Pollut 257:113637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113637
Shi QP, Wang SFQ, Yang L, Guo YY, Feng CL et al (2018) Developmental neurotoxicity of triphenyl phosphate in zebrafish larvae. Aquat Toxicol 203:80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.08.001
Simonich SL, Hites RA (1995) Organic pollutant accumulation in vegetation. Environ Sci Technol 29:2905–2914. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00012a004
Stachel B, Jantzen E, Knoth W, Krüge F, Lepom P, Oetken M et al (2005) The Elbe flood in August 2002—organic contaminants in sediment samples taken after the flood event. J of Environ Sci and Health Part A 40:265–287. https://doi.org/10.1081/ESE-200045531
Sühring R, Diamond ML, Scheringer M, Wong F, Pucko M, Stern G et al (2016) Organophosphate esters in Canadian Arctic Air: occurrence, levels and trends. Environ Sci Technol 50:7409–7415. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00365
Tang JF, Sun J, Ke ZY, Yin HL, Yang L, Yen H et al (2021) Organophosphate esters in surface soils from a heavily urbanized region of Eastern China: occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk assessment. Environ Pollut 291:118200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118200
Tarcau D, Cucu-Man S, Boruvkova J, Klanova J, Covaci A (2013) Organochlorine pesticides in soil, moss, and tree-bark from northeastern Romania. Sci Total Environ 456:317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.03.103
Trapp S, Miglioranza KSB, Mosbaek H (2001) Sorption of lipophilic organic compounds to wood and implications for their environmental fate. Environ Sci Technol 35:1561–1566. https://doi.org/10.1021/es000204f
Van der Veen I, de Boer J (2012) Phosphorus flame retardants: properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 88:1119–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.067
Wang Y, Kannan K (2018) Concentrations and dietary exposure to organophosphate esters in foodstuffs from Albany, New York, United States. J Agric Food Chem 66:13525–13532. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06114
Wang QQ, Zhao YL, Yan D, Yang LM, Li ZJ, Huang BL (2004) Historical records of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by analyzing dated corks of the bark pocket in a Long petiole Beech tree. Environ Sci Technol 38:4739–4744. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049685j
Wang Q, Lam JCW, Man YC, Lai NLS, Kwok KY, Guo YY et al (2015) Bioconcentration, metabolism and neurotoxicity of the organophorous flame retardant 1,3-dichloro 2-propyl phosphate (TDCPP) to zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 158:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.11.001
Wang Y, Yao Y, Han X, Li W, Zhu H, Wang L et al (2019a) Organophosphate di and tri-esters in indoor and outdoor dust from China and its implications for human exposure. Sci Total Environ 700:134502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134502
Wang Y, Yao Y, Li W, Zhu H, Wan L, Sun H et al (2019b) A nationwide survey of 19 organophosphate esters in soils from China: spatial distribution and hazard assessment. Sci Total Environ 671:528–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.335
Wang X, Zhu Q, Yan X, Wang Y, Liao C, Jiang G (2020) A review of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in the environment: analysis, occurrence and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 731:139071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139071
Wei GL, Li DQ, Zhuo MN, Liao YS, **e ZY, Guo TL et al (2015) Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers: sources, occurrence, toxicity and human exposure. Environ Pollut 196:29–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.09.012
Yadav IC, Devi NL, Zhong G, Li J, Zhang G, Covaci A (2017) Occurrence and fate of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in indoor air and dust of Nepal: implication for human exposure. Environ Pollut 229:668–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.06.089
Yadav IC, Devi NL, Li J, Zhang G, Covaci A (2018) Concentration and spatial distribution of organophosphate esters in the soil-sediment profile of Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: implication for risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 613–614:502–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.039
Yin HL, Li SP, Ye ZX, Liang JF, You JJ (2016) Pollution characteristics and sources of OPEs in the soil of Chengdu City. Acta Sci Circumst 36(2):606–613. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2015.0489 ((in Chinese))
Zhang B, Lu S, Huang M, Zhou M, Zhou Z, Zheng H et al (2018) Urinary metabolites of organophosphate flame retardants in 0–5-year-old children: potential exposure risk for inpatients and home-stay infants. Environ Pollut 243:318–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.051
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Jiang X, Xu H, Luo Y, Long T et al (2021) Spatial occurrence and composition profile of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in farmland soils from different regions of China: implications for human exposure. Environ Pollut 276:116729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116729
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Zhang C, Yao Y, Wang L, Sun H (2022) A review of organophosphate esters in soil: implications for the potential source, transfer, and transformation mechanism. Environ Res 204:112122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112122
Zhao YL, Yang LM, Wang QQ (2008) Modeling persistent organic pollutant (POP) partitioning between tree bark and air and its application to spatial monitoring of atmospheric POPs in mainland China. Environ Sci Technol 42:6046–6051. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800188q
Zhu L, Hites RA (2006) Brominated flame retardants in tree bark from North America. Environ Sci Technol 40:3711–3716. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060225v
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0085).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CW wrote the manuscript. RY sampled and conducted the experimental treatment. SW gave some suggestion about the manuscript. MH conceived the project and revised the manuscript. All of the authors contributed to the final review of the submitted manuscript and gave final approval for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
We the authors are giving our ethical approval and consent for this paper to be published in your journal if found publishable.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and approved this manuscript and take responsibility for its contents. The participant has consented to the submission of the manuscript to the journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Thomas D. Bucheli
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Yuan, RY., Wei, SQ. et al. Occurrence, correlation, and partitioning of organophosphate esters in soil and tree bark from a megacity, Western China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 4359–4371 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22444-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22444-8