Abstract
Background
Breast cancer (BC) accounts for a significant share of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Ongoing investigations have shown that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) drive BC progression but their underlying mechanisms remain largely undescribed. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 was previously identified in BC but its functional significance remained to be fully investigated.
Methods
KCNQ1OT1 and its downstream target genes were analyzed in breast cancer tissues and cell lines using methods including RT-qPCR, immunohistochemistry and Western blotting. The effects of KCNQ1OT1, miR-34a and Notch3 on BC cells were investigated using assays measuring proliferation (CCK-8, colony formation), apoptosis, and migration/invasion (scratch and Transwell assays). MS2-RIP and dual-luciferase reporter assays were used to study RNA interactions. Xenograft studies were employed to define the tumorigenic potential of KCNQ1OT1 in vivo.
Results
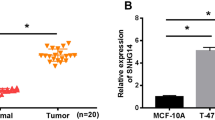
KCNQ1OT1 expression was up-regulated in BC tissues and high levels were associated with poorer prognosis. ShRNA inhibition of KCNQ1OT1 expression in BC cell lines retarded proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. Up-regulation of KCNQ1OT1 was shown to inhibit miR-34a which was associated with blocking the inhibitory effect of miR-34a on BC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Notch3 was found to be a downstream target of miR-34a with KCNQ1OT1 markedly inducing Notch3 expression in BC. Evidence for KCNQ1OT1/miR-34a/Notch3 axis was further established in clinical BC samples.
Conclusion
We identified a KCNQ1OT1/miR-34a/Notch3 axis which promotes BC progression through effects on cell proliferation and metastasis that was further associated with poor patient prognosis. These results propose targeting this axis as novel treatment approach for BC.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- BC:
-
Breast cancer
- KCNQ1OT1:
-
KCNQ1 overlap** transcript
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- HER-2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- KCNQ1OT1:
-
KCNQ1 overlap** transcript 1
- LncRNA:
-
Long non-coding RNA
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- ncRNA:
-
Non-coding RNA
References
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ (1999) Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284:770–776
Bader AG (2012) MiR-34 - a microRNA replacement therapy is headed to the clinic. Front Genet 3:120
Beg MS, Brenner AJ, Sachdev J, Borad M, Kang Y-K, Stoudemire J, Smith S, Bader AG, Kim S, Hong DS (2017) Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 35:180–188
Bhattacharya T, Maishu SP, Akter R, Rahman MH, Akhtar MF, Saleem A, Bin-Jumah M, Kamel M, Abdel-Latif MA, Abdel-Daim MM (2021) A Review on Natural Sources Derived Protein Nanoparticles as Anticancer Agents. Curr Top Med Chem 21:1014–1026
Browne G, Dragon JA, Hong D, Messier TL, Gordon JA, Farina NH, Boyd JR, VanOudenhove JJ, Perez AW, Zaidi SK (2016) MicroRNA-378-mediated suppression of Runx1 alleviates the aggressive phenotype of triple-negative MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Tumor Biology 37:8825–8839
Chiesa N, De Crescenzo A, Mishra K, Perone L, Carella M, Palumbo O, Mussa A, Sparago A, Cerrato F, Russo S (2012) The KCNQ1OT1 imprinting control region and non-coding RNA: new properties derived from the study of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and Silver-Russell syndrome cases. Hum Mol Genet 21:10–25
Dong Z, Yang P, Qiu X, Liang S, Guan B, Yang H, Li F, Sun L, Liu H, Zou G (2019) KCNQ1OT1 facilitates progression of non-small-cell lung carcinoma via modulating miRNA-27b-3p/HSP90AA1 axis. J Cell Physiol 234:11304–11314
Eichelser C, Flesch-Janys D, Chang-Claude J, Pantel K, Schwarzenbach HJCc (2013) Deregulated serum concentrations of circulating cell–free microRNAs miR-17, miR-34a, miR-155, and miR-373 in human breast cancer development and progression. Clin Chem 59:1489–1496
Feng W, Wang C, Liang C, Yang H, Chen D, Yu X, Zhao W, Geng D, Li S, Chen Z et al (2018) The dysregulated expression of KCNQ1OT1 and its interaction with downstream factors miR-145/CCNE2 in breast cancer cells. Cell Physiol 49:432–446
Gao J, Li N, Dong Y, Li S, Xu L, Li X, Li Y, Li Z, Ng S, Sung J (2015) miR-34a-5p suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis and predicts recurrence in patients with stage II/III colorectal cancer. Oncogene 34:4142–4152
Graziani I, Eliasz S, De Marco MA, Chen Y, Pass HI, Richard M, Strack PR, Miele L, Bocchetta M (2008) Opposite effects of Notch-1 and Notch-2 on mesothelioma cell survival under hypoxia are exerted through the Akt pathway. Can Res 68:9678–9685
Kabir MT, Rahman MH, Akter R, Behl T, Kaushik D, Mittal V, Pandey P, Akhtar MF, Saleem A, Albadrani GM, et al (2021) Potential Role of Curcumin and Its Nanoformulations to Treat Various Types of Cancers. Biomolecules 11:392
Kang L, Mao J, Tao Y, Song B, Ma W, Lu Y, Zhao L, Li J, Yang B, Li L (2015) Micro RNA-34a suppresses the breast cancer stem cell-like characteristics by downregulating Notch1 pathway. Cancer Sci 106:700–708
Kang Y, Jia Y, Wang Q, Zhao Q, Song M, Ni R, Wang JJO (2019) Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer via regulating miR-204–5p/ATG3 axis. Onco Targets Ther 12:10787-10797
Khan MJ, Singh P, Dohare R, Jha R, Rahmani AH, Almatroodi SA, Ali S, Syed MA (2020) Inhibition of miRNA-34a Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization and Improves LPS-Induced Lung Injury by Targeting Klf4. Genes 11:966
Leontovich AA, Jalalirad M, Salisbury JL, Mills L, Haddox C, Schroeder M, Tuma A, Guicciardi ME, Zammataro L, Gambino MWJBCR (2018) NOTCH3 expression is linked to breast cancer seeding and distant metastasis. Breast Cancer Res 20:1–19
Li L, Yuan L, Luo J, Gao J, Guo J, **e X (2013a) MiR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1. Clinical Experimental Medicine 13:109–117
Li H, Yu B, Li J, Su L, Yan M, Zhu Z, Liu B (2014) Overexpression of lncRNA H19 enhances carcinogenesis and metastasis of gastric cancer. OncoTargets 5:2318
Li Y, Li C, Li D, Yang L, ** J, Zhang B, therapy, (2019) lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 enhances the chemoresistance of oxaliplatin in colon cancer by targeting the miR-34a/ATG4B pathway. OncoTargets 12:2649
Li L, **e X, Luo J, Liu M, ** S, Guo J, Kong Y, Wu M, Gao J, **e ZJMT (2012). Targeted expression of miR-34a using the T-VISA system suppresses breast cancer cell growth and invasion. Mol Ther 20:2326–2334
Li L, Yuan L, Luo J, Gao J, Guo J, **e XJC (2013b) MiR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1. Clin Exp Med 13:109–117
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X, Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S (2011) The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med 17:211–215
Lu X, Wang F, Fu M, Li Y, and Wang L (2019). Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 accelerates the progression of ovarian cancer via microRNA-212–3/ LCN2 axis. Oncology Research Featuring Preclinical Clinical Cancer Therapeutics 28.
Nie ZL, Wang YS, Mei YP, Lin X, Zhang GX, Sun HL, Wang YL, **a YX, Wang SK (2018) Prognostic significance of long noncoding RNA Z38 as a candidate biomarker in breast cancer. J clin lab anal 32:e22193
Ren F, Zhang X, Liang H, Luo D, Rong M, Dang Y, Chen G (2015) Prognostic significance of MiR-34a in solid tumors: a systemic review and meta-analysis with 4030 patients. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:17377
Shen Y, Xu J, Pan X, Zhang Y, Weng Y, Zhou D, He S, disease, (2020) LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 sponges miR-34c-5p to promote osteosarcoma growth via ALDOA enhanced aerobic glycolysis. Cell Death Dis 11:1–14
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 71:7–33
Singh V, Kumar K, Purohit D, Verma R, Pandey P, Bhatia S, Malik V, Mittal V, Rahman MH, Albadrani GM et al (2021) Exploration of therapeutic applicability and different signaling mechanism of various phytopharmacological agents for treatment of breast cancer. Biomed pharmacother Biomed pharmacother 139:111584
Tao S, He H, Chen Q (2015) Estradiol induces HOTAIR levels via GPER-mediated miR-148a inhibition in breast cancer. J Transl Med 13:1–8
Wang J, Dan G, Zhao J, Ding Y, Ye F, Sun H, Jiang F, Cheng J, Yuan F, Zou Z et al (2015a) The predictive effect of overexpressed miR-34a on good survival of cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. OncoTargets 8:2709
Wang L, Cai Y, Zhao X, Jia X, Zhang J, Liu J, Zhen H, Wang T, Tang X, Liu Y (2015b) Down-regulated long non-coding RNA H19 inhibits carcinogenesis of renal cell carcinoma. Neoplasma 62:412–418
Wang B, He G, Xu G, Wen J, Yu X (2019) miRNA-34a inhibits cell adhesion by targeting CD44 in human renal epithelial cells: implications for renal stone disease. Urolithiasis 48:109-116
Wu L, Pan C, Wei X, Shi Y, Zheng J, Lin X, Shi L (2018a) lncRNA KRAL reverses 5-fluorouracil resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by acting as a ceRNA against miR-141. Cell Commun Signal 16:1–15
Wu Q-B, Sheng X, Zhang N, Yang M-W, Wang F (2018b) Role of microRNAs in the resistance of colorectal cancer to chemoradiotherapy. Mol Clin Oncol 8:523–527
Wu Y, Bi Q-J, Han R, Zhang Y, Biology C (2020) Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 is correlated with human breast cancer cell development through inverse regulation of hsa-miR-107. Biochemistry 98:338–344
**ng Z, Park PK, Lin C, Yang L (2015) LncRNA BCAR4 wires up signaling transduction in breast cancer. RNA Biol 12:681–689
Yen W-C, Fischer MM, Axelrod F, Bond C, Cain J, Cancilla B, Henner WR, Meisner R, Sato A, Shah J (2015) Targeting Notch signaling with a Notch2/Notch3 antagonist (tarextumab) inhibits tumor growth and decreases tumor-initiating cell frequency. Clin Cancer Res 21:2084–2095
Zhang Y, Wei C, Guo CC, Bi RX, **e J, Guan DH, Yang CH, Jiang YH (2017) Prognostic value of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. OncoTargets 8:107237
Zhang S, Ma H, Zhang D, **e S, Wang W, Li Q, Lin Z, Wang Y (2018) LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 regulates proliferation and cisplatin resistance in tongue cancer via miR-211-5p mediated Ezrin/Fak/Src signaling. Cell Death Dis 9:1–16
Zhao J, Pu J, Hao B, Huang L, Chen J, Hong W, Zhou Y, Li B, Ran P (2020) LncRNA RP11-86H7. 1 promotes airway inflammation induced by TRAPM2. 5 by acting as a ceRNA of miRNA-9-5p to regulate NFKB1 in HBECS. Sci Rep 10:1–14
Zhao W, Geng D, Li S, Chen Z, Sun MJCm (2018) Lnc RNA HOTAIR influences cell growth, migration, invasion, and apoptosis via the miR‐20a‐5p/HMGA 2 axis in breast cancer. Cancer Med 7:842–855
Zhou K, Ou Q, Wang G, Zhang W, Hao Y, Li W (2019) High long non-coding RNA NORAD expression predicts poor prognosis and promotes breast cancer progression by regulating TGF-β pathway. Cancer Cell Int 19:1–7
Zuo Y, Li Y, Zhou Z, Ma M, Fu K, Pharmacotherapy, (2017) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes proliferation and invasion via targeting miR-129-5p in triple-negative breast cancer. Biomedicine 95:922–928
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Wu Jie** Medical Foundation (No. 320.6750.2020-7-1) to MR. The authors would like to express their gratitude to EditSprings (https://www.editsprings.cn/) for the expert linguistic services provided.
Funding
This study was supported by Wu Jie** Medical Foundation (No. 320.6750.2020–7-1) to MR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZYR and MR conceived and designed the research. ZYR, YFX and XW carried out experiments and analyzed the data. ZYR, YFX and XW wrote the main manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the research in ensuring that the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The ethics approval and consent to participate was obtained from The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Z., Xu, Y., Wang, X. et al. KCNQ1OT1 affects cell proliferation, invasion, and migration through a miR-34a / Notch3 axis in breast cancer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 28480–28494 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18434-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18434-x