Abstract
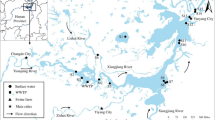
The objective of this study was to evaluate the occurrence, distribution, potential sources, and ecological risk of antibiotics in aqueous phase of Lake Guchenghu, China. Target antibiotics in surface water of Lake Guchenghu, adjacent streams, and crab ponds were detected seasonally. The results showed that erythromycin-H2O (1.60–2450 ng/L), sulfadiazine (ND–654 ng/L), and florfenicol (ND–919 ng/L) were the predominant antibiotics in Lake Guchenghu. The concentrations of antibiotics in Lake Guchenghu Basin showed obvious seasonal variation, with the highest concentration in summer. In general, the concentrations of antibiotics in crab ponds and streams were higher than those in the lake and spatial distributions of antibiotics were affected by pollution sources. The types and origins of antibiotics indicated that wastewater from ponds was the main source of antibiotics in the lake. Risk assessment suggested that as individual compound, erythromycin-H2O and clarithromycin posed a high risk to algae while other compounds might pose low or no risk. The mixture of antibiotics may pose a high risk to aquatic organisms in Lake Guchenghu. Overall, our study revealed the occurrence and spatiotemporal variation of antibiotics in Lake Guchenghu, which was related with crab culturing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderman DJ, Hastings TS (1998) Antibiotic use in aquaculture: development of antibiotic resistance—potential for consumer health risks. Int J Food Sci Technol 33(2):139–155
Andrieu M, Rico A, Phu TM, Huong do TT, Phuong NT, Van den Brink PJ (2015) Ecological risk assessment of the antibiotic enrofloxacin applied to Pangasius catfish farms in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Chemosphere 119:407–414
Backhaus T, Faust M (2012) Predictive environmental risk assessment of chemical mixtures: a conceptual framework. Environ Sci Technol 46:2564–2573
Backhaus T, Karlsson M (2014) Screening level mixture risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in STP effluents. Water Res 49:157–165
Boonsaner M, Hawker DW (2015) Transfer of oxytetracycline from swine manure to three different aquatic plants: implications for human exposure. Chemosphere 122:176–182
Cabello FC, Godfrey HP, Tomova A, Ivanova L, Dolz H, Millanao A, Buschmann AH (2013) Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ Microbiol 15(7):1917–1942
Cheng DM, Liu XH, Wang L, Gong WW, Liu GN, Fu WJ, Cheng M (2014) Seasonal variation and sediment–water exchange of antibiotics in a shallower large lake in North China. Sci Total Environ 476–477:266–275
Chen H, Liu S, Xu XR, Liu SS, Zhou GJ, Sun KF, Zhao JL, Ying GG (2015) Antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding Hailing Island, South China: occurrence, bioaccumulation and human dietary exposure. Mar Pollut Bull 90(1–2):181–187
Chen H, Liu S, Xu XR, Diao ZH, Sun KF, Hao QW, Liu SS, Ying GG (2018) Tissue distribution, bioaccumulation characteristics and health risk of antibiotics in cultured fish from a typical aquaculture area. J Hazard Mater 343:140–148
Dong DM, Zhang LW, Liu S, Guo ZY, Hua XY (2016) Antibiotics in water and sediments from Liao River in Jilin Province, China: occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment. Environ Earth Sci 75:1202
Du J, Zhao HX, Liu SS, **e HJ, Wang Y, Chen JW (2017) Antibiotics in the coastal water of the South Yellow Sea in China: occurrence, distribution and ecological risks. Sci Total Environ 595:521–527
FAO (2006) Cultured aquatic species information programme. Eriocheir sinensis. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department, Rome
Fisher WS, Nelson RT (1978) Application of antibiotics in the cultivation of Dungeness crab, Cancer magister. J Fish Res Board Can 35(10):1343–1349
García-Galána MJ, SilviaDíaz-Cruza M, Barcelóa D (2011) Occurrence of sulfonamide residues along the Ebro river basin: removal in wastewater treatment plants and environmental impact assessment. Environ Int 37(2):462–473
Gullberg E, Cao S, Berg OG, Ilback C, Sandegren L, Hughes D, Andersson DI (2011) Selection of resistant bacteria at very low antibiotic concentrations. PLoS Pathog 7(7):1002158–1002167
Haller MY, Müller SR, McArdell CS, Alder AC, Suter MJF (2002) Quantification of veterinary antibiotics (sulfonamides and trimethoprim) in animal manure by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 952:111–120
He Z, Cheng X, Kyzas GZ, Fu J (2016) Pharmaceuticals pollution of aquaculture and its management in China. J Mol Liq 223:781–789
Heberer T, Massmann G, Fanck B, Taute T, Duennbier U (2008) Behaviour and redox sensitivity of antimicrobial residues during bank filtration. Chemosphere 73:451–460
Heuer H, Focks A, Lamshöft M, Smalla K, Matthies M, Spiteller M (2008) Fate of sulfadiazine administered to pigs and its quantitative effect on the dynamics of bacterial resistance genes in manure and manured soil. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1892–1900
Hoa PT, Managaki S, Nakada N, Takada H, Shimizu A, Anh DH, Viet PH, Suzuki S (2011) Antibiotic contamination and occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquatic environments of northern Vietnam. Sci Total Environ 409(15):2894–2901
Karthikeyan KG, Meyer MT (2006) Occurrence of antibiotics in wastewater treatment facilities in Wisconsin, USA. Sci Total Environ 361(1–3):196–207
Kay P, Blackwell PA, Boxall ABA (2005) Transport of veterinary antibiotics in overland flow following the application of slurry to arable land. Chemosphere 59:951–959
Kümmerer K (2009a) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment–a review–part I. Chemosphere 75:417–434
Kümmerer K (2009b) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—a review—part II. Chemosphere 75:435–441
Lee YJ, Lee SE, Lee DS, Kim YH (2008) Risk assessment of human antibiotics in Korean aquatic environment. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 26(2):216–221
Le-Minh N, Khan SJ, Drewes JE, Stuetz RM (2010) Fate of antibiotics during municipal water recycling treatment processes. Water Res 44:4295–4323
Li W, Shi Y, Gao L, Liu J, Cai Y (2012) Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 89:1307–1315
Li Y, Li Q, Zhou K, Sun XL, Zhao LR, Zhang YB (2016) Occurrence and distribution of the environmental pollutant antibiotics in Gaoqiao mangrove area, China. Chemosphere 147:25–35
Li QZ, Gao JX, Zhang QL, Liang LZ, Tao H (2017) Distribution and risk assessment of antibiotics in a typical river in North China Plain. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98:478–483
Liu X, Steele JC, Meng XZ (2017) Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: A review. Environ Pollut 223:161–169
Luo Y, Xu L, Rysz M, Wang Y, Zhang H, Alvarez PJJ (2011) Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ Sci Technol 45(5):1827–1833
Matyar F, Gulnaz O, Guzeldag G, Mercimek HA, Akturk S, Arkut A, Sumengen M (2014) Antibiotic and heavy metal resistance in Gram-negative bacteria isolated from the Seyhan Dam Lake and Seyhan River in Turkey. Ann Microbiol 64(3):1033–1040
Peng X, Ou W, Wang C, Wang Z, Huang Q, ** J, Tan J (2014) Occurrence and ecological potential of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in groundwater and reservoirs in the vicinity of municipal landfills in China. Sci Total Environ 490:889–898
Pouliquen H, Delpepee R, Larhantec-Verdier M, Morvan ML, Le Bris H (2007) Comparative hydrolysis and photolysis of four antibacterial agents (oxytetracycline oxolinic acid, flumequine and florfenicol) in deionised water, freshwater and seawater under abiotic conditions. Aquaculture 262:23–28
Rico A, Phu TM, Satapornvanit K, Jiang M, Shahabuddin AM, Henriksson PJG, Murray FJ, Little DC, Dalsgaard A, Brink PJVD (2013) Use of veterinary medicines, feed additives and probiotics in four major internationally traded aquaculture species farmed in Asia. Aquaculture 412–413(2):231–243
Romero-González R, López-Martínez JC, Gómez-Milán E, Garrido-Frenich A, Martínez-Vidal JL (2007) Simultaneous determination of selected veterinary antibiotics in gilthead seabream (SparusAurata) by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 857(1):142–148
Rose PE, Pedersen JA (2005) Fate of oxytetracycline in streams receiving aquaculture discharges: model simulations. Environ Toxicol Chem 24(1):40–50
Santos L, Ramos F (2016) Analytical strategies for the detection and quantification of antibiotic residues in aquaculture fishes—a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 52:16–30
Sapkota A, Sapkota AR, Kucharski M, Burke J, McKenzie S, Walker P, Lawrence R (2008) Aquaculture practices and potential human health risks: current knowledge and future priorities. Environ Int 34:1215–1226
Sarmah AK, Meyer MT, Boxall AB (2006) A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 65:725–759
Seyfried EE, Newton RJ, Rubert KF, Pedersen JA, McMahon KD (2010) Occurrence of tetracycline resistance genes in aquaculture facilities with varying use of oxytetracycline. Microb Ecol 59(4):799–807
Song C, Zhang C, Fan LM, Qiu LP, Wu W, Meng SL, Hu GD, Kamira B, Chen JZ (2016) Occurrence of antibiotics and their impacts to primary productivity in fishponds around Tai Lake, China. Chemosphere 161:127–135
Tang J, Shi TZ, Wu XW, Cao HQ, Li XD, Hua RM, Tang F, Yue YD (2015) The occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in Lake Chaohu, China: seasonal variation, potential source and risk assessment. Chemosphere 122:154–161
Toroglu S, Toroglu E, Dincer S, Kara C, Kertmen M (2009) Resistances of antibiotics and heavy metals in Enterobacteriaceae spp. isolated from gills and intestines of Achanthobrama marmid (Heckel, 1843) from Sir Dam lake Turkey. J Environ Biol 30(1):23–31
Wang J (2009) Analysis of macrolide antibiotics, using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry, in food, biological and environmental matrices. Mass Spectrom Rev 28:50–92
Wang S, Dou H (eds) (1998) Chinese Limnology Record. Science Press, Bei**g
Wang M, Shen YU, Hong YW (2011) Residual characterization of multi-categorized antibiotics in five typical aquaculture waters. Ecol Environ Sci 20:934–939
Wang Z, Du Y, Yang C, Liu X, Zhang JQ, Li EH, Zhang Q, Wang XL (2017) Occurrence and ecological hazard assessment of selected antibiotics in the surface waters in and around Lake Honghu, China. Sci Total Environ 609:1423–1432
Xu W, Zhang G, Li X, Zou S, Li P, Hu Z, Li J (2007) Occurrence and elimination of antibiotics at four sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), South China. Water Res 41:4526–4534
Xu J, Zhang Y, Zhou CB, Guo CS, Wang DM, Du P, Luo Y, Wan J, Meng W (2014) Distribution, sources and composition of antibiotics in sediment, overlying water and pore water from Taihu Lake, China. Sci Total Environ 497:267–273
Xuan LT, Munekage Y (2004) Residues of selected antibiotics in water and mud from shrimp ponds in mangrove areas in Vietnam. Mar Pollut Bull 49:922–929
Yan CC, Yang Y, Zhou JL, Liu M, Nie MH, Shi H, Gu LJ (2013) Antibiotics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary: occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environ Pollut 175:22–29
Yao L, Wang Y, Tong L, Deng Y, Li Y, Gan Y, Guo W, Dong C, Duan Y, Zhao K (2017) Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in surface water and groundwater from different depths of aquifers: a case study at Jianghan Plain, central China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 135:236–242
Zeng QF, Gu XH, Chen X, Mao ZG (2013) The impact of Chinese mitten crab culture on water quality, sediment and the pelagic and macrobenthic community in the reclamation area of Guchenghu Lake. Fish Sci 79:689–697
Zhang R, Tang J, Li J, Zheng Q, Liu D, Chen Y, Zou Y, Chen X, Luo C, Zhang G (2013a) Antibiotics in the offshore waters of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea in China: occurrence, distribution and ecological risks. Environ Pollut 174:71–77
Zhang R, Tang J, Li J, Cheng Z, Chaemfa C, Liu D, Zheng Q, Song M, Luo C, Zhang G (2013b) Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the coastal aquatic environment of the Yellow Sea, North China. Sci Total Environ 450:197–204
Zhang QQ, Ying GG, Pan CG, Liu YS, Zhao JL (2015) Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ Sci Technol 49(11):6772–6782
Zheng Q, Zhang R, Wang Y, Pan X, Tang J, Zhang G (2012) Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Beibu Gulf, China: impacts of river discharge and aquaculture activities. Mar Environ Res 78:26–33
Zhou LJ, Ying GG, Liu S, Zhao JL, Chen F, Zhang RQ, Peng FQ, Zhang QQ (2012) Simultaneous determination of human and veterinary antibiotics in variousenvironmental matrices by rapid resolution liquid chromatography–electro spray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A1244:123–138
Zhou LJ, Wu QL, Zhang BB, Zhao YG, Zhao BY (2016) Occurrence, spatiotemporal distribution, mass balance and ecological risks of antibiotics in subtropical shallow Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Processes Impacts 18:500–513
Funding
This work was supported by National Key Technology R&D program of China (No. 2015BAD13B06), the Science and Technology Service Network Initiative (No. KFJ-SW-STS- 145), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31400399 and No. 31770551).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ester Heath
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 324 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Zhou, L., Gu, X. et al. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in surface water impacted by crab culturing: a case study of Lake Guchenghu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 22619–22628 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2054-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2054-7