Abstract
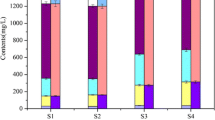
Drinking water treatment residuals (WTRs), nonhazardous by-products generated in a drinking water treatment plant, can be reused to immobilize phosphorus (P) to control the internal P loading from lake sediments for eutrophication control. Reasonably, before practical application, it is essential to determine the P immobilization capability of WTRs in lake sediments under various conditions. In this work, laboratory scale experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of light, microbial activity, and sediment resuspension on the P immobilization capability of WTRs. The results suggested that absence of light, low microbial activity, and sediment resuspension can increase the internal P loading from lake sediments. WTRs can, however, reduce the internal P loading significantly. Further analysis demonstrated that WTRs can stabilize P, decreasing the P bioavailability in the sediments under varied conditions. WTRs also presented little undesirable effects on the dissolved oxygen levels and pH of overlying water. Therefore, light, microbial activity, and sediment resuspension have little effect on the P immobilization capability of WTRs in lake sediments.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agyin-Birikorang S, O’Connor GA (2007) Lability of drinking water treatment residuals (WTR) immobilized phosphorus: aging and pH effects. J Environ Qual 36:1076–1085
Agyin-Birikorang S, Oladeji OO, O’Connor GA, Obreza TA, Capece JC (2009) Efficacy of drinking-water treatment residual in controlling off-site phosphorus losses: a field study in Florida. J Environ Qual 38:1076–1085
Babatunde AO, Zhao YQ (2007) Constructive approaches toward water treatment works sludge management: an international review of beneficial re-uses. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 37:129–164
Babatunde AO, Zhao YQ (2010) Leachability and leaching patterns from aluminium-based water treatment residual used as media in laboratory-scale engineered wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:1314–1322
Belyaeva ON, Haynes RJ (2012) Use of inorganic wastes as immobilizing agents for soluble P in green waste-based composts. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2138–2150
Boyer TH, Persaud A, Banerjee P, Palomino P (2011) Comparison of low-cost and engineered materials for phosphorus removal from organic-rich surface water. Water Res 45:4803–4814
Cassagne N, Remaury M, Gauquelin T, Fabre A (2000) Forms and profile distribution of soil phosphorus in alpine Inceptisols and Spodosols (Pyrenees, France). Geoderma 95:161–172
Christophoridis C, Fytianos K (2006) Conditions affecting the release of phosphorus from surface lake sediments. J Environ Qual 35:1181–1192
Chróst RJ, Münster U, Rai H, Albrecht D, Witzel PK, Overbeck J (1989) Photosynthetic production and exoenzymatic degradation of organic matter in the euphotic zone of a eutrophic lake. J Plankton Res 11:223–242
Dapeng L, Yong H, Chengxin F, Yan Y (2011) Contributions of phosphorus on sedimentary phosphorus bioavailability under sediment resuspension conditions. Chem Eng J 168:1049–1054
Dorich RA, Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1984) Availability of phosphorus to algae from eroded soil fractions. Agric Ecosys Environ 11:253–264
Egemose S, Reitzel K, Andersen FØ, Flindt MR (2010) Chemical lake restoration products: sediment stability and phosphorus dynamics. Environ Sci Technol 44:985–991
Eggleton J, Thomas KV (2004) A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events. Environ Int 30:973–980
Elliott HA, Dempsey BA, Maille PJ (1990) Content and fractionation of heavy metals in water treatment sludges. J Environ Qual 19:330–334
Hansen J, Reitzel K, Jensen HS, Andersen FØ (2003) Effects of aluminum, iron, oxygen and nitrate additions on phosphorus release from the sediment of a Danish soft water lake. Hydrobiologia 492:139–149
Huang P, Liu Z (2009) The effect of wave-reduction engineering on sediment resuspension in a large, shallow, eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu). Ecol Eng 35:1619–1623
Huang L, Du S, Fan L, Lin X, Wang H, Zhang Y (2011) Microbial activity facilitates phosphorus adsorption to shallow lake sediment. J Soil Sediment 11:185–193
Ippolito JA, Barbarick KA, Elliott HA (2011) Drinking water treatment residuals: a review of recent uses. J Environ Qual 40:1–12
Jiang X, ** X, Yao Y, Li L, Wu F (2008) Effects of biological activity, light, temperature and oxygen on phosphorus release processes at the sediment and water interface of Taihu Lake, China. Water Res 42:2251–2259
Kaiserli A, Voutsa D, Samara C (2002) Phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments—Lakes Volvi and Koronia, N. Greece. Chemosphere 46:1147–1155
Kisand A, Nõges P (2003) Sediment phosphorus release in phytoplankton dominated versus macrophyte dominated shallow lakes: importance of oxygen conditions. Hydrobiologia 506–509:129–133
Koenings JP, Hooper FF (1976) The influence of colloidal organic matter on iron and iron-phosphorus cycling in an acid bog lake. Limnol Oceanogr 21:684–696
Larkum AWD, Wood WF (1993) The effect of UV-B radiation on photosynthesis and respiration of phytoplankton, benthic macroalgae and seagrasses. Photosynth Res 36:17–23
Liu Y, Guo Y, Song C, **ao W, Huang D, Cao X, Zhou Y (2009) The effect of organic matter accumulation on phosphorus release in sediment of Chinese shallow lakes. Fund Appl limnol 175:143–150
Makris KC, Harris WG, O’Connor GA, Obreza TA (2004) Phosphorus immobilization in micropores of drinking-water treatment residuals: implications for long-term stability. Environ Sci Technol 38:6590–6596
Makris KC, Sarkar D, Salazar J, Punamiya P, Datta R (2010) Alternative amendment for soluble phosphorus removal from poultry litter. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:195–202
Montigny C, Prairie YT (1993) The relative importance of biological and chemical processes in the release of phosphorus from a highly organic sediment. Hydrobiologia 253:141–150
Mortula M, Bard SM, Walsh ME, Gagnon GA (2009) Aluminum toxicity and ecological risk assessment of dried alum residual into surface water disposal. Can J Civ Eng 36:127–136
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 26:31–36
Oliver IW, Grant CD, Murray RS (2011) Assessing effects of aerobic and anaerobic conditions on phosphorus sorption and retention capacity of water treatment residuals. J Environ Manage 92:960–966
Smith VH (2003) Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems—a global problem. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10:126–139
Søndergaard M, Kristensen P, Jeppesen E (1992) Phosphorus release from resuspended sediment in the shallow and wind-exposed Lake Arreso, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 228:91–99
Spears BM, Carvalho L, Perkins R, Paterson DM (2008) Effects of light on sediment nutrient flux and water column nutrient stoichiometry in a shallow lake. Water Res 42:977–986
Wang CH, Pei YS (2013) A comparison of the phosphorus immobilization capabilities of water treatment residuals before and after settling from lake water. Separ Purif Technol. doi:10.1016/ j.seppur .2013.04.003
Wang CH, Gao SJ, Wang TX, Tian BH, Pei YS (2011) Effectiveness of sequential thermal and acid activation on phosphorus removal by ferric and alum water treatment residuals. Chem Eng J 172:885–891
Wang CH, Fei CB, Pei YS (2012a) Stability of P saturated water treatment residuals under different levels of dissolved oxygen. Clean–Soil Air Water 40:844–849
Wang CH, Qi Y, Pei YS (2012b) Laboratory investigation of phosphorus immobilization in lake sediments using water treatment residuals. Chem Eng J 209:379–385
Wang CH, Gao SJ, Pei YS, Zhao YQ (2013) Use of drinking water treatment residuals to control the internal phosphorus loading from lake sediments: laboratory scale investigation. Chem Eng J 225:93–99
Wendling LA, Douglas GB, Coleman S, Yuan Z (2013) Nutrient and dissolved organic carbon removal from natural waters using industrial by-products. Sci Total Environ 442:63–72
Yuan XZ, Pan G, Chen H, Tian BH (2009) Phosphorus fixation in lake sediments using LaCl3-modified clays. Ecol Eng 35:1599–1602
Zhao YQ, Zhao XH, Babatunde AO (2009) Use of dewatered alum sludge as main substrate in treatment reed bed receiving agricultural wastewater: long-term trial. Bioresour Technol 100:644–648
Zhou QX, Gibson CE, Zhu YM (2001) Evaluation of phosphorus bioavailability in sediments of three contrasting lakes in China and the UK. Chemosphere 42:221–225
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51278055; 51179008), the National Science and Technology Major Project (2012ZX07203-003), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2012YBXS03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Pei, Y. Effects of light, microbial activity, and sediment resuspension on the phosphorus immobilization capability of drinking water treatment residuals in lake sediment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 8900–8908 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1865-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1865-9