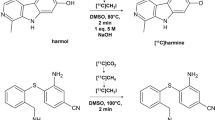
Abstract
Purpose
This study examined the feasibility of simultaneous dopamine and serotonin transporter imaging using [123I]ADAM and [99mTc]TRODAT-1 single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).
Procedures
Simultaneous [123I]ADAM (185 MBq) and [99mTc]TRODAT-1 (740 MBq) SPECT was performed in three age-matched female Formosan rock monkeys. An asymmetric energy window was used for dual, and symmetric energy windows were used for single-isotope imaging. Oral fluoxetine (20 mg) and intravenous methylphenidate HCl (1 mg/kg) were given 24 h and 10 min, respectively, before dual-isotope SPECT to test imaging specificities of [123I]ADAM and [99mTc]TRODAT-1.
Results
Comparable image quality and uptake ratios between dual- and single-isotope SPECT scans were found. Dual-isotope SPECT in fluoxetine-pretreated monkeys showed decreased uptake of [123I]-ADAM, but not of [99mTc]TRODAT-1. Dual-isotope SPECT in methylphenidate-pretreated monkeys showed decreased [99mTc]TRODAT-1 uptake without affecting [123I]-ADAM uptake.
Conclusion
Simultaneous [123I]-ADAM and [99mTc]TRODAT-1 SPECT appears promising in nonhuman primates and may provide a suitable preclinical model with further clinical implications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jellinger K (1990) New developments in the pathology of Parkinson’s disease. Adv Neurol 53:1–16
Uhl GR, Walther D, Mash D, Fauchaux B, Javoy-Agid F (1994) Dopamine transporter messenger RNA in Parkinson’s disease and control substantia nigra neurons. Ann Neurol 35:494–498
Graybiel AM, Hirsch EC, Agid Y (1990) The nigrostriatal system in Parkinson’s disease. Adv Neurol 53:17–29
Booij J, Tissingh G, Winogrodzka A, van Royen EZ (1999) Imaging of dopaminergic neurotransmission system using single-photon emission tomography and positron emission tomography in patients with parkinsonism. Eur J Nucl Med 26:171–182
Raisman R, Cach R, Agid Y (1986) Parkinson's disease: decreased density of 3H-imipramine and 3H-paroxetine binding sites in putamen. Neurology 36:556–560
Halliday GM, Blumbergs PC, Cotton RG et al (1990) Loss of brainstem serotonin- and substance P-containing neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 510:104–107
Guttman M, Boileau I, Warsh J et al (2007) Brain serotonin transporter binding in non-depressed patients with Parkinson's disease. Eur J Neurol 14:523–528
Karlsen KH, Larsen JP, Tandberg E, Maeland JM (1999) Influence of clinical and demographic variables on quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psych 66:431–435
Shulman LM, Taback RL, Bean J, Weiner WJ (2001) Comorbidity of the nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 16:507–510
Menza MA, Robertson-Hoffman DE, Bonapace AS (1993) Parkinson’s disease and anxiety: comorbidity with depression. Biol Psych 34:465–470
Kostic VS, Lecic D, Doder M et al (1996) Prolactin and cortisol responses to fennfluramine in Parkinson’s disease. Biol Psych 40:769–775
McCance-Katz EF, Marek KL, Price LH (1992) Serotonergic dysfunction in depression associated with Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 42:1813–1814
Lane RM (1998) SSROI-induced extrapyramidal side-effects and akinesia: implications for treatment. J Psychopharmacol 12:192–214
Uhl GR (1992) Neurotransmitter transporters (plus): a promising new gene family. Trends Neurosci 15:265–268
Owens MJ, Nemeroff CB (1994) Role of serotonin in the pathophysiology of depression: focus on the serotonin transporter. Clin Chem 40:288–295
Mozley PD, Schneider JS, Acton PD et al (2001) Binding of [99mTc]TRODAT-1 to dopamine transporters in patients with Parkinson’s disease and in healthy volunteers. J Nucl Med 41:584–589
Oya S, Choi SR, Hou C et al (2000) 2-((2-((Dimethylamino) methyl)phenyl)thio)-5-iodophenylamine (ADAM): an improved serotonin transporter ligand. Nucl Med Biol 27:249–254
Dresel SHJ, Kung MP, Huang XF et al (2006) Simultaneous SPECT studies of pre- and post-synaptic dopamine binding sites in baboons. J Nucl Med 33:87–92
El Fakhri G, Habert MO, Maksud P et al (2006) Quantitative simultaneous (99m)Tc- ECD/123I-FP-CIT SPECT in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Eur J Nucl Med Molec Imaging 33:87–92
Huang W-S, Ma KH, Cgeng CY et al (2004) Imaging serotonin transporters with 123I-ADAM brain SPECT in healthy non-human primates. Nucl Med Commun 25:515–519
Dresel SHJ, Kung MP, Huang XF et al (1999) In vivo imaging of serotonin transporters with [Tc-99m]TRODAT-1 in non-human primates. Eur J Nucl Med 26:342–347
Ma KH, Huang WS, Chen CH et al (2002) Dual SPECT of dopamine system using [99mTc]TRODAT-1 and [123I]IBZM in normal and 6-OHDA-lesioned Formosan rock monkeys. Nucl Med Biol 29:561–567
Ye XX, Chen JC, Liu RS et al (2004) Microautoradiography of [123]ADAM in mice treated with fluoxetine and serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Nucl Med Biol 31:557–562
Swanson RL, Newberg AB, Acton PD et al (2005) Differences in [99mTc]-TRODAT-1 SPECY binding to dopamine transporters in patients with multiple system atrophy and Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Imaging 32:302–307
Huang WS, Lee MS, Lin JC et al (2004) Usefulness of brain [99mTc]-TRODAT-1 SPET for the evaluation of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Molec Imaging 31:155–161
Shih MC, De Andrade LAF, Amaro E et al (2007) Higher nigrostriatal dopamine neuron loss in early than late onset Parkinson’s disease? A [99mTc]-TRODAT-1 SPECT study. Mov Disord 22:863–866
Acton PD, Choi S, Hou C et al (2001) Quantification of serotonin transporters in nonhuman primates using [123I] ADAM and SPECT. J Nucl Med 42:1556–1562
Catafou AM, Perez V, Penengo MM et al (2005) SPECT of serotonin transporters using 123I-ADAM: optimal imaging time after bolus injection and long-term test–retest in health volunteers. J Nucl Med 46:1301–1309
Newberg AB, Amsterdam JD, Wintering N et al (2005) [123I] ADAM binding to serotonin transporters in patients with major depression and healthy controls: a preliminary study. J Nucl Med 46:973–977
Wade PR, Chen J, Jaffe B et al (1996) Localization and function of a 5-HT transporter in crypt epithelia of the gastrointestinal tract. J Neurosci 16:2352–2364
Lesch KP, Wolozin BL, Murphy DL, Reiderer P (1993) Primary structure of the human platelet serotonin uptake site: identity with the brain serotonin transporter. J Neurosci 60:2319–2322
Lee SL, Fanburg BL (1986) Serotonin uptake by bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells in culture. I. Characterization. Am J Physiol 250:C761–C765
Lu NZ, Eshleman AJ, Janowsky A, Bethea CL (2003) Ovarian steroid regulation of serotonin reuptake transporter (SERT) binding, distribution, and function in female macaques. Mol Psych 8:353–360
Pecins-Thompson M, Brown NA, Bethea CL (1998) Regulation of serotonin re-uptake transporter mRNA expression by ovarian steroids in rhesus macaques. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 53:120–129
Black NF, McJames S, Rust TC, Kadrmas DJ (2008) Evaluation of rapid dual-tracer (62)Cu-PTSM + (62)Cu-ATSM PET in dogs with spontaneously occurring tumors. Phys Med Biol 53:217–232
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Institute of Nuclear Energy Research and National Science Council under grants 970945L, NSC94-2314-B016-042, and 97-2623-7-016-001-NU respectively. We thank Mr Jiang-Cherng Perng and Ms Tzu-Jou Chung for their technical help and preparation of the monkeys.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, KH., Lee, JK., Huang, SY. et al. Simultaneous [99mTc]TRODAT-1 and [123I]ADAM Brain SPECT in Nonhuman Primates. Mol Imaging Biol 11, 253–262 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-009-0197-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-009-0197-0