Abstract
Introduction
Neonatal cholestatic disorders are a group of hepatobiliary diseases occurring in the first 3 months of life. The most common causes of neonatal cholestasis are infantile hepatitis syndrome (IHS) and biliary atresia (BA). The clinical manifestations of the two diseases are too similar to distinguish them. However, early detection is very important in improving the clinical outcome of BA. Currently, a liver biopsy is the only proven and effective method used to differentially diagnose these two similar diseases in the clinic. However, this method is invasive. Therefore, sensitive and non-invasive biomarkers are needed to effectively differentiate between BA and IHS. We hypothesized that urinary metabolomics can produce unique metabolite profiles for BA and IHS.
Objectives
The aim of this study was to characterize urinary metabolomic profiles in infants with BA and IHS, and to identify differences among infants with BA, IHS, and normal controls (NC).
Methods
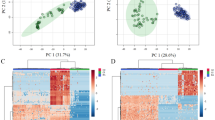
Urine samples along with patient characteristics were obtained from 25 BA, 38 IHS, and 38 NC infants. A non-targeted gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) metabolomics method was used in conjunction with orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) to explore the metabolomic profiles of BA, IHS, and NC infants.
Results
In total, 41 differentially expressed metabolites between BA vs. NC, IHS vs. NC, and BA vs. IHS were identified. N-acetyl-d-mannosamine and alpha-aminoadipic acid were found to be highly accurate at distinguishing between BA and IHS.
Conclusions
BA and IHS infants have specific urinary metabolomic profiles. The results of our study underscore the clinical potential of metabolomic profiling to uncover metabolic changes that could be used to discriminate BA from IHS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abukawa, D., Ohura, T., Iinuma, K., & Tazawa, Y. (2001). An undescribed subset of neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis associated with multiple hyperaminoacidemia. Hepatology Research, 21, 8–13.
Al Mardini, H., Douglass, A., & Record, C. (2006). Amino acid challenge in patients with cirrhosis and control subjects: Ammonia, plasma amino acid and EEG changes. Metabolic Brain Disease, 21, 1–10.
Allen, M. B., & Walker, D. G. (1980). The isolation and preliminary characterization of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine kinase from rat kidney and liver. Biochemical Journal, 185, 565–575.
Assimakopoulos, S. F., Grintzalis, K., Thomopoulos, K. C., Papapostolou, I., Georgiou, C. D., Gogos, C., et al. (2008). Plasma superoxide radical in jaundiced patients and role of xanthine oxidase. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences, 336, 230–236.
Attallah, A. M., Toson el, S. A., El-Waseef, A. M., Abo-Seif, M. A., Omran, M. M., & Shiha, G. E. (2006). Discriminant function based on hyaluronic acid and its degrading enzymes and degradation products for differentiating cirrhotic from non-cirrhotic liver diseased patients in chronic HCV infection. Clinica Chimica Acta, 369, 66–72.
Balistreri, W. F., Grand, R., Hoofnagle, J. H., Suchy, F. J., Ryckman, F. C., Perlmutter, D. H., et al. (1996) Biliary atresia: Current concepts and research directions. Summary of a symposium. Hepatology 23, 1682–1692.
Bernabeu, A., Alfaro, A., Garcia, M., & Fernandez, E. (2009). Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) reveals the presence of elevated myo-inositol in the occipital cortex of blind subjects. Neuroimage, 47, 1172–1176.
Bijl, E. J., Bharwani, K. D., Houwen, R. H., & de Man, R. A. (2013). The long-term outcome of the Kasai operation in patients with biliary atresia: A systematic review. The Netherlands Journal of Medicine, 71, 170–173.
Blemings, K. P., Crenshaw, T. D., Swick, R. W., & Benevenga, N. J. (1994). Lysine-alpha-ketoglutarate reductase and saccharopine dehydrogenase are located only in the mitochondrial matrix in rat liver. Journal of Nutrition, 124, 1215–1221.
Bogdanos, D. P., Baum, H., Okamoto, M., Montalto, P., Sharma, U. C., Rigopoulou, E. I., et al. (2005). Primary biliary cirrhosis is characterized by IgG3 antibodies cross-reactive with the major mitochondrial autoepitope and its Lactobacillus mimic. Hepatology, 42, 458–465.
Broadhurst, D., & Kell, D. (2006). Statistical strategies for avoiding false discoveries in metabolomics and related experiments. Metabolomics, 2, 171–196.
Cuzzolin, L., Mangiarotti, P., & Fanos, V. (2001). Urinary PGE(2) concentrations measured by a new EIA method in infants with urinary tract infections or renal malformations. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, 64, 317–322.
Davenport, M., Ong, E., Sharif, K., Alizai, N., McClean, P., Hadzic, N., et al. (2011). Biliary atresia in England and Wales: Results of centralization and new benchmark. Journal of Pediatric Surgery, 46, 1689–1694.
Dong, S., Zhan, Z. Y., Cao, H. Y., Wu, C., Bian, Y. Q., Li, J. Y., et al. (2017). Urinary metabolomics analysis identifies key biomarkers of different stages of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 23, 2771–2784.
Dunn, W. B., Broadhurst, D. I., Atherton, H. J., Goodacre, R., & Griffin, J. L. (2011). Systems level studies of mammalian metabolomes: The roles of mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Chemical Society Reviews, 40, 387–426.
Fanos, V., Antonucci, R., Barberini, L., & Atzori, L. (2012). Urinary metabolomics in newborns and infants. Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 58, 193–223.
Fiehn, O. (2001). Combining genomics, metabolome analysis, and biochemical modelling to understand metabolic networks. Comparative and Functional Genomics, 2, 155–168.
Finelli, C., & Tarantino, G. (2017). Retraction: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, diet and gut microbiota. EXCLI Journal, 16, 1164.
Forton, D. M., Hamilton, G., Allsop, J. M., Grover, V. P., Wesnes, K., O’Sullivan, C., et al. (2008). Cerebral immune activation in chronic hepatitis C infection: A magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Journal of Hepatology, 49, 316–322.
Fouquet, V., Alves, A., Branchereau, S., Grabar, S., Debray, D., Jacquemin, E., et al. (2005). Long-term outcome of pediatric liver transplantation for biliary atresia: A 10-year follow-up in a single center. Liver Transplantation, 11, 152–160.
Fujita, T., Hada, T., & Higashino, K. (1999). Origin of D- and L-pipecolic acid in human physiological fluids: A study of the catabolic mechanism to pipecolic acid using the lysine loading test. Clinica Chimica Acta, 287, 145–156.
Furukawa, K., Ohkawa, Y., Yamauchi, Y., Hamamura, K., Ohmi, Y., & Furukawa, K. (2012). Fine tuning of cell signals by glycosylation. Journal of Biochemistry, 151, 573–578.
Gou, X., Tao, Q., Feng, Q., Peng, J., Sun, S., Cao, H., et al. (2013). Urinary metabonomics characterization of liver fibrosis induced by CCl(4) in rats and intervention effects of **a Yu Xue Decoction. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 74, 62–65.
Grover, V. P., Pavese, N., Koh, S. B., Wylezinska, M., Saxby, B. K., Gerhard, A., et al. (2012). Cerebral microglial activation in patients with hepatitis C: In vivo evidence of neuroinflammation. Journal of Viral Hepatitis, 19, e89-96.
Gu, H., Zhang, P., Zhu, J., & Raftery, D. (2015). Globally optimized targeted mass spectrometry: Reliable metabolomics analysis with broad coverage. Analytical Chemistry, 87, 12355–12362.
Gu, H. W., Carroll, P. A., Du, J. H., Zhu, J. J., Neto, F. C., Eisenman, R. N., et al. (2016). Quantitative method to investigate the balance between metabolism and proteome biomass: Starting from glycine. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 55, 15646–15650.
Guyot, C., & Stieger, B. (2011). Interaction of bile salts with rat canalicular membrane vesicles: Evidence for bile salt resistant microdomains. Journal of Hepatology, 55, 1368–1376.
Harms, E., Kreisel, W., Morris, H. P., & Reutter, W. (1973). Biosynthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid in Morris hepatomas. European Journal of Biochemistry, 32, 254–262.
Hartley, J. L., Davenport, M., & Kelly, D. A. (2009). Biliary atresia. Lancet, 374, 1704–1713.
Higashino, K., Fujioka, M., & Yamamura, Y. (1971). The conversion of L-lysine to saccharopine and alpha-aminoadipate in mouse. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 142, 606–614.
Hinderlich, S., Stasche, R., Zeitler, R., & Reutter, W. (1997). A bifunctional enzyme catalyzes the first two steps in N-acetylneuraminic acid biosynthesis of rat liver. Purification and characterization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 24313–24318.
Holecek, M. (2017). Branched-chain amino acid supplementation in treatment of liver cirrhosis: Updated views on how to attenuate their harmful effects on cataplerosis and ammonia formation. Nutrition, 41, 80–85.
Hutzler, J., & Dancis, J. (1983). The determination of pipecolic acid: Method and results of hospital survey. Clinica Chimica Acta, 128, 75–82.
Kawasaki, H., Hori, T., Nakajima, M., & Takeshita, K. (1988). Plasma levels of pipecolic acid in patients with chronic liver disease. Hepatology, 8, 286–289.
Khanna, S., & Gopalan, S. (2007). Role of branched-chain amino acids in liver disease: The evidence for and against. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 10, 297–303.
Kikuchi, K., & Tsuiki, S. (1973). Purification and properties of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2′-epimerase from rat liver. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 327, 193–206.
Kind, T., Wohlgemuth, G., Lee, D. Y., Lu, Y., Palazoglu, M., Shahbaz, S., et al. (2009). FiehnLib: Mass spectral and retention index libraries for metabolomics based on quadrupole and time-of-flight gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 81, 10038–10048.
Kullak-Ublick, G. A., & Meier, P. J. (2000). Mechanisms of cholestasis. Clinical Liver Disease, 4, 357–385.
Lee, A., Chick, J. M., Kolarich, D., Haynes, P. A., Robertson, G. R., Tsoli, M., et al. (2011). Liver membrane proteome glycosylation changes in mice bearing an extra-hepatic tumor. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 10, M900538MCP200.
Lee, J. H., Seo, D. W., Lee, Y. S., Kim, S. T., Mun, C. W., Lim, T. H., et al. (1999). Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) findings for the brain in patients with liver cirrhosis reflect the hepatic functional reserve. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 94, 2206–2213.
Li, W. W., Shan, J. J., Lin, L. L., **e, T., He, L. L., Yang, Y., et al. (2017). Disturbance in plasma metabolic profile in different types of human cytomegalovirus-induced liver injury in infants. Scientific Reports, 7, 15696.
Majer, F., Trnka, L., Vitek, L., Jirkovska, M., Marecek, Z., & Smid, F. (2007). Estrogen-induced cholestasis results in a dramatic increase of b-series gangliosides in the rat liver. Biomedical Chromatography, 21, 446–450.
Mamas, M., Dunn, W. B., Neyses, L., & Goodacre, R. (2011). The role of metabolites and metabolomics in clinically applicable biomarkers of disease. Archives of Toxicology, 85, 5–17.
Marchesini, G., Bianchi, G., Merli, M., Amodio, P., Panella, C., Loguercio, C., et al. (2003). Nutritional supplementation with branched-chain amino acids in advanced cirrhosis: A double-blind, randomized trial. Gastroenterology, 124, 1792–1801.
McKiernan, P. (2012). Neonatal jaundice. Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology, 36, 253–256.
McKiernan, P. J. (2002). Neonatal cholestasis. Seminars in Neonatology, 7, 153–165.
Memon, N., Weinberger, B. I., Hegyi, T., & Aleksunes, L. M. (2016). Inherited disorders of bilirubin clearance. Pediatric Research, 79, 378–386.
Muto, Y., Sato, S., Watanabe, A., Moriwaki, H., Suzuki, K., Kato, A., et al. (2006). Overweight and obesity increase the risk for liver cancer in patients with liver cirrhosis and long-term oral supplementation with branched-chain amino acid granules inhibits liver carcinogenesis in heavier patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology Research, 35, 204–214.
Nicholson, J. K. (2006). Global systems biology, personalized medicine and molecular epidemiology. Molecular Systems Biology, 2, 52.
O’Toole, A., Alakkari, A., Keegan, D., Doherty, G., Mulcahy, H., & O’Donoghue, D. (2012). Primary sclerosing cholangitis and disease distribution in inflammatory bowel disease. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 10, 439–441.
Pascher, I., Lundmark, M., Nyholm, P. G., & Sundell, S. (1992). Crystal structures of membrane lipids. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1113, 339–373.
Pena, I. A., Marques, L. A., Laranjeira, A. B., Yunes, J. A., Eberlin, M. N., MacKenzie, A., et al. (2017). Mouse lysine catabolism to aminoadipate occurs primarily through the saccharopine pathway; implications for pyridoxine dependent epilepsy (PDE). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1863, 121–128.
Perez, M. J., & Briz, O. (2009). Bile-acid-induced cell injury and protection. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 15, 1677–1689.
Plitman, E., de la Fuente-Sandoval, C., Reyes-Madrigal, F., Chavez, S., Gomez-Cruz, G., Leon-Ortiz, P., et al. (2016). Elevated Myo-inositol, choline, and glutamate levels in the associative striatum of antipsychotic-naive patients with first-episode psychosis: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study with implications for glial dysfunction. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 42, 415–424.
Rajendran, L., & Simons, K. (2005). Lipid rafts and membrane dynamics. Journal of Cell Science, 118, 1099–1102.
Roberts, E. A. (2003). Neonatal hepatitis syndrome. Seminars in Neonatology, 8, 357–374.
Rovira, A., Alonso, J., & Cordoba, J. (2008). MR imaging findings in hepatic encephalopathy. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 29, 1612–1621.
Russo, P., Magee, J., Anders, R., & Spino, C. (2016). Key histopathologic features of liver biopsies that distinguish biliary atresia from other causes of infantile cholestasis and their correlation with outcome: a multicenter study. American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 40, 1.
Sano, H., Nakazawa, T., Ando, T., Hayashi, K., Naitoh, I., Okumura, F., et al. (2011). Clinical characteristics of inflammatory bowel disease associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Journal of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Sciences, 18, 154–161.
Sira, M. M., Taha, M., & Sira, A. M. (2014). Common misdiagnoses of biliary atresia. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 26, 1300–1305.
Smid, V., Petr, T., Vanova, K., Jasprova, J., Suk, J., Vitek, L., et al. (2016). Changes in liver ganglioside metabolism in obstructive cholestasis: The role of oxidative stress. Folia Biologica, 62, 148–159.
Sokol, R. J., Mack, C., Narkewicz, M. R., & Karrer, F. M. (2003). Pathogenesis and outcome of biliary atresia: Current concepts. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 37, 4–21.
Stirpe, F., Ravaioli, M., Battelli, M. G., Musiani, S., & Grazi, G. L. (2002). Xanthine oxidoreductase activity in human liver disease. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 97, 2079–2085.
Struys, E. A., & Jakobs, C. (2010). Metabolism of lysine in alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde dehydrogenase-deficient fibroblasts: Evidence for an alternative pathway of pipecolic acid formation. FEBS Letters, 584, 181–186.
Tam, P. K. H., Chung, P. H. Y., St Peter, S. D., Gayer, C. P., Ford, H. R., Tam, G. C. H., et al. (2017). Advances in paediatric gastroenterology. Lancet, 390, 1072–1082.
Tietge, U. J., Bahr, M. J., Manns, M. P., & Boker, K. H. (2003). Hepatic amino-acid metabolism in liver cirrhosis and in the long-term course after liver transplantation. Transplant International, 16, 1–8.
Tsugawa, H., Cajka, T., Kind, T., Ma, Y., Higgins, B., Ikeda, K., et al. (2015). MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nature Methods, 12, 523–526.
van den Berg, R. A., Hoefsloot, H. C., Westerhuis, J. A., Smilde, A. K., & van der Werf, M. J. (2006). Centering, scaling, and transformations: Improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genomics, 7, 142.
Verkade, H. J., Bezerra, J. A., Davenport, M., Schreiber, R. A., Mieli-Vergani, G., Hulscher, J. B., et al. (2016). Biliary atresia and other cholestatic childhood diseases: Advances and future challenges. Journal of Hepatology, 65, 631–642.
Vinayavekhin, N., Homan, E. A., & Saghatelian, A. (2010). Exploring disease through metabolomics. ACS Chemical Biology, 5, 91–103.
Wang, X., Lv, H., Zhang, G., Sun, W., Zhou, D., Jiao, G., et al. (2008). Development and validation of a ultra performance LC-ESI/MS method for analysis of metabolic phenotypes of healthy men in day and night urine samples. Journal of Separation Science, 31, 2994–3001.
Wang, X., Zhang, A., Han, Y., Wang, P., Sun, H., Song, G., et al. (2012). Urine metabolomics analysis for biomarker discovery and detection of jaundice syndrome in patients with liver disease. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 11, 370–380.
Weber-Mzell, D., Zaupa, P., Petnehazy, T., Kobayashi, H., Schimpl, G., Feierl, G., et al. (2006). The role of nuclear factor-kappa B in bacterial translocation in cholestatic rats. Pediatric Surgery International, 22, 43–49.
**a, J., Broadhurst, D. I., Wilson, M., & Wishart, D. S. (2013). Translational biomarker discovery in clinical metabolomics: An introductory tutorial. Metabolomics, 9, 280–299.
**a, J., Psychogios, N., Young, N., & Wishart, D. S. (2009). MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res, 37, W652-60.
Yang, J., Xu, G., Zheng, Y., Kong, H., Pang, T., Lv, S., et al. (2004). Diagnosis of liver cancer using HPLC-based metabonomics avoiding false-positive result from hepatitis and hepatocirrhosis diseases. Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 813, 59–65.
Yang, J., Xu, G., Zheng, Y., Kong, H., Wang, C., Zhao, X., et al. (2005). Strategy for metabonomics research based on high-performance liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1084, 214–221.
Yao, W., Gu, H., Zhu, J., Barding, G., Cheng, H., Bao, B., et al. (2014). Integrated plasma and urine metabolomics coupled with HPLC/QTOF-MS and chemometric analysis on potential biomarkers in liver injury and hepatoprotective effects of Er-Zhi-Wan. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 406, 7367–7378.
Ye, Q., Yin, W., Zhang, L., **ao, H., Qi, Y., Liu, S., et al. (2017). The value of grip test, lysophosphatidlycholines, glycerophosphocholine, ornithine, glucuronic acid decrement in assessment of nutritional and metabolic characteristics in hepatitis B cirrhosis. PLoS ONE, 12, e0175165.
Yu, J., Marsh, S., Hu, J., Feng, W., & Wu, C. (2016) The pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and genetic background. Gastroenterology Research and Practice 2016, 2862173.
Zerbini, M. C., Gallucci, S. D., Maezono, R., Ueno, C. M., Porta, G., Maksoud, J. G., et al. (1997). Liver biopsy in neonatal cholestasis: A review on statistical grounds. Modern Pathology, 10, 793–799.
Zhao, D., Han, L., He, Z., Zhang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2014). Identification of the plasma metabolomics as early diagnostic markers between biliary atresia and neonatal hepatitis syndrome. PLoS ONE, 9, e85694.
Zhou, K., Wang, J., **e, G., Zhou, Y., Yan, W., Pan, W., et al. (2015a). Distinct plasma bile acid profiles of biliary atresia and neonatal hepatitis syndrome. Journal of Proteome Research, 14, 4844–4850.
Zhou, K., **e, G., Wang, J., Zhao, A., Liu, J., Su, M., et al. (2015b). Metabonomics reveals metabolite changes in biliary atresia infants. Journal of Proteome Research, 14, 2569–2574.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (81473725 and 81373688) and Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX18_1550). In addition, Wei-Wei Li especially wishes to thank Ji-Xuan He for his support over the past decade.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY, SJJ and WSC designed the experiments. LWW and HLL involved in taking ethical clearance, collecting samples and managing their clinical details. LWW, DQG and TJL supervised GC–MS experiments. LWW, WSC, SJJ, XT and LLL contributed the reagents/materials/analysis tools, analysed the data and prepared the gures. LWW wrote the main manuscript. SJJ and WSC evaluated the manuscript critically and all the authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of Bei**g Children’s Hospital, Bei**g, China. All protocols and procedures were adhered to institutional ethical standards and/or research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Prior informed consent was obtained from all the participants in the study with institutional review approval.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, WW., Yang, Y., Dai, QG. et al. Non-invasive urinary metabolomic profiles discriminate biliary atresia from infantile hepatitis syndrome. Metabolomics 14, 90 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1387-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1387-z