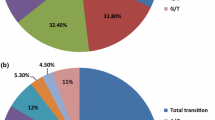
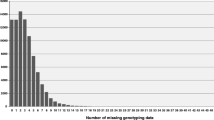
Abstract
High-throughput DNA and RNA sequencing technologies have resulted in the successful identification of Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). In order to develop a large SNP set for wide application in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.), we carried out RNA high-throughput sequencing (RNA-Seq) in two apricot genotypes, “Rojo Pasión” and “Z506-7.” After trimming and cleaning, 70 % of RNA-Seq reads were aligned to the reference peach genome. Sequences uniquely mapped on the peach genome allowed for the discovery of 300 k SNP/INDEL variations, with a density of one SNP per 850 bp. Some 95 SNPs of the 99 tested were analyzed in a set of 37 apricot accessions using SNPlex™ genoty** technology. The results provide accurate values for nucleotide diversity in coding sequences in apricot. The combination of a highly efficient RNA-Seq approach and SNPlex™ high-throughput genoty** technology thus provide a powerful tool for apricot genetic analysis. SNP markers produced a total of 267 allelic combinations in the 37 apricot accessions assayed with a mean of 2.8 combinations per locus, an observed heterozygosity per marker ranging from 0.06 to 0.65, and a power of discrimination ranging from 0.12 to 0.66. In addition, SNP markers confirmed parentage and also determined relationships between the accessions in a manner consistent with their pedigree relationships.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adami M, De Franceschi P, Brandi F, Liverani A, Giovannini D et al (2013) Identifying a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase (ccd4) gene controlling yellow/white fruit flesh color of peach. Plant Mol Biol Report 31:1166–1175
Ahmad R, Parfitt DE, Fass J, Ogundiwin E, Dhingra A et al (2011) Whole genome sequencing of peach (Prunus persica L.) for SNP identification and selection. BMC Genet 12:569
Alkio M, Jonas U, Declerq M, Van Nocker S, Knoche M (2014) Trancriptional dynamics of the develo** sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) fruit: sequencing, annotation and expression profiling of exocarp-associated genes. Hortic Res 1:11
Aranzana MJ, Abassi EK, Howad B, Arús P (2010) Genetic variation, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in peach commercial varieties. BMC Genet 11:69
Aranzana MJ, Illa E, Howad B, Arús P (2012) A first insight into peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] SNP variability. Tree Genet Genomes 8:1359–1369
Badenes ML, Hurtado MA, Sanz F, Archelos DM, Burgos L et al (2000) Searching for molecular markers linked to male sterility and self-compatibility in apricot. Plant Breed 119:157–160
Bielsa B, Jiwan D, Fernández i Martí A, Dhingra A, Rubio-Cabetas MJ (2014) Detection of SNP and validation of a SFP InDel (deletion) in inverted repeat region of the Prunus species chloroplast genome. Sci Hortic 168:108–112
Bourguiba H, Audergon JM, Krichen L, Trifi-Farah N, Mamouni A et al (2012) Loss of genetic diversity as a signature of apricot domestication and diffusion into the Mediterranean Basin. BMC Plant Biol 12:49
Byrne DH (1990) Isozyme variability in four diploid stone fruits compared with other woody perennial plants. J Heredity 81:68–71
Chen X, Wu Q, Sun R, Zhang L (2012) Two combinatorial optimization problems for SNP discovery using bas-specific cleavage and mass spectrometry. BMC Syst Biol 6(Suppl 2):S5
De La Vega FM, Lazaruk KD, Rhodes MD, Wenz MH (2005) Assessment of two flexible and compatible SNP genoty** platforms: TaqMan SNP genoty** assay and the SNPlex genoty** system. Mutant Res 573:111–135
de Vicente MC, Truco MJ, Egea J, Burgos L, Arús P (1998) RFLP variability in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). Plant Breed 117:153–158
Dondini L, Lain O, Geuna F, Banfi R, Gaiotti F et al (2007) Development of a new SSR-based linkage map in apricot and analysis of synteny with existing Prunus map. Tree Genet Genomes 3:239–249
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Eduardo I, Chietera G, Pirona R, Pacheco I, Troggio M et al (2013) Genetic dissection of aroma volatile compounds from the essential oil of peach fruit: QTL analysis and identification of candidate genes SNP maps. Tree Genet Genomes 9:189–204
Fang JG, Twito T, Zhang Z, Chao CCT (2006) Genetic relationships among fruiting-mei (Prunus mume Sieb et Zucc.) cultivars evaluated with AFLP and SNP markers. Genome 10:1256–1264
Fernández i Martí A, Athanson B, Koepke T, Font i Forcada C, Dhingra A et al (2012) Genetic diversity and relatedness of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars based on single nucleotide polymorphic markers. Front. Plant Sci 3:116
Gabriel S, Ziugara L, Tabba D (2009) SNP genoty** using the Sequenom MassARRAY iPLEX Platform. In Wiley Interscience (www.interscience.wiley.com). Current Protocols in Human Genetics, unit 2.12, p 1–18
Geuna F, Toschi M, Bassi D (2003) The use of AFLP markers for cultivar identification in apricot. Plant Breed 122:526–531
Hagen LS, Khadari B, Lambert P, Audergon JM (2002) Genetic diversity in apricot revealed by AFLP markers: species and cultivar comparisons. Theor Appl Genet 105:298–305
Hormaza JI (2002) Molecular characterization and similarity relationships among apricot genotypes using simple sequence repeats. Theor Appl Genet 104:321–328
Jung S, Jiwan D, Cho I, Abbott A, Tomkins J et al (2009) Synteny of Prunus and other model plant species. BMC Genet 10:76
Klagges C, Campoy JA, Quero-García J, Guzmán A, Mansur L et al (2013) Construction and comparative analyses of highly dense linkage maps of two sweet cherry intra-specific progenies of commercial cultivars. PLoS ONE 7:e54743
Kodad O, Hegedus A, Socias i Company R, Halász J (2013) Self-(in)compatibility genotypes of Moroccan apricots indicate differences and similarities in the crop history of European and North African apricot germplasm. BMC Plant Biol 13:196
Koepke T, Schaeffer S, Krishnan V, Jiwan D, Harper A et al (2012) Rapid gene-based SNP and haplotype marker development in non-model eukaryotes using 3′UTR sequencing. BMC Genet 13:18
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J et al (2009) The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079
Li X, Wang Y, Wang B, Wang C, Shangguan L et al (2002) Genetic relationships between fruiting and flowering mei (Prunus mume) cultivars using SNP markers. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 85:329–334
Lijavetzky D, Cabezas JA, Ibáñez A, Rodríguez V, Martínez-Zapater JM (2007) High throughput SNP discovery and genoty** in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) by combining a re-sequencing approach and SNPlex technology. BMC Genet 8:424
Lindner R, Friedel CC (2012) A comprehensive evaluation of alignment algorithms in the context of RNA-Seq. PLoS ONE 7:e52403
Martínez-García PJ, Parfitt DE, Bostock RM, Fresnedo-Ramírez J, Vázquez-Lobo A et al (2013a) Application of genomic and quantitative genetic tools to identify candidate resistance genes for brown rot resistance in peach. PLoS ONE 7:e78634
Martínez-García PJ, Parfitt DE, Ogundiwin EA, Fass J, Chan HM et al (2013b) High density SNP map** and QTL analysis for fruit quality characteristics in peach (P. persica L.). Tree Genet Genomes 9:19–36
Martínez-García PJ, Fresnedo-Ramírez J, Parfitt DE, Gradziel TM, Crisosto CH (2013c) Effect prediction of identified SNPs linked to fruit quality and chilling injury in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch]. Plant Mol Biol 81:175–188
Martínez-Gómez P, Crisosto C, Bonghi C, Rubio M (2011) New approaches to Prunus transcriptome analysis. Genetica 139:755–769
Martínez-Gómez P, Sánchez-Pérez R, Rubio M (2012) Clarifying omics concepts, challenges and opportunities for Prunus breeding in the post-genomic era. OMICS: J Integr Biol 16:268–283
Messina R, Lain O, Marrazo T, Cipriano G, Testolin R (2004) New set of microsatellite loci isolated in apricot. Mol Ecol Notes 4:432–434
Milne I, Stephen G, Bayer M, Cock PJ, Pritchard L et al (2013) Using Tablet for visual exploration of second-generation sequencing data. Brief Bioinform 14:193–202
Peace C, Bassil N, Main D, Ficklin S, Rosyara UR et al (2012) Development and evaluation of a genome-wide 6 K SNP array for diploid sweet cherry and tetraploid sour cherry. PLoS ONE 7:e48305
Pirona R, Eduardo I, Pacheco I, Da Silva Linge C, Miculan M et al (2013) Fine map** and identification of a candidate gene for a major locus controlling maturity date in peach. BMC Plant Biol 13:166
Rafalski A (2002) Applications of single nucleotide polymorphisms in crop genetics. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:94–100
Rosyara UR, Sebolt AM, Peace C, Iezzoni AF (2014) Identification of the parental parent of ‘Bing’ sweet cherry and confirmation of descendants using single nucleotide polymorphism markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 139:148–156
Salazar JA, Ruiz D, Campoy JA, Sánchez-Pérez R, Crisosto CH et al (2014) Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) and Mendelian Trait Loci (MTL) analysis in Prunus: a breeding perspective and beyond. Plant Mol Biol Report 32:1–18
Sánchez-Pérez R, Martínez-Gómez P, Dicenta F, Egea J, Ruiz D (2006) Level and transmission of genetic heterozygosity in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) using simple sequence repeat markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:763–770
Sánchez-Pérez R, Ruiz D, Dicenta F, Egea J, Martínez-Gómez P (2005) Application of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers in apricot breeding: molecular characterization, protection, and genetic relationships. Sci Hortic 103:305–315
Sun LD, Zhang QX, Xu ZD, Yang WR, Guo Y et al (2013) Genome-wide DNA polymorphisms in two mei (Prunus mume Sieb. Et Zucc.). BMC Genet 14:98
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tavassolian I, Rabiei G, Gregory D, Mnejja M, Wirthensohn MG et al (2010) Construction of an almond linkage map in an Australian population Nonpareil × Lauranne. BMC Genomics 11:551
Tobler AR, Short S, Anderse MR, Planer TM, Briggs JC et al (2005) The SNPlex genoty** system: a flexible and scalable platform for SNP genoty**. J Biomol Tech 16:398–406
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25:1105–1111
Vendramin E, Pea G, Dondini L, Pacheco I, Dettori MT et al (2014) A unique mutation in a MYB gene cosegregates with the nectarine phenotype in peach. PLoS ONE 9:e90574
Verde I, Abbott AG, Scalabrin S, Jung S, Shu S et al (2013) The high-quality draft of peach (Prunus persica) identifies unique patterns of genetic diversity, domestication and genome evolution. Nat Genet 45:487–494
Verde I, Bassil N, Scalabrin S, Gilmore B, Lawley CT et al (2012) Development and evaluation of a 9 K SNP array for peach by internationally coordinated SNP detection and validation in breeding germplasm. PLoS ONE 7:e35668
Wang L, Zhao S, Gu C, Zhou Y, Zhou H et al (2013) Deep RNA-Seq uncovers the peach transcriptome landscape. Plant Mol Biol 83:365–377
Wu SB, Tavassolian I, Francks TK, Hunt P, Wirthensohn MG et al (2010) Discrimination of SNP genotypes associated with complex haplotypes by high-resolution melting analysis in almond: implications for improved marker efficiencies. Mol Breed 25:351–357
Wu SB, Tavassolian I, Rabiei G, Hunt PW, Wirthensohn MG et al (2009) Map** SNP-anchored genes using high-resolution melting analysis in almond. Mol Genet Genomics 282:273–281
Zhong W, Gao Z, Zhuang W, Shi T et al (2013) Genome-wide expression profiles of seasonal bud dormancy at four critical stages in Japanese apricot. Plant Mol Biol 86:247–264
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the projects “Gene expression analysis of the resistance to Plum pox virus, PPV (sharka) in apricot by transcriptome deep-sequencing (RNA-Seq)” (AGL2010-16335) and “Apricot breeding” (AGL2010-21903) of the Spanish Ministry of Science. The authors would also like to thank the Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio in Bologna (Italy) for supporting the Sequenom analysis in the Centre for Applied Biomedical Research (CRBA) of Bologna as well as Manuel Castro de Moura of aScidea Computational Biology Solutions, S.L. in Barcelona (Spain) for his help in the bioinformatic analysis of the RNA-Seq data.
Data archiving statement
The plant material studied is registered in the Plant Variety Database (PLUTO; http://www.upov.int/pluto/en) belonging to the International Union for the Protection of New Varieties of Plants (UPOV) (http://www.upov.int). Apricot cultivars and new selections not included in PLUTO belong to the germplasm collection and breeding programs of CEBAS-CSIC and the Università degli Studi di Bologna, which includes some breeding research material in the Genome Database for Rosaceae (GDR, http://www.rosaceae.org). Part of the RNA-Seq reads from the sequencing of the Rojo Pasión transcriptome were included in the DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ) (http://trace.ddbj.nig.ac.jp) and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory-European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/) Sequence Read Archive (SRA). Submission SRA = 48787; DDBJ Reference SRP009939; EMBL-EBI Reference SRS283323. The rest of the reads not included in this file are available at the Department of Plant Breeding of CEBAS-CSIC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by A. G. Abbott
Juan Alfonso Salazar and Manuel Rubio contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Summary of the quality control and the Paired-end RNA-Seq reads conserved after preprocesing in the apricot transcriptomes of ‘Rojo Pasión’ (3 libraries: ceb1, ceb3, ceb4) and ‘Z506-7’ (2 libraries: ceb5, ceb6) sequenced. (DOCX 776 kb)
Table S2
Total variants (including SNPs and INDELs) and INDELs identified in the different scaffolds by RNA-Seq in the two apricot transcriptomes assayed of ‘Rojo Pasión’ and ‘Z506-7’. (XLSX 43518 kb)
Table S3
SNP markers identified in the apricot transcriptomes of ‘Rojo Pasión’ (3 libraries: ceb1, ceb3, ceb4) and ‘Z506-7’ (2 libraries: ceb5, ceb6) and related sequences. (XLSX 37 kb)
Table S4
Polymorphisms obtained in the application of 96 polymorphic SNP markers by Sequenom technology in the 37 apricot genotypes. (XLSX 29 kb)
Table S5
Number of genotypic classes, heterozygosity and power of discrimination of the SNP markers detected after Sequenom assay in the 37 apricot genotypes. (XLSX 25 kb)
Table S6
Pairwise genetic distances of the 37 apricot genotypes studied obtained via the application of the 96 validated SNP markers assayed by Sequenom technology and the MCL method. (XLSX 21 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salazar, J.A., Rubio, M., Ruiz, D. et al. SNP development for genetic diversity analysis in apricot. Tree Genetics & Genomes 11, 15 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-015-0845-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-015-0845-2