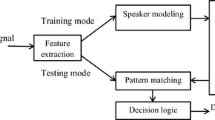
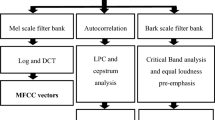
Abstract
This research work discusses automatic speaker recognition (ASR) using the cepstral characteristics of a speech sample. The enormous majority of efficient speaker recognition systems rely on cepstral learning techniques. We predict that using speech sample pitch frequency will enhance speaker recognition. The proposed speaker recognition framework employs an artificial neural network (ANN) classifier. We examine various transforms domain to extract precise information from the recorded speech signal. We carry out pre-processing interference detection before feature extractions to enhanced the efficiency of ASR. Imitations establish that the regularized pitch frequency (RPF) feature improves the speaker identification system’s performance using the discrete cosine transform (DCT), discrete wavelet transform (DWT), and discrete sine transform (DST). We have utilized the vector quantization technique for feature extraction, using Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs), to reduce the quantity of data that needs processing. The novelty of this proposed work is the ANN classification result for speaker identification derived by using DCT, DWT, and DST transforms after applying MFCC feature extraction techniques. In the proposed method, the objective of this research work was to compute the speaker recognition results of 71%, 73%, and 81% by using an ANN classifier with speech samples for features from the DWT, the DWT, the DCT, and the DST, respectively. It is also computed that the speaker recognition rate is 38%, 40%, and 48% by using an ANN classifier without a speech sample for features from DWT, DCT, and DST, respectively. From the result, it is observed that the classification result with a speech sample has a high recognition rate compared to the result without a speech sample.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This manuscript has no associated data.
References
Chauhan, N., & Chandra, M. (2017, March). Speaker recognition and verification using artificial neural network. In 2017 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET) (pp. 1147–1149). IEEE.
Yee, C. S., & Ahmad, A. M. (2008, December). Malay language text-independent speaker verification using NN-MLP classifier with MFCC. In 2008 International Conference on Electronic Design (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Nasr, M. A., Abd-Elnaby, M., El-Fishawy, A. S., El-Rabaie, S., & El-Samie, A., F. E (2018). Speaker identification based on normalized pitch frequency and Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients. International Journal of Speech Technology, 21, 941–951.
Singh, M. K., Singh, A. K., & Singh, N. (2018). Multimedia analysis for disguised voice and classification efficiency. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 78(20), 29395–29411.
Siam, A. I., Sedik, A., El-Shafai, W., Elazm, A. A., El‐Bahnasawy, N. A., El Banby, G. M., & Abd El‐Samie, F. E. (2021). Biosignal classification for human identification based on convolutional neural networks. International Journal of Communication Systems, 34(7), e4685.
Nandyal, S., Wali, S. S., & Hatture, S. M. (2015). MFCC based text-dependent speaker identification using BPNN. International Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 3(1), 30–34.
Singh, M. K. (2023). A text independent speaker identification system using ANN, RNN, and CNN classification technique. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 1–13.
Kung, H. Y., Chaisit, S., & Phuong, N. T. M. (2015). Optimization of an RFID location identification scheme based on the neural network. International Journal of Communication Systems, 28(4), 625–644.
Singh, M. K., Singh, A. K., & Singh, N. (2019). Multimedia utilization of non-computerized disguised voice and acoustic similarity measurement. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 1–16.
Gui, G., & Adachi, F. (2015). Adaptive sparse system identification using normalized least mean fourth algorithm. International Journal of Communication Systems, 28(1), 38–48.
Singh, M., Nandan, D., & Kumar, S. (2019). Statistical Analysis of Lower and Raised Pitch Voice Signal and its efficiency calculation. Traitement Du Signal, 36(5), 455–461.
Sher, M., Ahmad, N., & Sher, M. (2012, September). TESPAR feature based isolated word speaker recognition system. In 18th International Conference on Automation and Computing (ICAC) (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Nandan, D., Singh, M. K., Kumar, S., & Yadav, H. K. (2022). Speaker Identification based on Physical Variation of Speech Signal. Traitement Du Signal, 39(2).
Daqrouq, K., & Tutunji, T. A. (2015). Speaker identification using vowels features through a combined method of formants, wavelets, and neural network classifiers. Applied Soft Computing, 27, 231–239.
Singh, M. K. (2024). Speaker emotion Recognition System using Artificial neural network classification method for brain-inspired application. Journal of Circuits Systems and Computers, 2450187. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126624501871.
Jia, X., & Feng, Q. (2015). An improved anti-collision protocol for radio frequency identification tag. International Journal of Communication Systems, 28(3), 401–413.
Praveen, N., & Thomas, T. (2013). Text dependent speaker recognition using MFCC features and BPANN. International Journal of Computer Applications, 74(5), 31–39.
Singh, M. K., Singh, N., Singh, A. K., & March (2019). Speaker’s Voice Characteristics and Similarity Measurement using Euclidean Distances. In 2019 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication (ICSC) (pp. 317–322). IEEE.
Antony, A., & Gopikakumari, R. (2018). Speaker identification based on combination of MFCC and UMRT based features. Procedia Computer Science, 143, 250–257.
Sangwan, P., Deshwal, D., Kumar, D., & Bhardwaj, S. (2020). Isolated word language identification system with hybrid features from a deep belief network. International Journal of Communication Systems, e4418.
Hassan, E. S., Neyazi, B., Seddeq, H. S., Mahmoud, A. Z., Oshaba, A. S., El-Emary, A., & El–Samie, A., F. E (2024). Enhancing speaker identification through reverberation modeling and cancelable techniques using ANNs. Plos One, 19(2), e0294235. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0294235.
Arar, M. E., Sedef, H., & Signal (2023). Image and Video Processing, 17(8), 4385–4394.
Garain, A., Ray, B., Giampaolo, F., Velasquez, J. D., Singh, P. K., & Sarkar, R. (2022). GRaNN: Feature selection with golden ratio-aided neural network for emotion, gender and speaker identification from voice signals. Neural Computing and Applications, 34(17), 14463–14486.
Farhadipour, A., & Veisi, H. (2024). Gammatonegram representation for end-to-end dysarthric speech processing tasks: Speech recognition, speaker identification, and intelligibility assessment. Iran Journal of Computer Science, 1–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M.K. Speaker Identification Using MFCC Feature Extraction ANN Classification Technique. Wireless Pers Commun 136, 453–467 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11282-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-024-11282-1