Abstract
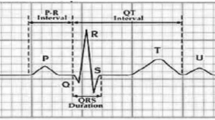
Heart rate is a vital sign that holds important information about cardiac signals. The measurement of heart rate is of particular interest since it reflects the dynamic changes of cardiac functions. Close examination of electrocardiogram (ECG) morphology is used to determine the specific value of heart rate as well as to distinguish between normal or abnormal heart functioning. Since ECG signal is contaminated by various noise components and artifacts like baseline wandering (BLW), power line interference (PLI), motion artifacts and electrode motion. Therefore, it is an immense task to separate the preferred signal from these noise contents and to measure physiological heart rate. Hence, this paper firstly presents wavelet transform based method to remove PLI and BLW noises, the major sources affecting recorded ECG. Furthermore for analyzing ECG signals and identifying characteristics features two methods have been proposed to calculate heart rate. They are: (i) temporal characteristics-based timing intervals between two consecutive R-peaks and (ii) local frequency-based ECG signal analysis used to identify number of R-peaks. At last according to the standard range of heart beats per minute, classification of normal and abnormal ECG is done and results obtained from both methods are compared. It includes simulation of 35 ECG records, out of which 24 are normal and 11 are abnormal, which are further classified in 4 fast heart beats and 7 slow heart beats called tachycardia and bradycardia respectively. The efficiency of proposed work is validated from MIT BIH arrhythmia database.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sundnes, J., Lines, G. T., Grøttum, P., & Tveito, A. (2003). Electrical activity in the human heart. Advanced topics in computational partial differential equations (pp. 401–449). Springer.
Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation. (1998). Testing and reporting performance results of cardiac rhythm and ST segment measurement algorithms. ANSI/AAMI EC, 38, 1998.
Chu Duc, H., NguyenPhan, K., & NguyenViet, D. (2013). A review of heart rate variability and its applications. APCBEE Procedia, 7, 80–85.
Pietilä, J., Mehrang, S., Tolonen, J., Helander, E., Jimison, H., Pavel, M., & Korhonen, I. (2017). Evaluation of the accuracy and reliability for photoplethysmography based heart rate and beat-to-beat detection during daily activities. EMBEC & NBC 2017 (pp. 145–148). Springer.
Valenti, G., &Westerterp, K. R. (2013). Optical heart rate monitoring module validation study. In 2013 IEEE international conference on consumer electronics (ICCE) (pp. 195–196). IEEE.
Luz, E. J. D. S., Schwartz, W. R., Cámara-Chávez, G., & Menotti, D. (2016). ECG-based heartbeat classification for arrhythmia detection: A survey. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine, 127, 144–164.
Tadi, M. J., Lehtonen, E., Saraste, A., Tuominen, J., Koskinen, J., Teräs, M., ... & Koivisto, T. (2017). Gyrocardiography: A new non-invasive monitoring method for the assessment of cardiac mechanics and the estimation of hemodynamic variables. Scientific reports, 7(1), 1–11.
Rao, P. T., Rao, S. K., Manikanta, G., & Kumar, S. R. (2016). Distinguishing normal and abnormal ECG signal. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 9(10), 1–5.
Houssein, E. H., Kilany, M., & Hassanien, A. E. (2017). ECG signals classification: A review. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering Informatics, 5(4), 376–396.
Novak, V. E. R. A., Novak, P. E. T. E. R., de Champlain, J. A. C. Q. U. E. S., Le Blanc, A. R., Martin, R., & Nadeau, R. (1993). Influence of respiration on heart rate and blood pressure fluctuations. Journal of Applied Physiology, 74(2), 617–626.
Berkaya, S. K., Uysal, A. K., Gunal, E. S., Ergin, S., Gunal, S., & Gulmezoglu, M. B. (2018). A survey on ECG analysis. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 43, 216–235.
Satija, U., Ramkumar, B., & Manikandan, M. S. (2018). A review of signal processing techniques for electrocardiogram signal quality assessment. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering, 11, 36–52.
Fehér, Á. (2017). Denoising ECG signals by applying discrete wavelet transform. In 2017 International conference on optimization of electrical and electronic equipment (OPTIM) & 2017 intl aegean conference on electrical machines and power electronics (ACEMP) (pp. 863–868). IEEE.
Hamiane, M., & Ali, M. H. (2017). Wavelet-based ECG signal analysis and classification. International Journal of Computer and Information Engineering, 11(7), 895–909.
AlMahamdy, M., & Riley, H. B. (2014). Performance study of different denoising methods for ECG signals. Procedia Computer Science, 37, 325–332.
Kathirvel, P., Manikandan, M. S., Prasanna, S. R. M., & Soman, K. P. (2011). An efficient R-peak detection based on new nonlinear transformation and first-order Gaussian differentiator. Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology, 2(4), 408–425.
Chanwimalueang, T., von Rosenberg, W., & Mandic, D. P. (2015). Enabling R-peak detection in wearable ECG: Combining matched filtering and Hilbert transform. In 2015 ieee international conference on digital signal processing (DSP) (pp. 134–138). IEEE.
Arteaga-Falconi, J., Al Osman, H., & El Saddik, A. (2015). R-peak detection algorithm based on differentiation. In 2015 IEEE 9th international symposium on intelligent signal processing (WISP) proceedings (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Qin, Q., Li, J., Yue, Y., & Liu, C. (2017). An adaptive and time-efficient ECG R-peak detection algorithm. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 5980541, 1–15.
Khriji, L., & Al-Busaidi, A. M. (2018, March). New adaptive thresholding-based ECG R-peak detection technique. In 2018 IEEE 4th Middle East Conference on Biomedical Engineering (MECBME) (pp. 147–152). IEEE.
Kaur, H., & Rajni, R. (2017). Electrocardiogram signal analysis for R-peak detection and denoising with hybrid linearization and principal component analysis. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences, 25(3), 2163–2175.
Rakshit, M., Panigrahy, D., & Sahu, P. K. (2016). An improved method for R-peak detection by using Shannon energy envelope. Sādhanā, 41(5), 469–477.
Park, J. S., Lee, S. W., & Park, U. (2017). R peak detection method using wavelet transform and modified shannon energy envelope. Journal of healthcare engineering, 1–14.
John, A. A., Subramanian, A. P., Jaganathan, S. K., & Sethuraman, B. (2015). Evaluation of cardiac signals using discrete wavelet transform with MATLAB graphical user interface. Indian Heart Journal, 67(6), 549–551.
D’Aloia, M., Longo, A., & Rizzi, M. (2019). Noisy ECG signal analysis for automatic peak detection. Information, 10(35), 1–12.
Gul, M. U., Kadir, K., Azman, H. K., & Iqbal, S. (2019). Detection of r-peaks using single-scale wavelet transform. In 2019 13th international conference on mathematics, actuarial science, computer science and statistics (MACS) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Addison, P. S. (2005). Wavelet transforms and the ECG: A review. Physiological Measurement, 26(5), R155.
Peng, Z. K., Jackson, M. R., Rongong, J. A., Chu, F. L., & Parkin, R. M. (2009). On the energy leakage of discrete wavelet transform. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 23(2), 330–343.
Saxena, S., & Vijay, R. (2019). Optimal selection of wavelet transform for de-noising of ECG signal on the basis of statistical parameters. In international conference on soft computing and signal processing (pp. 731–739). Springer.
Nagendra, H., Mukherjee, S., & Kumar, V. (2013). Wavelet based nonlinear thresholding techniques for pre-processing ECG signals. International Journal of Biomedical and Advance Research, 4(8), 534–544.
**g-Yi, L., Hong, L., Dong, Y., & Yan-Sheng, Z. (2016). A new wavelet threshold function and denoising application. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 1–8.
Donoho, D. L., & Johnstone, I. M. (1994) Threshold selection for wavelet shrinkage of noisy data. In Proceedings of 16th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, (Vol. 1, pp. 24–25). IEEE.
The MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database [online] http://www.physionet.org/cgi-bin/atm/ATM. Accessed on 10 January 2020.
Benjamin, E. J., Virani, S. S., Callaway, C. W., Chamberlain, A. M., Chang, A. R., Cheng, S., & Muntner, P. (2018). Heart disease and stroke statistics—2018 update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation, 137(12), e67–e492.
Using MATLAB Wavelet tool box (2013) Wavelet 1D GUI, Math Works version.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The study did not have funding from any agency. There is no conflict of interest for any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, S., Vijay, R., Saxena, G. et al. Classification of Cardiac Signals with Automated R-Peak Detection Using Wavelet Transform Method. Wireless Pers Commun 123, 655–669 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09151-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09151-2