Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to investigate the urinary caspase-3 and cytochrome c levels in patients with unilateral antenatal hydronephrosis and to determine whether changes in urinary biomarker levels could be useful for both predicting the need for surgical intervention due to ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) and postoperative surgical success.
Methods
Sixty-five children with a history of unilateral antenatal hydronephrosis and postnatal anteroposterior diameter ≥ 10 mm were included in this prospective case–control study between January 2013 and December 2021. The obstruction group consisted of 33 patients (28 boys, 84.8%) who underwent open dismembered pyeloplasty due to UPJO. The non-obstructive dilatation (NOD) group consisted of 32 patients (27 boys, 84.4%) with stable or improving hydronephrosis and no significant reduction in ipsilateral split renal function during follow-up, whereas 34 healthy children were enrolled in the study as a control group. Urinary urinary caspase-3 and cytochrome c levels using ELISA were measured.
Results
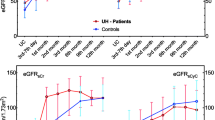
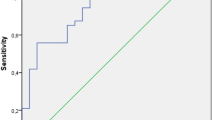
The median preoperative urinary caspase-3 level was significantly higher in the obstruction group when compared to the NOD group (4.82 ng/mgCr vs. 2.61 ng/mgCr, p = 0.013) as well as the control group (4.82 ng/mgCr vs. 1.72 ng/mgCr, p = 0.002). In the postoperative period, urinary caspase-3 levels significantly decreased compared to preoperative measurements (4.82 ng/mgCr vs. 2.51 ng/mgCr, p = 0.006) and became similar to the control group (2.51 ng/mgCr vs. 1.72 ng/mgCr, p = 0.422). On the other hand, no significant differences were observed in urinary cytochrome c levels between the groups. All patients who underwent pyeloplasty achieved postoperative resolution in hydronephrosis and improved drainage on MAG-3, so none of the patients required re-do pyeloplasty. Postoperative decrease in caspase-3 level was found to be compatible with adequate urine drainage on MAG-3 scan. The cut-off value of urinary caspase-3 to predict patients requiring pyeloplasty was found to be 3.31 ng/mg creatinine with 63.6% sensitivity, 62.5% specificity (AUC = 0.679). In the multivariable analysis, urinary caspase-3 level (OR: 1.653, p = 0.019), anteroposterior pelvic diameter (OR: 1.401, p = 0.001), and split renal function on MAG-3 (OR: 1.277, p = 0.011) were found to be independent factors in determining patients who require surgery.
Conclusion
Based on our preliminary findings, urinary caspase-3 levels could be a useful biomarker not only for predicting the need for surgical intervention but also for determining the postoperative surgical success in children with UPJO.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- APD:
-
Anteroposterior pelvic diameter
- AUC:
-
Area under curve
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- HSP70:
-
Heat shock protein 70
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- max:
-
Maximum
- min:
-
Minimum
- NOD:
-
Non-obstructive dilatation
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- SFU:
-
The Society of Fetal Urology
- SRF:
-
Split renal function
- UPJO:
-
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction
- VCUG:
-
Voiding cystourethrography
References
Nguyen HT, Herndon CD, Cooper C, Gatti J, Kirsch A, Kokorowski P et al (2010) The Society for Fetal Urology consensus statement on the evaluation and management of antenatal hydronephrosis. J Pediatr Urol 6(3):212–231
Chertin B, Pollack A, Koulikov D, Rabinowitz R, Hain D, Hadas-Halpren I et al (2006) Conservative treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction in children with antenatal diagnosis of hydronephrosis: Lessons learned after 16 years of follow-up. Eur Urol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2006.01.046
Karakus S, Oktar T, Kucukgergin C, Kalelioglu I, Seckin S, Atar A et al (2016) Urinary IP-10, MCP-1, NGAL, Cystatin-C, and KIM-1 levels in prenatally diagnosed unilateral hydronephrosis: the search for an ideal biomarker. Urology 87:185–192
Atar A, Oktar T, Kucukgergin C, Kalelioglu I, Seckin S, Ander H et al (2015) The roles of serum and urinary carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in the management of patients with antenatal hydronephrosis. J Pediatr Urol 11(3):133.e1–5
Oktar T, Küçükgergin C, Dönmez Mİ, Özkuvancı Ü, Yılmaz A, Yürük Yıldırım Z et al (2022) Urinary HSP70 can predict the indication of surgery in unilateral ureteropelvic junction obstruction. Pediatr Surg Int 38(3):499–503
Özkuvancı Ü, Dönmez Mİ, Ziylan O, Oktar T, Küçükgergin C, Çetin B et al (2020) Can urinary biomarkers detect obstruction defined by renal functional loss in antenatal hydronephrosis? J Pediatr Urol 16(6):844.e1-844.e7
Chevalier RL (2004) Biomarkers of congenital obstructive nephropathy: past, present and future. J Urol 172:852–857
Cachat F, Lange-Sperandio B, Chang A, Kiley SC, Thornhill BA, Forbes MS et al (2003) Ureteral obstruction in neonatal mice elicits segment-specific tubular cell responses leading to nephron loss. Kidney Int 63:564–575
Truong LD, Choi Y, Tsao CC, Ayala G, Sheikh-Hamad D, Nasssar G et al (2001) Renal cell apoptosis in chronic obstructive uropathy: the rolees of caspases. Kidney Int 60:924–934
Zager RA, Johnson ACM, Hanson SY (2004) Proximal tubular cytochrome c efflux: determinant, and potential marker, of mitochondrial injury. Kidney Int 65:2123–2134
Yang B, Nahas ME, Thomas GL, Haylor JL, Watson PF, Wagner B et al (2001) Caspase-3 and apoptosis in experimental chronic renal scarring. Kidney Int 60:1765–1776
Radmayr C, Bogaert G, Burgu B, Castagnetti MS, Dogan HS, O’Kelly F, et al. European association of urology guidelines on paediatric urology: the 2023 update. EAU Guidelines Office; 2023. Arnhem, The Netherlands. Available from: https://uroweb.org/guideline/paediatric-urology [Accessed 01 November 2023]
Peters CA, Skoog SJ, Arant BS Jr, Copp HL, Elder JS, Hudson RG, et al. American Urological Association guidelines on management and screening of primary vesicoureteral reflux in children: the 2017 update. Available from: https://www.auanet.org/guidelines-and-quality/guidelines/vesicoureteral-reflux-guideline [Accessed 01 November 2023]
Papachristou F, Pavlaki A, Printza N (2014) Urinary and serum biomarkers in ureteropelvic junction obstruction: a systematic review. Biomarkers 19(7):531–540
Truong LD, Choi Y, Tsao CC, Ayala G, Sheikh-Hamad D, Nasssar G et al (2001) Renal cell apoptosis in chronic obstructive uropathy: the roles of caspases. Kidney Int 60:924–934
Manucha W, Valles PG (2008) Cytoprotective role of nitric oxide associated with Hsp70 expression in neonatal obstructive nephropathy. Nitric Oxide 18:204–215
Hosoya M, Kawasaki Y, Katayose M, Sakuma H, Watanabe M, Igarashi E et al (2006) Prognostic predictive values of serum cytochrome c, cytokines, and other laboratory measurements in acute encephalopathy with multiple organ failure. Arch Dis Child 91:469–472
Sibarani J, Tjahjodjati T, Atik N, Rachmadi D, Mustafa A (2020) Urinary cytochrome c and caspase-3 as novel biomarker of renal function impairment in unilateral ureteropelvic junction obstruction model of wistar rats. Res Rep Urol 12:217–224
Yücel ÖB, Dönmez Mİ, Küçükgergin C, Ziylan O, Seçkin Ş, Oktar T (2022) Urinary biomarkers can identify the need for pyeloplasty in presence of supranormal differential renal function in antenatally diagnosed unilateral hydronephrosis. J Pediatr Urol 18(1):6–12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zeybek SG: Conception and design, Acquisition of data, Analysis and Interpretation of data, Statistical analysis, Literature Search. Selvi I: Analysis and Interpretation of data, Statistical analysis, Literature Search, Drafting of the manuscript. Oktar T: Conception and design, Administrative, Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, Supervision. Dönmez Mİ: Conception and design, Administrative, Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. Ziylan O: Administrative, Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, Supervision. Seçkin Ş: Administrative, Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, Supervision. Küçükgergin C: Conception and design, Acquisition of data, Technical or material support, Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest and has nothing to disclose.
Funding
This study was supported by the Research Fund of Istanbul University (No. TYL-2021-37576).
Ethical approval
The study received Institutional Review Board approval (Ethical IRB number: 29624016-050.99- 1854). All procedures performed in our study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the local research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeybek, S.G., Selvi, İ., Oktar, T. et al. Can urinary caspase-3 and cytochrome c levels be used as predictive biomarkers in the management of unilateral antenatal hydronephrosis?. Int Urol Nephrol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-024-04008-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-024-04008-6