Abstract
Objectives
The current study aimed to examine the incidence of perioperative infections and graft viability in ABO-compatible and ABO-incompatible renal transplant recipients.
Methods
We included 643 living donor renal transplant recipients registered in the Michinoku Renal Transplant Network from 1998 to 2021. Patients were divided into the ABO-compatible and ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation groups. We compared the characteristics of the two groups and evaluated the incidence of postoperative viral infections (cytomegalovirus and BK virus), graft loss-free survival, and overall survival between the two groups.
Results
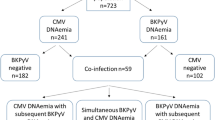
Of 643 patients, 485 (75%) and 158 (25%) were ABO-compatible and ABO-incompatible renal transplant recipients, respectively. Postoperative viral infections, rituximab use, and plasma exchange were significantly more common in ABO-incompatible than in ABO-compatible transplant recipients. However, there were no significant differences in terms of other background characteristics. The ABO-incompatible group was more likely to develop viral infections than the ABO-compatible group. Graft loss-free survival and overall survival did not significantly differ between the two groups. According to the multivariate Cox regression analysis, ABO compatibility was not significantly associated with graft loss-free survival and overall survival.
Conclusion
Although the incidence of postoperative viral infections in ABO-incompatible renal transplant recipients increased, there was no significant difference in terms of rejection events, graft loss-free survival, and overall survival.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data sharing and data accessibility
Data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Takahashi K, Saito K (2013) ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Transplant Rev (Orlando) 27(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trre.2012.07.003
Habicht A, Bröker V, Blume C, Lorenzen J, Schiffer M, Richter N, Klempnauer J, Haller H, Lehner F, Schwarz A (2011) Increase of infectious complications in ABO-incompatible kidney transplant recipients–a single centre experience. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(12):4124–4131. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr215
Scurt FG, Ewert L, Mertens PR, Haller H, Schmidt BMW, Chatzikyrkou C (2019) Clinical outcomes after ABO-incompatible renal transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 393(10185):2059–2072. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)32091-9
Okumi M, Toki D, Nozaki T, Shimizu T, Shirakawa H, Omoto K, Inui M, Ishida H, Tanabe K (2016) ABO-Incompatible living kidney transplants: evolution of outcomes and immunosuppressive management. Am J Transplant 16(3):886–896. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13502
Uchida J, Kosoku A, Naganuma T, Tanaka T, Nakatani T (2020) Latest insights on ABO-incompatible living-donor renal transplantation. Int J Urol 27(1):30–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.14109
Roufosse C, Simmonds N, Clahsen-van Groningen M, Haas M, Henriksen KJ, Horsfield C, Loupy A, Mengel M, Perkowska-Ptasińska A, Rabant M, Racusen LC, Solez K, Becker JU (2018) A 2018 reference guide to the Banff classification of renal allograft pathology. Transplantation 102(11):1795–1814. https://doi.org/10.1097/tp.0000000000002366
Loupy A, Haas M, Roufosse C, Naesens M, Adam B, Afrouzian M, Akalin E, Alachkar N, Bagnasco S, Becker JU, Cornell LD, Clahsen-van Groningen MC, Demetris AJ, Dragun D, Duong van Huyen JP, Farris AB, Fogo AB, Gibson IW, Glotz D, Gueguen J, Kikic Z, Kozakowski N, Kraus E, Lefaucheur C, Liapis H, Mannon RB, Montgomery RA, Nankivell BJ, Nickeleit V, Nickerson P, Rabant M, Racusen L, Randhawa P, Robin B, Rosales IA, Sapir-Pichhadze R, Schinstock CA, Seron D, Singh HK, Smith RN, Stegall MD, Zeevi A, Solez K, Colvin RB, Mengel M (2020) The Banff 2019 kidney meeting report (I): updates on and clarification of criteria for T cell- and antibody-mediated rejection. Am J Transplant 20(9):2318–2331. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.15898
Austin PC, Stuart EA (2015) Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies. Stat Med 34(28):3661–3679. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.6607
Lee HR, Kim K, Lee SW, Song JH, Lee JH, Hwang SD (2021) Effect of rituximab dose on induction therapy in ABO-incompatible living kidney transplantation: a network meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 100(10):e24853. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000024853
Okada M, Narumi S, Hasegawa Y, Futamura K, Hiramitsu T, Ichimori T, Goto N, Kobayashi T, Uchida K, Takeda A, Watarai Y (2023) Optimal dose of rituximab in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in patients with low anti-A/B antibody titers: a single-center retrospective cohort study. Clin Transplant 37(2):e14915. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.14915
Hatakeyama S, Fujita T, Murakami R, Suzuki Y, Sugiyama N, Yamamoto H, Okamoto A, Imai A, Tobisawa Y, Yoneyama T, Mori K, Yoneyama T, Hashimoto Y, Koie T, Narumi S, Ohyama C (2014) Outcome comparison of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation with low-dose rituximab and ABO-compatible kidney transplantation: a single-center experience. Transplant Proc 46(2):445–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.09.036
Wiseman AC (2016) Immunosuppressive Medications. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(2):332–343. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.08570814
Marcén R (2009) Immunosuppressive drugs in kidney transplantation: impact on patient survival, and incidence of cardiovascular disease, malignancy and infection. Drugs 69(16):2227–2243. https://doi.org/10.2165/11319260-000000000-00000
Aiyegbusi O, McGregor E, McManus SK, Stevens KI (2022) Immunosuppression therapy in kidney transplantation. Urol Clin North Am 49(2):345–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ucl.2021.12.010
Tanabe K, Takahashi K, Sonda K, Agishi T, Kawaguchi H, Ishikawa N, Kimata N, Oshima S, Goya N, Nakazawa H et al (1995) ABO-incompatible living kidney donor transplantation: results and immunological aspects. Transplant Proc 27(1):1020–1023
Fuchinoue S, Ishii Y, Sawada T, Murakami T, Iwadoh K, Sannomiya A, Koyama I, Kubota K, Tojimbara T, Nakajima I, Teraoka S (2011) The 5-year outcome of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation with rituximab induction. Transplantation 91(8):853–857. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e31820f08e8
Takahashi K, Saito K, Takahara S, Okuyama A, Tanabe K, Toma H, Uchida K, Hasegawa A, Yoshimura N, Kamiryo Y (2004) Excellent long-term outcome of ABO-incompatible living donor kidney transplantation in Japan. Am J Transplant 4(7):1089–1096. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2004.00464.x
de Weerd AE, Betjes MGH (2018) ABO-incompatible kidney transplant outcomes: a meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 13(8):1234–1243. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.00540118
Okumi M, Kakuta Y, Unagami K, Takagi T, Iizuka J, Inui M, Ishida H, Tanabe K (2019) Current protocols and outcomes of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation based on a single-center experience. Transl Androl Urol 8(2):126–133. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau.2019.03.05
Jeon HJ, Koo TY, Ju MK, Chae DW, Choi SJN, Kim MS, Ryu JH, Jeon JC, Ahn C, Yang J (2022) The Korean organ transplantation registry (KOTRY): an overview and summary of the kidney-transplant cohort. Kidney Res Clin Pract 41(4):492–507. https://doi.org/10.23876/j.krcp.21.185
Japanese Society for Clinical Renal Transplantation TJSfT (2021) Annual Progress Report from the Japanese Renal Transplant Registry: Number of Renal Transplantations in 2020 and Follow-up Survey. Japanese J Transplant 56(3):195–216. https://doi.org/10.11386/jst.56.3_195
Axelrod D, Segev DL, **ao H, Schnitzler MA, Brennan DC, Dharnidharka VR, Orandi BJ, Naik AS, Randall H, Tuttle-Newhall JE, Lentine KL (2016) Economic impacts of ABO-incompatible live donor kidney transplantation: a national study of medicare-insured recipients. Am J Transplant 16(5):1465–1473. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13616
Schwartz J, Stegall MD, Kremers WK, Gloor J (2006) Complications, resource utilization, and cost of ABO-incompatible living donor kidney transplantation. Transplantation 82(2):155–163. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.tp.0000226152.13584.ae
Ferrari P, Weimar W, Johnson RJ, Lim WH, Tinckam KJ (2015) Kidney paired donation: principles, protocols and programs. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30(8):1276–1285. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfu309
Biró P, Remport Á, Mihály S, Illésy L, Nemes B (2018) Kidney exchange programmes in Europe. What is the status of Hungary? A summary of the first results of the ENCKEP (European Network for Collaboration on Kidney Exchange Programmes) COST Action. Orv Hetil 159(46):1905–1912. https://doi.org/10.1556/650.2018.31296
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Yukie Nishizawa and Satomi Sakamoto for their invaluable support with data collection. The authors thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for their English language review.
Funding
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI (grant numbers: 19H05556, 20K09517 and 20K18083) and the Japan Science and Technology Agency, Center of Innovation Program (grant number: JPMJCE1302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HK, SH, HT, HS, NT, TH, WO, and CO developed and supervised the study. HK, SH, TM, MS, HN, TH, SM, and RM collected the study data. HK and SH performed the statistical analysis. HK and SH wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Approval of the research protocol by an institutional reviewer board
The current study was approved by the institutional review board (2014-015 and 2019-099-1).
Informed consent
All participants provided a written informed consent prior to study participation.
Registry and the registration no. of the study/trial
Not available.
Animal studies
Not available.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kodama, H., Hatakeyama, S., Matsuura, T. et al. Incidence of postoperative cytomegalovirus and BK-polyoma virus infections and graft loss in ABO-incompatible renal transplant recipients: a multicenter retrospective study. Int Urol Nephrol 56, 2187–2193 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03934-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03934-1