Abstract
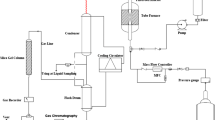
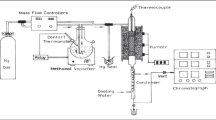
The effect of the binders, such as silica, alumina, and aluminum phosphate solution (APS), was studied on the acidity and catalytic performance of HZSM-5 zeolite (SiO2/Al2O3 = 80) in methanol-to-propylene (MTP) process. The strong acidity of catalyst increased slightly with alumina binder but decreased with silica and APS binders. It is noted that the catalyst with APS binder showed the highest bulk crush strength. Catalytic performance of the alumina or silica bound catalyst was comparable to that of pure HZSM-5 catalyst while that of APS bound catalyst was completely different depending on the binder content. Low content (10 wt%) of APS resulted in a dramatically enhanced propylene selectivity (>40 C mol%) due to the decrease in strong acidity. On the other hand with high content (>20 wt%) of APS, methanol was mostly dehydrated into dimethylether without further transformation into hydrocarbons even if the mechanical strength was significantly improved. The binary binder system was proposed not only to improve the mechanical strength of catalyst with small amount of APS binder but also to keep a high propylene selectivity. The catalyst bound with APS-and-alumina or APS-and-silica showed a comparable propylene selectivity to that of HZSM-5 with the 10 wt% of APS single binder while demonstrated much higher bulk crush strengths.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mei C, Wen P, Liu Z, Liu H, Wang Y, Yang W, **e Z, Hua W, Gao Z (2008) J Catal 258:243
Stöcker M (1999) Micropor Mesopor Mater 29:3
Chang CD, Chu CT-W, Socha RF (1984) J Catal 86:289
Prinz D, Riekert L (1988) Appl Catal 37:139
Zhao TS, Takemoto T, Tsubaki N (2006) Catal Commun 7:647
Marchi AJ, Froment GF (1993) Appl Catal 94:91
Haw JF, Marcus DM (2005) Top Catal 34:41
Bleken F, Bjorgen M, Palumbo L, Bordiga S, Svelle S, Lillerud KP, Olsbye U (2009) Top Catal 52:218
Choudhary VR, Devadas P, Kinage AK, Guisnet M (1997) Appl Catal A. 162:223
Wu X, Alkhawaldeh A, Anthony RG (2002) Stud Surf Sci Catal 143:217
Dorado F, Romero R, Canizares P (2002) Appl Catal A 236:235
Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Qiu A, Wang Y, Xu Y, Wu P (2006) Ind Eng Chem Res 45:2213
Lucas AD, Sanchez P, Funez A, Ramos MJ, Valverde JL (2006) J Mol Catal A 259:259
Sanchez P, Dorado F, Funez A, Jimenez V, Ramos MJ, Valverde JL (2007) J Mol Catal A 273:109
Designation: D 7084-04, ASTM international
Kim SD, Baek SC, Lee YJ, Jun KW, Kim MJ, Yoo IS (2006) Appl Catal A 309:139
Freiding J, Patcas FC, Czarmetzki BK (2007) Appl Catal A 328:210
Khattaf SA, Pavlackova ZM, Ali MA, Cejka J (2009) Top Catal 52:140
Martin A, Berndt H (1994) React Kinet Catal Lett 52:405
Vinek H, Rumplmayr G, Lercher JA (1989) J Catal 115:291
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Next-Generation Novel Technology Development project and the Brain Korea 21 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, KY., Lee, HK. & Ihm, SK. Influence of Catalyst Binders on the Acidity and Catalytic Performance of HZSM-5 Zeolites for Methanol-to-Propylene (MTP) Process: Single and Binary Binder System. Top Catal 53, 247–253 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-009-9412-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-009-9412-0