Abstract
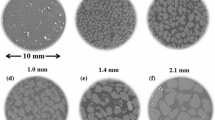
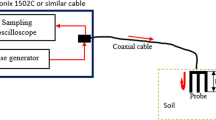
When aqueous sodium chloride evaporates, crystals can form. Salt crystallisation can take place within voids resulting in subflorescence which can culminate in surface heave, or can lead to efflorescence on exposed surfaces. Evaporation can be measured using relative humidity sensors, and thus salt crystallisation be inferred. A series of laboratory experiments were conducted using vertical flow columns packed with dry medium-grained sand with their exposed surfaces subjected to air at low relative humidity while stood in a shallow container of deionised water or brine. Experiments using deionised water showed that the degree of saturation above the capillary fringe was initially insufficient for transporting salt to the surface through diffusion. Nevertheless, repeated tests using concentrated sodium chloride solution showed that internal changes in relative humidity, and surface heave, were consistent with the upward migration of salt by autogenous internal ‘wicking’. The results indicate that relative humidity sensors can be used as a practical way to detect salt crystallisation and the conditions which promote its transportation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castellazzi, G., Colla, C., de Miranda, S., Formica, G., Gabrielli, E., Molari, L., Ubertini, F.: A coupled multiphase model for hygrothermal analysis of masonry structures and prediction of stress induced by salt crystallisation. Constr. Build. Mater. 41, 717–731 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.12.045
Colston, B.J., Watt, D.S., Munro, H.L.: Environmentally induced stone decay: the cumulative effects of crystallisation-hydration cycles on a Lincolnshire oopelsparite limestone. J. Cult. Herit. 4, 297–307 (2001). doi:10.1016/S1296-2074(01)01129-3
Culligan, P.J., Ivanov, V., Germaine, J.T.: Sorptivity and liquid infiltration into dry soil. Adv. Water Resour. 28, 1010–1020 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.04.003
Desarnaud, J., Derluyn, H., Molari, L., de Miranda, S., Cnudde, V., Shahidzadeh, N.: Drying of salt contaminated porous media: effect of primary and secondary nucleation. J. Appl. Phys. 118(11), 114901 (2015). doi:10.1063/1.4930292
Desarnaud, J., Shahidzadeh-Bonn, N.: Salt crystal purification by deliquescence/crystallisation cycling. EPL. 95(48002), 1–6 (2011). doi:10.1209/0295-5075/95/48002
Dopfer, D., Palzer, S., Heinrich, S., Fries, L., Antonyuk, S., Haider, C., Salman, A.D.: Adhesion mechanisms between water soluble particles. Powder Technol. 238, 35–49 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2012.06.029
Eloukabi, H., Sghaier, N., Nasrallah, S.B., Prat, M.: Experimental study of the effect of sodium chloride on drying of porous media: the crusty-patchy efflorescence transition. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 56(1), 80–93 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.09.045
Gao, Y., Chen, S.B., Yu, L.E.: Efflorescence relative humidity of airborne sodium chloride particles: a theoretical investigation. Atmos. Environ. 41(9), 2019–2023 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.12.014
Hazlehurst, T.H., Martin, H.C., Brewer, L.: The cree** of saturated salt solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 40(4), 439–452 (1935). doi:10.1021/j150373a003
Hird, R., Bolton, M.D.: Migration of sodium chloride in dry porous materials. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 2016 471, (2186) (2016). doi:10.1098/rspa.2015.0710
Hird, R., Bolton, M.D.: Upward migration of sodium chloride by crystallisation on non-porous surfaces. Phil. Mag. 94(1), 78–91 (2014). doi:10.1080/14786435.2013.843794
Langlet, M., Benali, M., Pezron, I., Saleh, K., Guigon, P., Metlas-Komunjer, L.: Caking of sodium chloride. Role of ambient relative humidity in dissolution and recrystallization process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 86, 78–86 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.ces.2012.05.014
Likos, W. J., Lu, N.: Automated humidity system for measuring total suction characteristics of clay. Geotech. Test. J. 126(2), 1–12 (2003). doi:10.1520/GTJ11321J
Mohamad, A.A., Sasaki, T., Watanabe, K.: Solute transport through unsaturated soil due to evaporation. J. Environ. Eng., Vol. 126, No. 9 (2000). doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2000)126:9(842)
Mullin, J.W.: Crystallisation, 4th edn. Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford (2001)
Norouzi Rad, M., Shokri, N., Keshmiri, A., Withers, P.J.: Effects of grain and pore size on salt precipitation during evaporation from porous media. Transp. Porous Media. 110(2), 281–294 (2015). doi:10.1007/s11242-015-0515-8
Or, D., Lehmann, P., Shahraeeni, E., Shokri, N.: Advances in soil evaporation physics—a review. Vadose Zone J. 12(4), 1–16 (2013). doi:10.2136/vzj2012.0163
Ozdemir, O., Karakashev, S.I., Nguyen, A.V., Miller, J.D.: Adsorption and surface tension analysis of concentrated alkali halide brine solutions. Miner. Eng. 22(3), 263–271 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2008.08.001
Robert, D., Soga, K.: Soil-pipeline interaction in unsaturated soils. In: Laloui, L. (ed.) Mechanics of Unsaturated Geomaterials, pp. 303–325. Wiley, Hoboken (2010)
Robinson, D.A., Jones, S.B., Wraith, J.M., Or, D., Friedman, S.P.: A review of advances in dielectric and electrical conductivity measurement in soils using time domain reflectometry. Vadose Zone J. 2, 444–475 (2003). doi:10.2136/vzj2003.4440
Rodriguez-Navarro, C., Doehne, E.: Salt weathering: influence of evaporation rate, supersaturation and crystallization pattern. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 24, 191–209 (1999). doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9837(199903)
Sadeghi, M., Taghikhani, V., Ghotbi, C.: Measurement and correlation of surface tension for single aqueous electrolyte solutions. Int. J. Thermophys. 31, 852–859 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10765-010-0725-9
Sandrolini, F., Franzoni, E.: An operative protocol for reliable measurements of moisture content in porous materials of ancient buildings. Build. Environ. 41, 1372–1380 (2006)
Sghaier, N., Prat, M., Nasrallah, S.B.: On the influence of sodium chloride concentration on equilibrium contact angle. Chem. Eng. J. 122, 47–53 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.cej.2006.02.017
Sghaier, N., Geoffroy, S., Prat, M., Eloukabi, H., Ben Nasrallah, S.: Evaporation-driven growth of large crystallized salt structures in a porous medium. Am. Phys. Soc. Phys. Rev. E 90, 042402 (2014). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.90.042402
Sghaier, N., Prat, M.: Effect of efflorescence formation on drying kinetics of porous media. Transp. Porous Media 80(3), 441–451 (2009). doi:10.1007/s11242-009-9373-6
Stokes, M., Charman, J., Epps, R.J., Griffiths, J.S.: Engineering group working party. Soil and rock description and characteristics. In: Walker, M.J. (ed.) Hot Deserts: Engineering, Geology and Geomorphology, pp. 143–157. Geological Society Engineering Special Publications, London (2012)
Tanaka, M., Girard, G., Davis, R., Peuto, A., Bignell, N.: Recommended table for the density of water between 0C and 40C based on recent experimental reports. Metrologia 38, 301–309 (2001). doi:10.1088/0026-1394/38/4/3
Terzaghi, K., Peck, R.B.: Soil mechanics in engineering practise. Wiley, New York (1964)
Topp, G.C., Davis, J.L., Annan, A.P.: Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: measurement in coaxial transmission lines. Water Resour. Res. 16(3), 574–582 (1980). doi:10.1029/WR016i003p00574
Van Enckevort, W.J.P., Los, J.H.: On the cree** of saturated salt solutions. Cryst. Growth Des. 13(5), 1838–1848 (2013). doi:10.1021/cg301429g
Vargaftik, N.B., Volkov, B.N., Voljak, L.D.: International tables of the surface tension of water. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 12(3), 817–820 (1983). doi:10.1063/1.555688
Vickers, T., Moukwa, M.: Evaluation of test methods and environmental conditions to promote efflorescence formation under laboratory conditions. J. Test. Eval. 24(2), 80–83 (1996)
Washburn, E.R.: The cree** of solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 31(8), 1246–1248 (1926). doi:10.1021/j150278a009
Yang, H., Rahardjo, H., Leong, E.-C., Fedlund, D.G.: Factors affecting drying and wetting soil-water characteristic curves of sandy soils. Can. Geotech. J. 41, 908–920 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hird, R., Bolton, M.D. Measurement of Relative Humidity to Monitor Salt Migration in Unsaturated Porous Media. Transp Porous Med 112, 749–763 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-016-0675-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-016-0675-1