Abstract
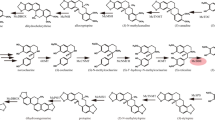
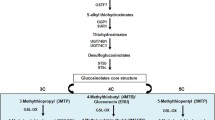
Sulforaphane (SF) is a potential secondary metabolite with anticancer activity and its metabolic pathway has been revealed in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Generally, the SF extraction cycle from broccoli is long and the yield is low, which means that it no longer meets cancer treatment requirements. Therefore, the SF content needs to be urgently improved.
In this study, MAM1, FMOGS–OX2, and Myrosinase, which are required for SF biosynthesis, were introduced into broccoli by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. To obtain plants with a higher SF content, broccoli was transformed using Myrosinase-FMOGS–OX2-MAM1 (M-F-A) triple genes in tandem and by adding each of the genes on their own. The results showed that the SF contents in the MAM1, FMOGS–OX2, or Myrosinase transgenic plants improved by 1.7–3.4, 1.6–2.7, and 3.7-fold compared to the wild type (WT), respectively, However, the SF contents in transgenic plants with all three genes improved by 1.86–5.5fold. Furthermore, we examined the anticancer effect of the SF extracts from transgenic plants via cell viability detection of HCT116 colon cancer cells. The results showed that SF extracts from transgenic plants had more obvious anticancer activity than SF extracts from WT, and the SF extracts from the multiple genes plants had stronger anticancer activity than the single gene plants. In summary, the multiple genes transformation increased the SF content in broccoli more than single gene introductions.
Key message
The aim of this research was to improve sulforaphane content by introducing FMOGS–OX2, MAM1, and Myrosinase genes, and Myrosinase-FMOGS–OX2-MAM1 (M-F-A) serial triple genes into broccoli.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Benderoth M, Textor S, Windsor A, Mitchell-Olds T, Gershenzon J, Kroymann J (2006) Positive selection driving diversification in plant secondary metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:9118–9123. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601738103
Cheng YM, Tsai CC, Hsu YC (2016) Sulforaphane, a dietary isothiocyanate, induces G2/M arrest in cervical cancer cells through cyclinB1 downregulation and GADD45β/CDC2 association. Int J Mol Sci 17:1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091530
Chiang WCK, Pusateri DJ, Leitz REA (1998) Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry method for the determination of sulforaphane and sulforaphane nitrile in broccoli. J Agric Food Chem 46:1018–1021. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf970572b
Datta K, Baisakh N, Thet KM, Tu J, Datta S (2002) Pyramiding transgenes for multiple resistance in rice against bacterial blight, yellow stem borer and sheath blight. Theor Appl Genet 106:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1014-1
Farhi M, Marhevka E, Ben-Ari J, Algamas-Dimantov A, Liang Z, Zeevi V, Edelbaum O, Spitzer-Rimon B, Abeliovich H, Schwartz B (2011) Generation of the potent anti-malarial drug artemisinin in tobacco. Nat Biotechnol 29:1072–1074. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2054
Guo L, Yang R, Gu Z (2016) Cloning of genes related to aliphatic glucosinolate metabolism and the mechanism of sulforaphane accumulation in broccoli sprouts under jasmonic acid treatment. J Sci Food Agric 96:4329–4336. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7629
Halkier BA, Gershenzon J (2006) Biology and biochemistry of glucosinolates. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:303–333. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105228
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1994.6020271.x
Hirai MY, Sugiyama K, Sawada Y, Tohge T, Obayashi T, Suzuki A, Araki R, Sakurai N, Suzuki H, Aoki K, Goda H, Nishizawa OI, Shibata D, Saito K (2007) Omics-based identification of Arabidopsis Myb transcription factors regulating aliphatic glucosinolate biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:6478–6483. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0611629104
Huang K, Lin JC, Wu QY, Yan JY, Liu MY, Zhang S, **ao WJ (2016) Changes in sulforaphane and selenocysteine methyltransferase transcript levels in broccoli treated with sodium selenite. Plant Mol Biol Rep 34:807–814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-015-0960-0
Jobling SA, Westcott RJ, Tayal A, Jeffcoat R, Schwall GP (2002) Production of a freeze–thaw-stable potato starch by antisense inhibition of three starch synthase genes. Nat Biotechnol 20:295–299. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0302-295
Juge N, Mithen RF, Traka M (2007) Molecular basis for chemoprevention by sulforaphane: a comprehensive review. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1105–1127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-6484-5
Kroymann J, Textor S, Tokuhisa JG, Falk KL, Bartram S, Gershenzon J, Mitchell-Olds T (2001) A gene controlling variation in Arabidopsis glucosinolate composition is part of the methionine chain elongation pathway. Plant Physiol 127:1077–1088. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.010416
Li J, Hansen BG, Ober JA, Kliebenstein DJ, Halkier BA (2008) Subclade of flavin-monooxygenases involved in aliphatic glucosinolate biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 148:1721–1733. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.125757
Liu Z, Hammerlindl J, Keller W, McVetty PBE, Daayf F, Quiros CF, Li G (2011) MAM gene silencing leads to the induction of C3 and reduction of C4 and C5 side-chain aliphatic glucosinolates in Brassica napus. Mol Breed 27:467–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9444-y
Mikkelsen MD, Olsen CE, Halkier BA (2010) Production of the cancer-preventive glucoraphanin in tobacco. Mol Plant 3:751–759. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssq020
Shen J, **ng T, Yuan H, Liu Z, ** Z, Zhang L, Pei Y (2013) Hydrogen sulfide improves drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana by microRNA expressions. PLoS ONE 8:e77047. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077047
Sønderby IE, Hansen BG, Bjarnholt N, Ticconi C, Halkier BA, Kliebenstein DJ (2007) A systems biology approach identifies a R2R3 MYB gene subfamily with distinct and overlap** functions in regulation of aliphatic glucosinolates. PLoS ONE 2:e1322. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001322
Sonderby IE, Geu-Flores F, Halkier BA (2010) Biosynthesis of glucosinolates–gene discovery and beyond. Trends Plant Sci 15:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2010.02.005
Wood EJ (1983) Molecular cloning A. Laboratory manual. In: Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (eds) Biochemical education, vol 11. Wiley, New York, pp 182–183
Wu L, Nandi S, Chen L, Rodriguez RL, Huang N (2002) Expression and inheritance of nine transgenes in rice. Transgenic Res 11:533–541. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020331608590
Wu Q, Lin J, Huang K, Liu M (2013) Characterization and expression analysis of myrosinase for sulforaphane synthesis in broccoli. Int J Agric Biol 15:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1684/agr.2012.0578
**e LX, Huang K, Li B, Huang ZW, Zheng JG (2008) Cloning and prokaryotic expression of myrosinase gene from Chinese kale(Brassica oleracea L. var. alboglabra Bailey). J Fujian Agric For Univ 37:501–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-008-0073-x
Ye X (2000) Engineering the provitamin A (-carotene) biosynthetic pathway into (carotenoid-free) rice endosperm. Science 287:303–305. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5451.303
Zang YX, Kim JH, Park YD, Kim DH, Hong SB (2008) Metabolic engineering of aliphatic glucosinolates in Chinese cabbage plants expressing Arabidopsis MAM1, CYP79F1, and CYP83A1. BMB Rep 41:472–478. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2008.41.6.472
Zhang YY, Huai DX, Yang QY, Cheng Y, Ma M, Kliebenstein DJ, Zhou YM (2015) Overexpression of three glucosinolate biosynthesis genes in Brassica napus identifies enhanced resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLoS ONE 10:e0140491. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140491
Zhang JH, Guo N, Yang Y, Li QP, Guo Q, Duan YQ, Ha YM (2019) Studies on extraction, purification and identification of sulforaphane frombroccoli by-product. Food Sci 40:248–255. https://doi.org/10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180907-077(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu C, Naqvi S, Breitenbach J, Sandmann G, Christou P, Capell T (2008) Combinatorial genetic transformation generates a library of metabolic phenotypes for the carotenoid pathway in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:18232–18237. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0809737105
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Shanxi Province Excellent Talents Science and Technology Innovation Project (Grant No. 2018050211016), China Scholarship Council Foundation (2020-1417) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31972428).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HYC, YXP and ZPJ designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. HYC and RNL performed the experiments. HYC, ZQL and JHZ analyzed the data. SHF and GDY revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Sergio Rosales-Mendoza.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, H., Liu, R., Zhang, J. et al. Improving sulforaphane content in transgenic broccoli plants by overexpressing MAM1, FMOGS–OX2, and Myrosinase. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 146, 461–471 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02079-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02079-2