Abstract
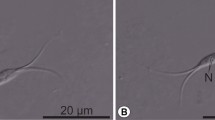
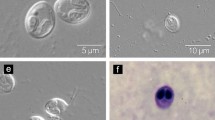
With growing scale of intensive fish cultivation, the risk of parasite infection in commercial fish is increased. Precisely identifying and characterizing the parasites that infect the farmed fish is critical to understanding the dynamics of their communities. Here, two species of Myxobolus were identified in farmed yellow catfish Tachysurus fulvidraco (Richardson) in China. Myxobolus distalisensis n. sp. developed plasmodia in the gill filaments, with oval to elliptical myxospores measuring 11.3 ± 0.6 (10.4-12.6) × 8.1 ± 0.3 (7.5-8.6) × 5.5 ± 0.2 (5.2-5.8) μm. Two pyriform polar capsules of equal size were measured 5.3 ± 0.4 (4.5-6.3) × 2.7 ± 0.1 (2.3-3) μm. Myxobolus voremkhai (Akhmerov, 1960) Landsberg and Lom, 1991 developed plasmodia in the gill arch and had a myxospore morphology similar to the conspecific isolates described in previous studies. The consensus sequences of M. distalisensis was remarkably distinct from those deposited in the GenBank, with exception of whereas M. voremkhai showing 99.84% identity. The genetic data on both isolates differed considerably from each other, revealing only 86.96% molecular identity. Histologically, M. distalisensis resided in the filament cartilage, and the aggressive proliferation of the sporogenic stages led to lytic cartilage corrosion. In contrast, plasmodia of M. voremkhai grossly observed at the base of the gill filament were embedded by the connective tissue in the gills arch. Phylogenetically, both isolates were separately placed in different subclades, indicating difference in their evolutionary history. Besides, the taxon under the family Myxobolidae was demonstrated non-monophyletic origins, and parasite radiation largely followed their host affinity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Two SSU rDNA sequences were obtained in the present study and submitted to the NCBI database under accession numbers OQ917121 (Myxobolus distalisensis), and OP458784 (M. voremkhai). Holotype specimens of M. distalisensis fixed by 10% formaldehyde solution and correlated digitized photomicrographs were deposited in the College of Fisheries, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China (accession no. MTR 20190702).
References
Adriano, E. A., Arana, S., Alves, A. L., Silva, M. R., Ceccarelli, P. S., Henrique-Silva, F., & Maia, A. A. (2009). Myxobolus cordeiroi n. sp., a parasite of Zungaro jahu (Siluriformes: Pimelodiade) from Brazilian Pantanal: morphology, phylogeny and histopathology. Veterinary Parasitology 162(3-4), 221-229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.03.030
Akhmerov, A. K. (1960). Myxosporidia of Amur River basin fish. Rybnoe Khozyaistvo Vnutrennikh Vodoemov Latviiskoi SSR 5, 239-308.
Banerjee, S., Dash, G., & Abraham, T. J. (2015). Histopathology of gill myxosporean infection in cultured Indian major and minor carps, West Bengal, India. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 31(6), 1137-1141. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/jai.12917
Borzák, R., Molnár, K., Cech, G., Papp, M., Deák-Paulus, P., & Székely, C. (2016). Description of two new species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1892, M. peleci n. sp. and M. cultrati n. sp., detected during an intensive mortality of the sichel, Pelecus cultratus (L.)(Cyprinidae), in Lake Balaton, Hungary. Systematic Parasitology 93(7), 667-677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-016-9651-y
Carriero, M. M., Adriano, E. A., Silva, M. R., Ceccarelli, P. S., & Maia, A. A. (2013). Molecular phylogeny of the Myxobolus and Henneguya genera with several new South American species. PLoS One 8(9), e73713. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073713
Chen, C. L., & Ma, C. L. (1998). Myxozoa: Myxosporea. Science Press.
Chu, X., Zheng, B., & Dai, D. (1999). Fauna Sinica. Science Press.
Darriba, D., Taboada, G. L., Doallo, R., & Posada, D. (2012). jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and high-performance computing. Nature Methods 9(8), 772. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
Duhamel, G. E., Kent, M. L., Dybdal, N. O., & Hedrick, R. P. (1986). Henneguya exilis Kudo associated with granulomatous branchitis of channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque). Veterinary Pathology 23(4), 354-361. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1177/030098588602300402
Eiras, J. C., Cruz, C. F., Saraiva, A., & Adriano, E. A. (2021). Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus (Cnidaria, Myxozoa, Myxosporea) described between 2014 and 2020. Folia Parasitologica 68(012). https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2021.012
Eiras, J. C., Molnár, K., & Lu, Y. S. (2005). Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae). Systematic Parasitology 61(1), 1-46. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-004-6343-9
Eiras, J. C., Zhang, J. Y., & Molnár, K. (2014). Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea, Myxobolidae) described between 2005 and 2013. Systematic Parasitology 88(1), 11-36. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-014-9484-5
Eszterbauer, E., & Székely, C. (2004). Molecular phylogeny of the kidney-parasitic Sphaerospora renicola from common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and Sphaerospora sp. from goldfish (Carassius auratus auratus). Acta Veterinaria Hungarica 52(4), 469-478. https://doi.org/10.1556/AVet.52.2004.4.9
Fariya, N., Kaur, H., Singh, M., Abidi, R., El-Matbouli, M., & Kumar, G. (2022). Morphological and molecular characterization of a new Myxozoan, Myxobolus grassi sp. nov. (Myxosporea), infecting the grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella in the Gomti River, India. Pathogens 11(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030303
Fiala, I. (2006). The phylogeny of Myxosporea (Myxozoa) based on small subunit ribosomal RNA gene analysis. International Journal for Parasitology 36(14), 1521-1534. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.06.016
Fiala, I., Bartošová-Sojková, P., & Whipps, C. M. (2015). Classification and phylogenetics of Myxozoa. In Okamura, B., Gruhl, A., & Bartholomew, J. L. (Eds.), Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development. Springer International Publishing.
Fujita, T. (1927). Studies on Myxosporidia of Japan. 16(5), 229-247.
Gao, L., Zhang, J., Yang, C., & Zhao, Y. (2020). Myxobolus jialingensis n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) infecting urinary bladder and hepatopancreas of yellowhead catfish Tachysurus fulvidraco from China. Zootaxa 4819(1), 179-186. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4819.1.10
Goswami, U., Molnár, K., Cech, G., Eiras, J. C., Bandyopadhyay, P. K., Ghosh, S., Czeglédi, I., & Székely, C. (2021). Evidence of the American Myxobolus dechtiari was introduced along with its host Lepomis gibbosus in Europe: molecular and histological data. International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife 15, 51-57. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijppaw.2021.04.005
Huang, L. F. (1983). Preliminary investigations on Myxosporea of freshwater fishes in Zhejiang province. Journal of Zhejiang College of Fisheries 2(2), 167-174.
Katoh, K., & Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30(4), 772-780. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
Kent, M. L., Andree, K. B., Bartholomew, J. L., El-Matbouli, M., Desser, S. S., Devlin, R. H., Feist, S. W., Hedrick, R. P., Hoffmann, R. W., Khattra, J., Hallett, S. L., Lester, R. J., Longshaw, M., Palenzeula, O., Siddall, M. E., & **ao, C. (2001). Recent advances in our knowledge of the Myxozoa. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 48(4), 395-413. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2001.tb00173.x
Landsberg, J. H., & Lom, J. (1991). Taxonomy of the genera of the Myxobolus-Myxosoma group (Myxobolidae, Myxosporea), current listing of species and revision of synonyms. Systematic Parasitology 18(3), 165-186. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/Bf00009358
Li, D. P., **e, C. X., He, X. G., Tang, R., Tian, X., Zhang, Z. M., & Gao, Y. (2018a). The success of yellow catfish aquaculture in China: from rare wild fish to popular farmed fish. In Gui, J., Tang, Q., Li, Z., Liu, J., & Silva, S. S. D. (Eds.), Aquaculture in China-Success Stories and Modern Trends Wiley.
Li, Z. F., & Wu, B. H. (1983). Parasitic fauna of Myxosporidia in freshwater fishes from the West Lake, Hangzhou. Journal of Hangzhou University 10(2), 207-220.
Li, Z. J., Liu, J. S., Wang, Q. D., & Silva, S. S. D. (2018b). Inland Aquaculture: Trends and Prospects. In Gui, J., Tang, Q., Li, Z., Liu, J., & Silva, S. S. D. (Eds.), Aquaculture in China-Success Stories and Modern Trends Wiley.
Liu, Y. (2014) Revision on genus Myxobolus (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) and taxonomy of some Myxobolus species in China. Huazhong Agricultural University
Liu, Y., Lövy, A., Gu, Z., & Fiala, I. (2019). Phylogeny of Myxobolidae (Myxozoa) and the evolution of myxospore appendages in the Myxobolus clade. International Journal for Parasitology 49(7), 523-530. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2019.02.009
Lom, J., & Arthur, J. R. (1989). A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in Myxosporea. Journal of Fish Diseases 12(2), 151-156. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1989.tb00287.x
Lom, J., & Dyková, I. (2006). Myxozoan genera: definition and notes on taxonomy, life-cycle terminology and pathogenic species. Folia Parasitologica 53(1), 1-36. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2006.001
Ma, C. L., Dong, X., & Wang, C. (1998). The Myxosporidia of freshwater fishes from Sichuan province III. Myxobolus Bütschli (Myxosporidia: Bivalvulidia). Journal of Chongqing Teachers College 15(4), 1-6.
Mathews, P. D., Maia, A. A. M., & Adriano, E. A. (2016). Morphological and ultrastructural aspects of Myxobolus niger n. sp. (Myxozoa) gill parasite of Corydoras melini (Siluriformes: Callichthyidae) from Brazilian Amazon. Acta Tropica 158, 214-219. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.03.016
Molnár, K. (1994). Comments on the host, organ and tissue specificity of fish myxosporeans and on the types of their intrapiscine development. Parasitologia hungarica 27, 5-20. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2014.08.036
Molnár, K. (2002). Site preference of fish myxosporeans in the gill. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 48(3), 197-207. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3354/dao048197
Molnár, K., & Eszterbauer, E. (2015). Specificity of infection sites in vertebrate hosts. In Okamura, B., Gruhl, A., & Bartholomew, J. L. (Eds.), Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development. Springer International Publishing.
Molnár, K., Marton, S., Székely, C., & Eszterbauer, E. (2010). Differentiation of Myxobolus spp. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) infecting roach (Rutilus rutilus) in Hungary. Parasitology Research 107(5), 1137-1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1982-z
Molnár, K., Varga, Á., & Székely, C. (2018). Cross section of gill filaments in histological preparations helps better identification of the location of myxosporean plasmodia in gill tissues. Acta Veterinaria Hungarica 66(2), 241-249. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1556/004.2018.022
Mumford, S., Heidel, J., Smith, C., Morrison, J., Macconnell, B., & Blazer, V. (2007). Fish histology and histopathology. Fish and Wildlife National Conservation Training Center.
Rocha, S., Rangel, L. F., Castro, R., Severino, R., Azevedo, C., Santos, M. J., & Casal, G. (2019). The potential role of the sphaeractinomyxon collective group (Cnidaria, Myxozoa) in the life cycle of mugiliform-infecting myxobolids, with the morphological and molecular description of three new types from the oligochaete Tubificoides insularis. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 160, 33-42. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2018.12.001
Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D. L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M. A., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2012). MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology 61(3), 539-542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Rosser, T. G., Khoo, L. H., Wise, D. J., Mischke, C. C., Greenway, T. E., Alberson, N. R., Reichley, S. R., Woodyard, E. T., Steadman, J., Ware, C., Pote, L. M., & Griffin, M. J. (2019). Arrested development of Henneguya ictaluri (Cnidaria: Myxobolidae) in female symbol channel catfish x male symbol blue catfish hybrids. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health 31(2), 201-213. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/aah.10070
Stamatakis, A. (2014). RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30(9), 1312-1313. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
Tahir, U. B., Guo, Q., & Gu, Z. (2021). Fins infestation induced by Myxobolus xiantaoensis in yellow catfish Tachysurus fulvidraco Richardson, 1846: some pathophysiological and molecular insights. Microbial Pathogenesis 153, 104772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104772
Tahir, U. B., Guo, Q., Zhao, D., Liu, Y., & Gu, Z. (2019). Description of Myxobolus xiantaoensis n. sp. from the fins of yellow catfish in China: a species previously attributed to Myxobolus physophilus Reuss, 1906 in Chinese records. Parasitology Research 118(4), 1137-1146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06244-7
Wang, Z., Zhou, T., Yang, H., & Gu, Z. (2019). First diagnosis of ectoparasitic ciliates (Trichodina and Chilodonella) on farmed juvenile yellow catfish, Tachysurus fulvidraco in China. Aquacult Res 50(11), 3275-3285. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14285
Whipps, C. M., Adlard, R. D., Bryant, M. S., Lester, R. J., Findlay, V., & Kent, M. L. (2003). First report of three Kudoa species from eastern Australia: Kudoa thyrsites from mahi mahi (Coryphaena hippurus), Kudoa amamiensis and Kudoa minithyrsites n. sp. from sweeper (Pempheris ypsilychnus). Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 50(3), 215-219. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2003.tb00120.x
Yang, H., Tu, X., **ao, J., Hu, J., & Gu, Z. (2023). Investigations on white spot disease reveal high genetic diversity of the fish parasite, Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Fouquet, 1876) in China. Aquaculture 562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738804
Zhang, B., Zhai, Y., Liu, Y., & Gu, Z. (2017). Myxobolus pseudowulii sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea), a new skin parasite of yellow catfish Tachysurus fulvidraco (Richardson) and redescription of Myxobolus voremkhai (Akhmerov, 1960). Folia Parasitologica 64. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2017.030
Acknowledgements
We thank Chenxin Zhang for her assistance in fieldwork. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070431); the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-46); and the Hubei Agricultural Sciences and Technology Innovation Center (2021-620-000-001-33).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070431); the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-46); and the Hubei Agricultural Sciences and Technology Innovation Center (2021-620-000-001-33).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bo Zhang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Investigation, Data Curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing. Qingxiang Guo: Conceptualization, Writing - Review & Editing. **ao Tu: Project administration, Writing - Review & Editing. Zemao Gu: Conceptualization, Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest or competing interests.
Ethical approval
All animal care protocols complied with the guidelines established by the National Institutes of Health and the International Society for Development Psychobiology (Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, P77, Aquatic Animals, National Research Council, 2010). The research protocol was approved by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of Huazhong Agricultural University.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Guo, Q., Tu, X. et al. Identification of Myxobolus distalisensis n. sp. (Cnidaria: Myxozoa) infecting yellow catfish Tachysurus fulvidraco (Richardson), with a supplement description of M. voremkhai (Akhmerov, 1960) Landsberg and Lom, 1991. Syst Parasitol 100, 473–485 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-023-10098-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-023-10098-0