Abstract
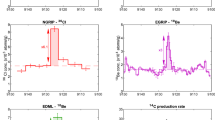
We revisited assessments of the occurrence probability distribution of large events in solar energetic particles (SEP), based on measurements of cosmogenic radionuclides in lunar rocks. We present a combined cumulative occurrence probability distribution of SEP events based on three timescales: directly measured SEP fluences for the past 60 years; estimates based on the terrestrial cosmogenic radionuclides 10Be and 14C for the multi-millennial (Holocene) timescale; and cosmogenic radionuclides measured in lunar rocks on a timescale of up to 1 Myr. These three timescales yield a consistent distribution. The data suggest a strong roll-over of the occurrence probability, so that SEP events with a proton fluence with energy > 30 MeV greater than 1011 (protons cm−2 yr−1) are not expected on a Myr timescale.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fink, D., Klein, J., Middleton, R., Vogt, S., Herzog, G.F., Reedy, R.C.: 1998, 41Ca, 26Al, and 10Be in lunar basalt 74275 and 10Be in the double drive tube 74002/74001. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 62, 2389 – 2402. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00134-3 .
Grismore, R., Llewellyn, R.A., Brown, M.D., Dowson, S.T., Cumblidge, K.: 2001, Measurements of the concentrations of 26Al in lunar rocks 15555 and 60025. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 187, 163 – 171. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00271-0 .
Hudson, H.S.: 2010, Solar flares add up. Nature Phys. 6, 637 – 638. doi: 10.1038/nphys1764 .
Jull, A.J.T., Cloudt, S., Donahue, D.J., Sisterson, J.M., Reedy, R.C., Masarik, J.: 1998, 14C depth profiles in Apollo 15 and 17 cores and lunar rock 68815. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 62, 3025 – 3036. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00193-8 .
Jun, I., Swimm, R.T., Ruzmaikin, A., Feynman, J., Tylka, A.J., Dietrich, W.F.: 2007, Statistics of solar energetic particle events: fluences, durations, and time intervals. Adv. Space Res. 40, 304 – 312. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2006.12.019 .
Kohl, C.P., Murrell, M.T., Russ III, G.P., Arnold, J.R.: 1978, Evidence for the constancy of the solar cosmic ray flux over the past ten million years: 53Mn and 26Al measurements. In: Proceeding of the Ninth Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta Suppl. 10, Pergamon, New York, 2299 – 2310.
McCracken, K.G., Dreschhoff, G.A.M., Zeller, E.J., Smart, D.F., Shea, M.A.: 2001, Solar cosmic ray events for the period 1561 – 1994: 1. Identification in polar ice, 1561 – 1950. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 21585 – 21598. doi: 10.1029/2000JA000237 .
Michel, R., Leya, I., Borges, L.: 1996, Production of cosmogenic nuclides in meteoroids: accelerator experiments and model calculations to decipher the cosmic ray record in extraterrestrial matter. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 113, 434 – 444. doi: 10.1016/0168-583X(95)01345-8 .
Miyake, F., Nagaya, K., Masuda, K., Nakamura, T.: 2012, A signature of cosmic-ray increase in AD 774 – 775 from tree rings in Japan. Nature 486, 240 – 242. doi: 10.1038/nature11123 .
Nishiizumi, K., Imamura, M., Kohl, C.P., Nagai, H., Kobayashi, K., Yoshida, K., Yamashita, H., Reedy, R.C., Honda, M., Arnold, J.R.: 1988, 10Be profiles in lunar surface rock 68815. In: Ryder, G. (ed.) Proceeding of the Eighteenth Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 79 – 85.
Nishiizumi, K., Arnold, J.R., Kohl, C.P., Caffee, M.W., Masarik, J., Reedy, R.C.: 2009, Solar cosmic ray records in lunar rock 64455. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 73, 2163 – 2176. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.12.021 .
Nymmik, R.: 1999, SEP event distribution function as inferred from spaceborne measurements and lunar rock isotopic data. In: Kieda, D., Salamon, M., Dingus, B. (eds.), Proc. 26th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 6, 268 – 271.
Reames, D.V.: 2004, Solar energetic particle variations. Adv. Space Res. 34, 381 – 390. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2003.02.046 .
Reedy, R.C.: 1999, Variations in solar-proton fluxes over the last million years. In: Lunar and Planetary Institute Science Conference Abstracts 30, 1643.
Reedy, R.C.: 1996, Constraints on solar particle events from comparisons of recent events and million-year averages. In: Balasubramaniam, K.S., Keil, S.L., Smartt, R.N. (eds.) Solar Drivers of the Interplanetary and Terrestrial Disturbances, ASP Conf. Ser. 95, 429 – 436.
Schrijver, C.J., Beer, J., Baltensperger, U., Cliver, E.W., Güdel, M., Hudson, H.S., McCracken, K.G., Osten, R.A., Peter, T., Soderblom, D.R., Usoskin, I.G., Wolff, E.W.: 2012, Estimating the frequency of extremely energetic solar events, based on solar, stellar, lunar, and terrestrial records. J. Geophys. Res. 117, A08103. doi: 10.1029/2012JA017706 .
Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F.: 2012, Space weather and the ground-level solar proton events of the 23rd solar cycle. Space Sci. Rev. 171, 161 – 188. doi: 10.1007/s11214-012-9923-z .
Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F.: 1990, A summary of major solar proton events. Solar Phys. 127, 297 – 320. doi: 10.1007/BF00152170 .
Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F., McCracken, K.G., Dreschhoff, G.A.M., Spence, H.E.: 2006, Solar proton events for 450 years: The Carrington event in perspective. Adv. Space Res. 38, 232 – 238. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2005.02.100 .
Smart, D.F., Shea, M.A., Spence, H.E., Kepko, L.: 2006, Two groups of extremely large > 30 MeV solar proton fluence events. Adv. Space Res. 37, 1734 – 1740. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2005.09.008 .
Thomas, B.C., Melott, A.L., Arkenberg, K.R., Snyder, B.R. II: 2013, Terrestrial effects of possible astrophysical sources of an AD 774 – 775 increase in 14C production. Geophys. Res. Lett. 40, 1237 – 1240. doi: 10.1002/grl.50222 .
Usoskin, I.G., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2012, Occurrence of extreme solar particle events: assessment from historical proxy data. Astrophys. J. 757, 92. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/757/1/92 .
Usoskin, I.G., Kromer, B., Ludlow, F., Beer, J., Friedrich, M., Kovaltsov, G.A., Solanki, S.K., Wacker, L.: 2013, The AD775 cosmic event revisited: the Sun is to blame. Astron. Astrophys. 552, L3. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201321080 .
Usoskin, I.G., Solanki, S.K., Kovaltsov, G.A., Beer, J., Kromer, B.: 2006, Solar proton events in cosmogenic isotope data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L08107. doi: 10.1029/2006GL026059 .
Vogt, S., Herzog, G.F., Reedy, R.C.: 1990, Cosmogenic nuclides in extraterrestrial materials. Rev. Geophys. 28, 253 – 275. doi: 10.1029/RG028i003p00253 .
Wolff, E.W., Bigler, M., Curran, M.A.J., Dibb, J.E., Frey, M.M., Legrand, M., McConnell, J.R.: 2012, The Carrington event not observed in most ice core nitrate records. Geophys. Res. Lett. 39, L08503. doi: 10.1029/2012GL051603 .
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Peggy Shea and Don Smart for data on SEP fluences. GA acknowledges partial support from Program No. 22 of the Presidium RAS and from the Academy of Finland. We thank the International Space Studies Institute in Bern, Switzerland, for support of the team “Extreme Solar Flares as Drivers of Space Weather”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovaltsov, G.A., Usoskin, I.G. Occurrence Probability of Large Solar Energetic Particle Events: Assessment from Data on Cosmogenic Radionuclides in Lunar Rocks. Sol Phys 289, 211–220 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0333-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0333-5