Abstract
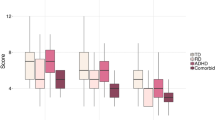
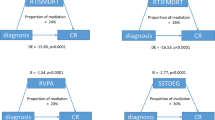
Reading comprehension skills, which involve numerous executive functions (EFs), are crucial for the academic success of school-aged children. Because children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) have difficulties with language comprehension and EFs, achieving reading comprehension may be challenging for them. This study evaluated the distinct contributions of language comprehension and EF components to reading comprehension in order to reveal the possible mechanisms underlying poor reading comprehension among children with ADHD. A total of 69 Chinese-speaking children aged 8–12 years who were typically develo** (TD, n = 36) or had ADHD (n = 33) participated in this study. All participants were assessed through intelligence, reading, and language comprehension tests. EF skills were measured using a verbal working memory (WM) test and four behavior tasks: the go/no-go task, a spatial WM (SWM) task, the Tower of London (ToL) task, and the Wisconsin Card Sorting Task (WCST). Results indicated that the ADHD group exhibited significantly lower language and reading comprehension scores than did the TD group. Moreover, the TD and ADHD groups had equivalent ToL scores but notably different go/no-go, WCST, SWM, and verbal WM test scores. After age, sex, and nonverbal intelligence quotient were controlled for, hierarchical regression models revealed the contributions of language skills to reading comprehension in both groups, but the contributions of EFs differed between the groups. Inhibition and verbal WM were significant predictors of reading comprehension in the ADHD group. In sum, the abilities to disregard irrelevant information and maintaining linguistic information of multiple episodes are important for Chinese-speaking children with ADHD to build a coherent mental representation of the text during reading comprehension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderson, R. M., Kasper, L. J., Hudec, K. L., & Patros, C. H. (2013). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and working memory in adults: a meta-analytic review. Neuropsychology, 27(3), 287–302. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0032371
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: Author
Baddeley, A. (2007). Working memory, thought, and action. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/978019852012.001.0001
Barth, A. E., Barnes, M., Francis, D., Vaughn, S., & York, M. (2015). Inferential processing among adequate and struggling adolescent comprehenders and relations to reading comprehension. Reading and Writing, 28, 587–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-014-9540-1
Bauermeister, J. J., Matos, M., Reina, G., Salas, C. C., Martínez, J. V., Cumba, E., & Barkley, R. A. (2005). Comparison of the DSM-IV combined and inattentive types of ADHD in a school-based sample of Latino/Hispanic children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 46(2), 166–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.00343.x
Biederman, J., Petty, C. R., Clarke, A., Lomedico, A., & Faraone, S. V. (2011). Predictors of persistent ADHD: an 11-year follow-up study. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 45(2), 150–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.06.009
Bignell, S., & Cain, K. (2007). Pragmatic aspects of communication and language comprehension in groups of children differentiated by teacher ratings of inattention and hyperactivity. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 25(4), 499–512. https://doi.org/10.1348/026151006X171343
Brock, S. E., & Knapp, P. K. (1996). Reading comprehension abilities of children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Journal of Attention Disorders, 1(3), 173–185. https://doi.org/10.1177/108705479600100305
Bussing, R., Mason, D. M., Bell, L., Porter, P., & Garvan, C. (2010). Adolescent outcomes of childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a diverse community sample. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 49(6), 595–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypsy.2010.09.006
Cain, K., & Bignell, S. (2013). Reading and listening comprehension and their relation to inattention and hyperactivity. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 84(1), 108–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12009
Cartwright, K. B. (2015). Executive skills and reading comprehension: A guide for educators. Guilford Publications
Cartwright, K. B., Marshall, T. R., & Hatfield, N. A. (2020). Concurrent and Longitudinal Contributions of a Brief Assessment of Reading-Specific Executive Function to Reading Comprehension in First and Second Grade Students. Mind Brain and Education, 14(2), 114–123. https://doi.org/10.1111/mbe.12236
Catts, H., Fey, M., Zhang, X., & Tomblin, J. (1999). Language Basis of Reading and Reading Disabilities: Evidence From a Longitudinal Investigation. Scientific Studies of Reading, 3, 331–361. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532799xssr0304_2
Catts, H. W., Adlof, S. M., Hogan, T. P., & Weismer, S. E. (2005). Are specific language impairment and dyslexia distinct disorders? Journal of Speech Language and Hearing Research, 48(6), 1378–1396. https://doi.org/10.1044/1092-4388(2005/096)
Chamberlain, S. R., Robbins, T. W., Winder-Rhodes, S., Müller, U., Sahakian, B. J., Blackwell, A. D., & Barnett, J. H. (2011). Translational approaches to frontostriatal dysfunction in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder using a computerized neuropsychological battery. Biological Psychiatry, 69(12), 1192–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.08.019
Chen, H. Y., Hua, M. S., Chang, B. S., & Chen, Y. H. (2011). Development of Factor-Based WISC-IV Tetrads: A Guild to Clinical Practice. Psychological Testing, 58, 585–611. https://doi.org/10.7108/PT.201112.0028
Chen, M. F., & Wu, I. C. (2007). Listening Comprehension Test. Taipei, Taiwan: Ministry of Education
Chung, K. K. H., & McBride-Chang, C. (2011). Executive functioning skills uniquely predict Chinese word reading. Journal of Educational Psychology, 103(4), 909–921. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0024744
Colé, P., Duncan, L. G., & Blaye, A. (2014). Cognitive flexibility predicts early reading skills. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 565. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00565
Cragg, L., & Gilmore, C. (2014). Skills underlying mathematics: The role of executive function in the development of mathematics proficiency. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 3(2), 63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tine.2013.12.001
Culbertson, W. C., & Zillmer, E. A. (1998). The Tower of London (DX): a standardized approach to assessing executive functioning in children. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology: The Official Journal of the National Academy of Neuropsychologists, 13 3, 285–301
Cutting, L. E., Materek, A., Cole, C. A., Levine, T. M., & Mahone, E. M. (2009). Effects of fluency, oral language, and executive function on reading comprehension performance. Annals of Dyslexia, 59(1), 34–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-009-0022-0
Dally, K. (2006). The influence of phonological processing and inattentive behavior on reading acquisition. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98(2), 420–437. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.98.2.420
Danckaerts, M., Sonuga-Barke, E. J., Banaschewski, T., Buitelaar, J., Döpfner, M., Hollis, C. … Coghill, D. (2010). The quality of life of children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 19(2), 83–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-009-0046-3
Diakidoy, I. A. N., Stylianou, P., Karefillidou, C., & Papageorgiou, P. (2005). The Relationship Between Listening and Reading Comprehension of Different Types of Text at Increasing Grade Levels. Reading Psychology, 26(1), 55–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/02702710590910584
Diamond, A. (2013). Executive functions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64, 135–168. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750
Daucourt, M. C., Erbeli, F., Little, C. W., Haughbrook, R., & Hart, S. A. (2020). A meta-analytical review of the genetic and environmental correlations between reading and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms and reading and math. Scientific Studies of Reading, 24(1), 23–56. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2019.1631827
Follmer, D. J. (2018). Executive function and reading comprehension: A meta-analytic review. Educational Psychologist, 53(1), 42–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2017.1309295
Frazier, T. W., Youngstrom, E. A., Glutting, J. J., & Watkins, M. W. (2007). ADHD and achievement: Meta-analysis of the child, adolescent, and adult literatures and a concomitant study with college students. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 40(1), 49–65. https://doi.org/10.1177/00222194070400010401
Friedman, N. P., & Miyake, A. (2004). The relations among inhibition and interference control functions: a latent-variable analysis. Journal of experimental psychology : General, 133, 101–135. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.133.1.101
García, J. R., & Cain, K. (2014). Decoding and reading comprehension: A meta-analysis to identify which reader and assessment characteristics influence the strength of the relationship in English. Review of Educational Research, 84(1), 74–111. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654313499616
Gau, S. S., Shang, C. Y., Liu, S. K., Lin, C. H., Swanson, J. M., Liu, Y. C., et al. (2008). Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham, version IV scale— parent form. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research, 17, 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsn133
Gau, S. S. F., Ni, H. C., Shang, C. Y., Soong, W. T., Wu, Y. Y., Lin, L. Y., & Chiu, Y. N. (2010). Psychiatric comorbidity among children and adolescents with and without persistent attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 44(2), 135–143. https://doi.org/10.3109/00048670903282733
Gau, S. S. F., & Shang, C. Y. (2010). Executive functions as endophenotypes in ADHD: evidence from the Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Battery (CANTAB). Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry,51, 838–849.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02215.x
Georgiou, G. K., Wei, W., Inoue, T., Das, J. P., & Deng, C. (2020). Cultural influences on the relation between executive functions and academic achievement. Reading and Writing, 33(4), 991–1013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-019-09961-8
Ghelani, K., Sidhu, R., Jain, U., & Tannock, R. (2004). Reading comprehension and reading related abilities in adolescents with reading disabilities and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Dyslexia, 10(4), 364–384. https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.285
Gottardo, A., Mirza, A., Koh, P. W., Ferreira, A., & Javier, C. (2018). Unpacking listening comprehension: the role of vocabulary, morphological awareness, and syntactic knowledge in reading comprehension. Reading and Writing, 31(8), 1741–1764. https://doi.org/10/1007/s11145-017-9736-2
Gough, P. B., & Tunmer, W. E. (1986). Decoding, Reading, and Reading Disability. Remedial and Special Education, 7(1), 6–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/074193258600700104
Graesser, A. C. (2015). Deeper learning with advances in discourse science and technology. Policy Insights from the Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 2, 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1177/2372732215600888
Greven, C. U., Rijsdijk, F. V., Asherson, P., & Plomin, R. (2012). A longitudinal twin study on the association between ADHD symptoms and reading. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53(3), 234–242. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02445.x
Harpin, V., Mazzone, L., Raynaud, J. P., Kahle, J., & Hodgkins, P. (2016). Long-Term Outcomes of ADHD: A Systematic Review of Self-Esteem and Social Function. Journal of Attention Disorders, 20(4), 295–305. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054713486516
Kendeou, P., van den Broek, P., Helder, A., & Karlsson, J. (2014). A cognitive view of reading comprehension: Implications for reading difficulties. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 29(1), 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/ldrp.12025
Kent, K. M., Pelham, W. E. Jr., Molina, B. S. G., Sibley, M. H., Waschbusch, D. A., Yu, J. … Karch, K. M. (2011). The academic experience of male high school students with ADHD. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 39, 451–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-010-9472-4
Kieffer, M. J., Vukovic, R. K., & Berry, D. (2013). Roles of attention shifting and inhibitory control in fourth-grade reading comprehension. Reading Research Quarterly, 48(4), 333–348. https://doi.org/10.1002/rrq.54
Kieffer, M. J., Petscher, Y., Proctor, C. P., & Silverman, R. D. (2016). Is the whole greater than the sum of its parts? Modeling the contributions of language comprehension skills to reading comprehension in the upper elementary grades. Scientific Studies of Reading, 20(6), 436–454. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2016.1214591
Kim, Y., Koh, M. K., Park, K. J., Lee, H. J., Yu, G. E., & Kim, H. W. (2020). WISC-IV intellectual profiles in Korean children and adolescents with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatry investigation, 17(5), 444. https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2019.0312
Ko, H. W., & Chan, Y. L. (2007). Reading Comprehension Screening Test. Taipei, Taiwan: Ministry of Education
Kofler, M. J., Spiegel, J. A., Soto, E. F., Irwin, L. N., Wells, E. L., & Austin, K. E. (2019). Do working memory deficits underlie reading problems in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)? Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 47(3), 433–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-018-0447-1
Korrel, H., Mueller, K. L., Silk, T., Anderson, V., & Sciberras, E. (2017). Research Review: Language problems in children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder–a systematic meta‐analytic review. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 58(6), 640–654. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12688
Lan, X., Legare, C. H., Ponitz, C. C., Li, S., & Morrison, F. J. (2011). Investigating the links between the subcomponents of executive function and academic achievement: A cross-cultural analysis of Chinese and American preschoolers. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 108, 677–692. https://doi.org/10/1016/j.jecp/2010.11.001
Language and Reading Research Consortium (LARRC). (2015). Learning to read: Should we keep things simple? Reading Research Quarterly, 50, 151–169. https://doi.org/10.1002/rrq.99
Language and Reading Research Consortium (LARRC). (2017). Oral language and listening comprehension: Same or different constructs? Journal of Speech Language and Hearing Research, 60(5), 1273–1284. https://doi.org/10.1044/2017_JSLHR-L-16-0039
Lamminmäki, T., Ahonen, T., Närhi, V., Lyytinen, H., & de Barra, H. T. (1995). Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder subtypes: Are there differences in academic problems? Developmental Neuropsychology, 11(3), 297–310. https://doi.org/10.1080/87565649509540621
Lervåg, A., Hulme, C., & Melby-Lervåg, M. (2017). Unpicking the Developmental Relationship Between Oral Language Skills and Reading Comprehension: It’s Simple, But Complex. Child Development, 89(5), 1821–1838. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12861
Liu, Y., Sun, H., Lin, D., Li, H., Yeung, S. S. S., & Wong, T. T. Y. (2018). The unique role of executive function skills in predicting Hong Kong kindergarteners’ reading comprehension. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 88, 628–644. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12207
Loe, I. M., & Feldman, H. M. (2007). Academic and educational outcomes of children with ADHD. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 32(6), 643–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ambp.2006.05.005
Lorch, E. P., Milich, R., Sanchez, R. P., van den Broek, P., Baer, S., Hooks, K. … Welsh, R. (2000). Comprehension of televised stories in boys with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and nonreferred boys. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 109(2), 321–330. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.109.2.321
Lorch, E. P., O’Neil, K., Berthiaume, K. S., Milich, R., Eastham, D., & Brooks, T. (2004). Story comprehension and the impact of studying on recall in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 33(3), 506–515. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15374424jccp3303_8
Martinussen, R., Grimbos, T., & Ferrari, J. L. (2014). Word-level reading achievement and behavioral inattention: exploring their overlap and relations with naming speed and phonemic awareness in a community sample of children. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 29(7), 680–690. https://doi.org/10.1093/arclin/acu040
Martinussen, R., Hayden, J., Hogg-Johnson, S., & Tannock, R. (2005). A meta-analysis of working memory impairments in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 44(4), 377–384. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.chi.0000153228.72591.73
Martinussen, R., & Mackenzie, G. (2015). Reading comprehension in adolescents with ADHD: Exploring the poor comprehender profile and individual differences in vocabulary and executive functions. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 38, 329–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.12.007
Mayes, S. D., & Calhoun, S. L. (2006). WISC-IV and WISC-III profiles in children with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 9, 486–493. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054705283616
McInnes, A., Humphries, T., Hogg-Johnson, S., & Tannock, R. (2003). Listening comprehension and working memory are impaired in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder irrespective of language impairment. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 31(4), 427–443. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023895602957
Miller, A. C., Keenan, J. M., Betjemann, R. S., Willcutt, E. G., Pennington, B. F., & Olson, R. K. (2013). Reading comprehension in children with ADHD: Cognitive underpinnings of the centrality deficit. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 41(3), 473–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-012-9686-8
Miyake, A., Friedman, N. P., Emerson, M. J., Witzki, A. H., Howerter, A., & Wager, T. D. (2000). The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex “frontal lobe” tasks: A latent variable analysis. Cognitive psychology, 41(1), 49–100. https://doi.org/10.1006/cogp.1999.0734
Nouwens, S., Groen, M. A., Kleemans, T., & Verhoeven, L. (2021). How executive functions contribute to reading comprehension. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 91(1), 169–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2015.12.008
Pan, J., & Lin, D. (2020). Visuospatial memory uniquely predicts Chinese reading comprehension in Hong Kong typically develo** kindergarteners. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 33, 2205–2221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-020-10033-5
Papaeliou, C. F., Maniadaki, K., & Kakouros, E. (2015). Association between story recall and other language abilities in schoolchildren with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 19(1), 53–62. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054712446812
Peng, P., Sha, T., & Li, B. (2013). The deficit profile of working memory, inhibition, and updating in Chinese children with reading difficulties. Learning and Individual Differences, 25, 111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2013.01.012
Peng, P., Barnes, M., Wang, C., Wang, W., Li, S., Swanson, H. L. … Tao, S. (2018). A meta-analysis on the relation between reading and working memory. Psychological Bulletin, 144(1), 48–76. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000124
Peng, P., Lee, K., Luo, J., Li, S., Joshi, R. M., & Tao, S. (2020). Simple View of Reading in Chinese: A One-Stage Meta-Analytic Structural Equation Modeling. Review of Educational Research, 91, 3–33. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654320964198
Polanczyk, G., de Lima, M. S., Horta, B. L., Biederman, J., & Rohde, L. A. (2007). The Worldwide Prevalence of ADHD: A Systematic Review and Metaregression. Analysis American Journal of Psychiatry, 164(6), 942–948. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.164.6.942
Qian, Y., Shuai, L., Chan, R. C., Qian, Q. J., & Wang, Y. (2013). The developmental trajectories of executive function of children and adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34(5), 1434–1445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2013.01.033
Samuelsson, S., Lundberg, I., & Herkner, B. (2004). ADHD and reading disability in male adults: Is there a connection? Journal of Learning Disabilities, 37(2), 155–168. https://doi.org/10.1177/00222194040370020601
Sesma, H. W., Mahone, E. M., Levine, T., Eason, S. H., & Cutting, L. E. (2009). The contribution of executive skills to reading comprehension. Child Neuropsychology, 15(3), 232–246. https://doi.org/10.1080/09297040802220029
Shaywitz, B. A., Fletcher, J. M., & Shaywitz, S. E. (1995). Defining and classifying learning disabilities and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Child Neurology, 10(1_suppl), S50–S57. https://doi.org/10.1177/08830738950100S111
Steele, S. D., Minshew, N. J., Luna, B., & Sweeney, J. A. (2007). Spatial Working Memory Deficits in Autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37(4), 605–612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-006-0202-2
Thaler, N. S., Barchard, K. A., Parke, E., Jones, W. P., Etcoff, L. M., & Allen, D. N. (2015). Factor structure of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children: in children with ADHD. Journal of attention disorders, 19, 1013–1021. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054712459952
Tsuchiya, E., Oki, J., Yahara, N., & Fujieda, K. (2005). Computerized version of the Wisconsin card sorting test in children with high-functioning autistic disorder or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Brain and Development, 27(3), 233–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.braindev.2004.06.008
Van der Sluis, S., de Jong, P. F., & van der Leij, A. (2007). Executive functioning in children, and its relations with reasoning, reading, and arithmetic. Intelligence, 35(5), 427–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2006.09.001
Van Eylen, L., Boets, B., Steyaert, J., Wagemans, J., & Noens, I. (2015). Executive functioning in autism spectrum disorders: Influence of task and sample characteristics and relation to symptom severity. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 24(11), 1399–1417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-015-0689-1
Wang, L. J., Lee, S. Y., Yuan, S. S., Yang, C. J., Yang, K. C., Huang, T. S. … Shyu, Y. C. (2017). Prevalence rates of youths diagnosed with and medicated for ADHD in a nationwide survey in Taiwan from 2000 to 2011. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences, 26(6), 624–634. https://doi.org/10.1017/S2045796016000500
Willcutt, E. G., Doyle, A. E., Nigg, J. T., Faraone, S. V., & Pennington, B. F. (2005). Validity of the executive function theory of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analytic review. Biological Psychiatry, 57(11), 1336–1346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.02.006
Willcutt, E. G., & Pennington, B. F. (2000). Comorbidity of Reading Disability and Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder: Differences by Gender and Subtype. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 33(2), 179–191. https://doi.org/10.1177/002221940003300206
Yeniad, N., Malda, M., Mesman, J., Van IJzendoorn, M. H., & Pieper, S. (2013). Shifting ability predicts math and reading performance in children: A meta-analytical study. Learning and Individual Differences, 23, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2012.10.004
Yerys, B. E., Kenworthy, L., Jankowski, K. F., Strang, J., & Wallace, G. L. (2013). Separate components of emotional go/no-go performance relate to autism versus attention symptoms in children with autism. Neuropsychology, 27(5), 537. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0033615
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the “Institute for Research Excellence in Learning Sciences” of National Taiwan Normal University (NTNU) from The Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan, and Ministry of Science and Technology grant to Yuchun Chen (MOST109-2410-1-1-030-051-MY2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Tsao, FM., Liu, HM. et al. Distinctive patterns of language and executive functions contributing to reading development in chinese-speaking children with ADHD. Read Writ 37, 1011–1034 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-022-10323-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-022-10323-0