Abstract
Aims
Shrub encroachment has profound influences on regional carbon cycling. However, few studies have examined the changes in soil organic carbon (SOC) components at the molecular level along a climate gradient. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effects of biotic and abiotic factors on the patterns of SOC components in the shrub patches and the grassy matrix.
Methods
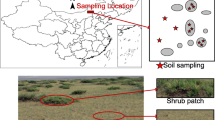
We analyzed the distribution and controlling factors of SOC components (including free lipids, bound lipids, and lignin-derived phenols) in the topsoil of shrub-encroached grasslands along natural climate gradients in Inner Mongolia, China.
Results
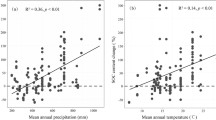
We found that the concentrations of bound lipids and lignin-derived phenols were significantly higher and the vanillic acid to vanillin ratio ((Ad/Al)v) was significantly lower in the shrub patches than in the grassy matrix (p < 0.05). After excluding variables exhibiting collinearity, redundancy analysis showed that shrub patch cover and soil pH were the most important variables that influenced SOC composition in the shrub patches, while herb characteristics and shrub density were the most important in the grassy matrix. Structural equation modeling showed that shrub characteristics at the plot scale greatly contributed to the variance in all components in the grassy matrix, whereas soil properties were more important in the shrub patches.
Conclusions
Our results highlight that although the topsoil carbon content did not change, shrub encroachment altered the SOC components and their drivers in the Inner Mongolian grasslands.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amelung W, Flach KW, Zech W (1999) Lignin in particle-size fractions of native grassland soils as influenced by climate. Soil Sci Soc Am J 63:1222–1228. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1999.6351222x
Angst G, John S, Mueller CW, Kögel-Knabner I, Rethemeyer J (2016) Tracing the sources and spatial distribution of organic carbon in subsoils. Sci Rep 6:29478. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29478
Angst G, Nierop KGJ, Angst Š, Frouz J (2018) Abundance of lipids in differently sized aggregates depends on their chemical composition. Biogeochemistry 140:111–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-018-0481-7
Armas-Herrera CM, Dignac MF, Rumpel C, Arbelo CD, Chabbi A (2016) Management effects on composition and dynamics of cutin and suberin in topsoil under agricultural use. Eur J Soil Sci 67:360–373. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12328
Bai Y, Wu J, Pan Q et al (2007) Positive linear relationship between productivity and diversity: evidence from the Eurasian steppe. J Appl Ecol 44:1023–1034. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01351.x
Bull ID, van Bergen PF NCJ, Poulton PR, Evershed RP (2000) Organic geochemical studies of soils from the Rothamsted classical experiments-VI. The occurrence of organic acids in an experimental grassland soil. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1367–1376. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00054-7
Cai Y, Tang Z, **ong G, **e Z, Liu Z, Feng X (2017) Different composition and distribution patterns of mineral-protected versus hydrolyzable lipids in shrubland soils. J Geophys Res-Biogeo 122:2206–2218. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JG003759
Chen L, Li H, Zhang P, Zhao X, Zhou L, Liu T, Hu H, Bai Y, Shen H, Fang J (2015) Climate and native grassland vegetation as drivers of the community structures of shrub-encroached grasslands in Inner Mongolia, China. Landsc Ecol 30:1627–1641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-014-0044-9
Chen S, Wang W, Xu W, Wang Y, Wan H, Chen D, Tang Z, Tang X, Zhou G, **e Z, Zhou D, Shangguan Z, Huang J, He JS, Wang Y, Sheng J, Tang L, Li X, Dong M, Wu Y, Wang Q, Wang Z, Wu J, Chapin FS III, Bai Y (2018) Plant diversity enhances productivity and soil carbon storage. P Natl Acad Sci USA 115:4027–4032. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700298114
Dai G, Ma T, Zhu S, Liu Z, Chen D, Bai Y, Chen L, He JS, Zhu J, Zhang Y, Lü X, Wang X, Han X, Feng X (2018) Large-scale distribution of molecular components in Chinese grassland soils: the influence of input and decomposition processes. J Geophys Res-Biogeo 123:239–255. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017jg004233
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Eldridge DJ, Ochoa V, Gozalo B, Singh BK, Maestre FT (2017) Soil microbial communities drive the resistance of ecosystem multifunctionality to global change in drylands across the globe. Ecol Lett 20:1295–1305. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12826
Eldridge DJ, Bowker MA, Maestre FT, Roger E, Reynolds JF, Whitford WG (2011) Impacts of shrub encroachment on ecosystem structure and functioning: towards a global synthesis. Ecol Lett 14:709–722. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01630.x
Fang J, Bai Y, Wu J (2015) Towards a better understanding of landscape patterns and ecosystem processes of the Mongolian plateau. Landsc Ecol 30:1573–1578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0277-2
Feng X, Simpson MJ (2008) Temperature responses of individual soil organic matter components. J Geophys Res 113:G03036. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008jg000743
Feng X, Simpson AJ, Simpson MJ (2005) Chemical and mineralogical controls on humic acid sorption to clay mineral surfaces. Org Geochem 36:1553–1566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2005.06.008
Feng X, Simpson AJ, Schlesinger WH, Simpson MJ (2010) Altered microbial community structure and organic matter composition under elevated CO2 and N fertilization in the duke forest. Glob Chang Biol 16:2104–2116. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02080.x
Filley TR, Boutton TW, Liao JD, Jastrow JD, Gamblin DE (2008) Chemical changes to nonaggregated particulate soil organic matter following grassland-to-woodland transition in a subtropical savanna. J Geophys Res 113. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007jg000564
Grace JB (2006) Structural equation modeling and natural systems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Huang Z, Davis MR, Condron LM, Clinton PW (2011) Soil carbon pools, plant biomarkers and mean carbon residence time after afforestation of grassland with three tree species. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1341–1349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.03.008
Jackson RB, Banner JL, Jobbágy EG, Pockman WT, Wall DH (2002) Ecosystem carbon loss with woody plant invasion of grasslands. Nature 418:623–626. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00910
Knapp AK, Briggs JM, Collins SL et al (2008) Shrub encroachment in north American grasslands: shifts in growth form dominance rapidly alters control of ecosystem carbon inputs. Glob Chang Biol 14:615–623. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01512.x
Kögel-Knabner I (2002) The macromolecular organic composition of plant and microbial residues as inputs to soil organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 34:139–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00158-4
Kögel-Knabner I, Rumpel C (2018) Advances in molecular approaches for understanding soil organic matter composition, origin, and turnover: a historical overview. Advances Agron 149:1–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2018.01.003
Kohl L, Philben M, Edwards KA, Podrebarac FA, Warren J, Ziegler SE (2017) The origin of soil organic matter controls its composition and bioreactivity across a Mesic boreal forest latitudinal gradient. Glob Chang Biol 242:458–473. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13887
Li H, Zhang J, Hu H, Chen L, Zhu Y, Shen H, Fang J (2017) Shift in soil microbial communities with shrub encroachment in Inner Mongolia grasslands, China. Eur J Soil Sci 79:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2017.02.004
Li H, Shen H, Zhou L, Zhu Y, Chen L, Hu H, Zhang P, Fang J (2019) Shrub encroachment increases soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in temperate grasslands in China. Land Degrad Dev 30:756–767. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3259
Lin LH, Simpson MJ (2016) Enhanced extractability of cutin- and suberin-derived organic matter with demineralization implies physical protection over chemical recalcitrance in soil. Org Geochem 97:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2016.04.012
Ma T, Zhu S, Wang Z, Chen D, Dai G, Feng B, Su X, Hu H, Li K, Han W, Liang C, Bai Y, Feng X (2018) Divergent accumulation of microbial necromass and plant lignin components in grassland soils. Nat Commun 9:3480. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05891-1
Maestre FT, Bowker MA, Puche MD, Belén Hinojosa M, Martínez I, García-Palacios P, Castillo AP, Soliveres S, Luzuriaga AL, Sánchez AM, Carreira JA, Gallardo A, Escudero A (2009) Shrub encroachment can reverse desertification in semi-arid Mediterranean grasslands. Ecol Lett 12:930–941. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01352.x
Nierop KGJ, Naafs DFW, Verstraten JM (2003) Occurrence and distribution of ester-bound lipids in Dutch coastal dune soils along a pH gradient. Org Geochem 34:719–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0146-6380(03)00042-1
Otto A, Simpson MJ (2006) Evaluation of CuO oxidation parameters for determining the source and stage of lignin degradation in soil. Biogeochemistry 80:121–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-006-9014-x
Peng H, Li X, Jiang Z et al (2013) Shrub encroachment with increasing anthropogenic disturbance in the semiarid inner Mongolian grasslands of China. Catena 109:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.05.008
Pisani O, Haddix ML, Conant RT, Paul EA, Simpson MJ (2016) Molecular composition of soil organic matter with land-use change along a bi-continental mean annual temperature gradient. Sci Total Environ 573:470–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.154
Rascher KG, Hellmann C, Maguas C, Werner C (2012) Community scale 15N isoscapes: tracing the spatial impact of an exotic N2 -fixing invader. Ecol Lett 15:484–491. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2012.01761.x
Rasmussen J, Gylfadóttir T, Loges R, Eriksen J, Helgadóttir Á (2013) Spatial and temporal variation in N transfer in grass–white clover mixtures at three northern European field sites. Soil Biol Biochem 57:654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.07.004
Reynolds JF, Smith MS, Lambin EF et al (2007) Global desertification: building a science for dryland development. Science 316:847–851. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1131634
Six J, Bossuyt H, Degryze S, Denef K (2004) A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Till Res 79:7–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2004.03.008
Soliveres S, Eldridge DJ (2014) Do changes in grazing pressure and the degree of shrub encroachment alter the effects of individual shrubs on understorey plant communities and soil function? Funct Ecol 28:530–537. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12196
Tamura M, Tharayil N (2014) Plant litter chemistry and microbial priming regulate the accrual, composition and stability of soil carbon in invaded ecosystems. New Phytol 203:110–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12795
Temperton VM, Mwangi PN, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Schmid B, Buchmann N (2007) Positive interactions between nitrogen-fixing legumes and four different neighbouring species in a biodiversity experiment. Oecologia 151:190–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-006-0576-z
Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Klironomos JN, Setälä H, van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science 304:1629–1633. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094875
Wilkinson MT, Richards PJ, Humphreys GS (2009) Breaking ground: pedological, geological, and ecological implications of soil bioturbation. Earth-Sci Rev 97:257–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2009.09.005
Wu XB, Archer SR (2005) Scale-dependent influence of topography-based hydrologic features on patterns of woody plant encroachment in savanna landscapes. Landsc Ecol 20:733–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-005-0996-x
Zhang H, Yu Q, Lu X, Trumbore SE, Yang JJ, Han XG (2016) Impacts of leguminous shrub encroachment on neighboring grasses include transfer of fixed nitrogen. Oecologia 180:1213–1222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-015-3538-5
Zhang H, Lü X, Knapp AK et al (2018) Facilitation by leguminous shrubs increases along a precipitation gradient. Funct Ecol 32:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12941
Zhao L, Wu W, Xu X, Xu Y (2014) Soil organic matter dynamics under different land use in grasslands in Inner Mongolia (northern China). Biogeosciences 11:5103–5113. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-5103-2014
Zhou L, Li H, Shen H, Xu Y, Wang Y, **ng A, Fang J (2017) Shrub-encroachment induced alterations in input chemistry and soil microbial community affect topsoil organic carbon in an Inner Mongolian grassland. Biogeochemistry 136:311–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-017-0396-8
Zhou L, Li H, Shen H, Xu Y, Wang Y, **ng A, Zhu Y, Zhou S, Fang J (2018) Effects of shrub encroachment on vertical changes in soil organic carbon in Mongolian grasslands: using a multi-biomarker approach. Plant Soil 431:217–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3761-z
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31330012, 31470525), the National Basic Research Program of China on Global Change (2014CB954001), the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, CAS, (QYZDY-SSW-SMC011), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M641074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ingrid Koegel-Knabner.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 997 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Shen, H., Xu, Y. et al. Soil organic carbon components in inner Mongolian shrub-encroached grasslands. Plant Soil 442, 199–213 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04166-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04166-y