ABSTRACT
Purpose
In order to improve siRNA delivery for possible clinical applications, we developed biodegradable chitosan-modified poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) (CHT-PLGA) nanoparticles with positive surface charge, high siRNA loading, high transfection efficiency and low toxicity.
Methods
CHT-PLGA nanoparticles were prepared, and siRNA was loaded by emulsion evaporation method with poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) as emulsifier. siRNA loading efficiency, particle size, and Zeta potential of nanoparticles were measured. Gel retardation and protection assays were conducted to determine the loading and binding of siRNA in the formulation. Cell transfection was performed to study in vitro siRNA silencing efficiency. XTT assay was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity.
Results
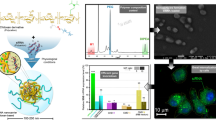
It was found that the nanoparticle diameter and positive Zeta potential increase as the chitosan coating concentration increases. CHT-PLGA nanoparticles showed excellent siRNA binding ability and effective protection of oligos from RNase degradation. siRNA-loaded nanoparticles were successfully delivered into the HEK 293 T cell line, and the silencing of green fluorescence protein (GFP) expression was observed using fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry. In addition, the cytotoxicity assay revealed that CHT-PLGA nanoparticles had relatively low cytotoxicity.
Conclusion
This study suggests that biodegradable cationic CHT-PLGA nanoparticles possess great potential for efficient and safer siRNA delivery in future clinical applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Jiang HL, Kim YK, Arote R, Nah JW, Cho MH, Choi YJ et al. Chitosan-graft-polyethylenimine as a gene carrier. J Control Release. 2007;117:273–80.
Relano-Gines A, Gabelle A, Lehmann S, Milhavet O, Crozet C. Gene and cell therapy for prion diseases. Infectious disorders drug targets. 2009;9:58–68.
Kima T-H, Jianga H-L, Jerea D, Parka I-K, Chob M-H, Nahc J-W et al. Chemical modification of chitosan as a gene carrier in vitro and in vivo. Prog Polym Sci. 2007;32:726–53.
Katas H, Alpar HO. Development and characterisation of chitosan nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. J Control Release. 2006;115:216–25.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–8.
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–11.
Jones SW, Souza PM, Lindsay MA. siRNA for gene silencing: a route to drug target discovery. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004;4:522–7.
McManusand MT, Sharp PA. Gene silencing in mammals by small interfering RNAs. Nat Rev. 2002;3:737–47.
Lima RT, Martins LM, Guimaraes JE, Sambade C, Vasconcelos MH. Specific downregulation of bcl-2 and xIAP by RNAi enhances the effects of chemotherapeutic agents in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2004;11:309–16.
Fraser AG, Kamath RS, Zipperlen P, Martinez-Campos M, Sohrmann M, Ahringer J. Functional genomic analysis of C. elegans chromosome I by systematic RNA interference. Nature. 2000;408:325–30.
Gonczy P, Echeverri C, Oegema K, Coulson A, Jones SJ, Copley RR et al. Functional genomic analysis of cell division in C. elegans using RNAi of genes on chromosome III. Nature. 2000;408:331–6.
Nabatiyan A, Krude T. Silencing of chromatin assembly factor 1 in human cells leads to cell death and loss of chromatin assembly during DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:2853–62.
Suri SS, Fenniri H, Singh B. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems. J Occup Med Toxicol. 2007;2:16.
Quong D, Neufeld RJ. DNA protection from extracapsular nucleases, within chitosan- or poly-L-lysine-coated alginate beads. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1998;60:124–34.
Smith AE. Viral vectors in gene therapy. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995;49:807–38.
Pinnaduwage P, Schmitt L, Huang L. Use of a quaternary ammonium detergent in liposome mediated DNA transfection of mouse L-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989;985:33–7.
Legendre JY, Szoka Jr FC. Cyclic amphipathic peptide-DNA complexes mediate high-efficiency transfection of adherent mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:893–7.
Gao X, Huang L. Potentiation of cationic liposome-mediated gene delivery by polycations. Biochemistry. 1996;35:1027–36.
Yuan X, Li L, Rathinavelu A, Hao J, Narasimhan M, He M et al. SiRNA drug delivery by biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. 2006;6:2821–8.
Boussif O, Lezoualc’h F, Zanta MA, Mergny MD, Scherman D, Demeneix B et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:7297–301.
Haensler J, Szoka Jr FC. Polyamidoamine cascade polymers mediate efficient transfection of cells in culture. Bioconjug Chem. 1993;4:372–9.
Ihm JE, Han KO, Han IK, Ahn KD, Han DK, Cho CS. High transfection efficiency of poly(4-vinylimidazole) as a new gene carrier. Bioconjug Chem. 2003;14:707–8.
Rolland AP. From genes to gene medicines: recent advances in nonviral gene delivery. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1998;15:143–98.
Montag ME, Morales Jr L, Daane S. Bioabsorbables: their use in pediatric craniofacial surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 1997;8:100–2.
Eppley BL, Reilly M. Degradation characteristics of PLLA-PGA bone fixation devices. J Craniofac Surg. 1997;8:116–20.
Panyam J, Labhasetwar V. Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55:329–47.
Miyamoto S, Takaoka K. Bone induction and bone repair by composites of bone morphogenetic protein and biodegradable synthetic polymers. Ann Chir Gynaecol. 1993;207:69–75.
Aiba S. Studies on chitosan: 2. Solution stability and reactivity of partially N-acetylated chitosan derivatives in aqueous media. Int J Biol Macromol. 1989;11:249–52.
Tomihata K, Ikada Y. In vitro and in vivo degradation of films of chitin and its deacetylated derivatives. Biomaterials. 1997;18:567–75.
Chandy T, Sharma CP. Chitosan-as a biomaterial. Biomater Artif Cells Artif Organs. 1990;18:1–24.
Mao HQ, Roy K, Troung-Le VL, Janes KA, Lin KY, Wang Y et al. Chitosan-DNA nanoparticles as gene carriers: synthesis, characterization and transfection efficiency. J Control Release. 2001;70:399–421.
Erbacher P, Zou S, Bettinger T, Steffan AM, Remy JS. Chitosan-based vector/DNA complexes for gene delivery: biophysical characteristics and transfection ability. Pharm Res. 1998;15:1332–9.
Yang R, Yang SG, Shim WS, Cui F, Cheng G, Kim IW et al. Lung-specific delivery of paclitaxel by chitosan-modified PLGA nanoparticles via transient formation of microaggregates. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98:970–84.
Nafee N, Taetz S, Schneider M, Schaefer UF, Lehr CM. Chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles for DNA/RNA delivery: effect of the formulation parameters on complexation and transfection of antisense oligonucleotides. Nanomedicine. 2007;3:173–83.
Beisner J, Dong M, Taetz S, Nafee N, Griese EU, Schaefer U, et al. Nanoparticle mediated delivery of 2′-O-methyl-RNA leads to efficient telomerase inhibition and telomere shortening in human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 2009.
Taetz S, Nafee N, Beisner J, Piotrowska K, Baldes C, Murdter TE et al. The influence of chitosan content in cationic chitosan/PLGA nanoparticles on the delivery efficiency of antisense 2′-O-methyl-RNA directed against telomerase in lung cancer cells. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;72:358–69.
Kim WJ, Kim SW. Efficient siRNA delivery with non-viral polymeric vehicles. Pharm Res. 2009;26:657–66.
Park MR, Han KO, Han IK, Cho MH, Nah JW, Choi YJ et al. Degradable polyethylenimine-alt-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers as novel gene carriers. J Control Release. 2005;105:367–80.
Huang M, Fong CW, Khor E, Lim LY. Transfection efficiency of chitosan vectors: effect of polymer molecular weight and degree of deacetylation. J Control Release. 2005;106:391–406.
Zauner W, Farrow NA, Haines AM. In vitro uptake of polystyrene microspheres: effect of particle size, cell line and cell density. J Control Release. 2001;71:39–51.
Bivas-Benita M, Romeijn S, Junginger HE, Borchard G. PLGA-PEI nanoparticles for gene delivery to pulmonary epithelium. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2004;58:1–6.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank Ms. Myongcha Shin for her technical assistance in conducting FACS study at Columbia University. We would also like to thank Dr. Robert Chapman in the College of Pharmacy at Midwestern University for taking time to review the manuscript and giving us invaluable advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, X., Shah, B.A., Kotadia, N.K. et al. The Development and Mechanism Studies of Cationic Chitosan-Modified Biodegradable PLGA Nanoparticles for Efficient siRNA Drug Delivery. Pharm Res 27, 1285–1295 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0103-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0103-0