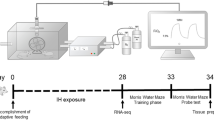
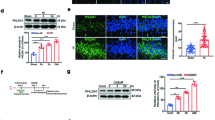
Abstract
Intermittent hypoxia (IH) is the predominant pathophysiological disturbance in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), characterized by neuronal cell death and neurocognitive impairment. We focus on the accumulated mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in the cytosol, which acts as a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) and activates the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)—stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway, a known trigger for immune responses and neuronal death in degenerative diseases. However, the specific role and mechanism of the mtDNA-cGAS-STING axis in IH-induced neural damage remain largely unexplored. Here, we investigated the involvement of PANoptosis, a novel type of programmed cell death linked to cytosolic mtDNA accumulation and the cGAS-STING pathway activation, in neuronal cell death induced by IH. Our study found that PANoptosis occurred in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons and HT22 cell lines exposed to IH. In addition, we discovered that during IH, mtDNA released into the cytoplasm via the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) activates the cGAS-STING pathway, exacerbating PANoptosis-associated neuronal death. Pharmacologically inhibiting mPTP opening or depleting mtDNA significantly reduced cGAS-STING pathway activation and PANoptosis in HT22 cells under IH. Moreover, our findings indicated that the cGAS-STING pathway primarily promotes PANoptosis by modulating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Inhibiting or silencing the cGAS-STING pathway substantially reduced ER stress-mediated neuronal death and PANoptosis, while lentivirus-mediated STING overexpression exacerbated these effects. In summary, our study elucidates that cytosolic escape of mtDNA triggers cGAS-STING pathway-dependent neuronal PANoptosis in response to IH, mainly through regulating ER stress. The discovery of the novel mechanism provides theoretical support for the prevention and treatment of neuronal damage and cognitive impairment in patients with OSA.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Jordan AS, McSharry DG, Malhotra A (2014) Adult obstructive sleep apnoea. Lancet 383:736–747
Dempsey JA, Veasey SC, Morgan BJ, O’Donnell CP (2010) Pathophysiology of sleep apnea. Physiol Rev 90:47–112
Lavie P, Herer P, Hoffstein V (2000) Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome as a risk factor for hypertension: population study. BMJ 320:479–482
Idris I, Hall AP, O’Reilly J, Barnett A, Allen M, Andrews R, Grunstein P, Lewis K, Goenka N, Wilding JP (2009) Obstructive sleep apnoea in patients with type 2 diabetes: aetiology and implications for clinical care. Diabetes Obes Metab 11:733–741
Tasali E, Mokhlesi B, Van Cauter E (2008) Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes: interacting epidemics. Chest 133:496–506
Yacoub M, Youssef I, Salifu MO, McFarlane SI (2017) Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Obstructive Sleep apnea: an update. J Sleep Disord Ther 7:283
Han Q, Li G, Ip MS, Zhang Y, Zhen Z, Mak JC, Zhang N (2018) Haemin attenuates intermittent hypoxia-induced cardiac injury via inhibiting mitochondrial fission. J Cell Mol Med 22:2717–2726
Wallace A, Bucks RS (2013) Memory and obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Sleep 36:203–220
Jackson ML, Howard ME, Barnes M (2011) Cognition and daytime functioning in sleep-related breathing disorders. Prog Brain Res 190:53–68
Macey KE, Macey PM, Woo MA, Henderson LA, Frysinger RC, Harper RK, Alger JR, Yan-Go F, Harper RM (2006) Inspiratory loading elicits aberrant fMRI signal changes in obstructive sleep apnea. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 151:44–60
Macey PM, Harper RM (2005) OSA brain morphology differences: magnitude of loss approximates age-related effects. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172:1056–1057 author reply 1057–1058
Woo MA, Macey PM, Keens PT, Kumar R, Fonarow GC, Hamilton MA, Harper RM (2005) Functional abnormalities in brain areas that mediate autonomic nervous system control in advanced heart failure. J Card Fail 11:437–446
Xu W, Chi L, Row BW, Xu R, Ke Y, Xu B, Luo C, Kheirandish L, Gozal D, Liu R (2004) Increased oxidative stress is associated with chronic intermittent hypoxia-mediated brain cortical neuronal cell apoptosis in a mouse model of sleep apnea. Neuroscience 126:313–323
Shan X, Chi L, Ke Y, Luo C, Qian S, Gozal D, Liu R (2007) Manganese superoxide dismutase protects mouse cortical neurons from chronic intermittent hypoxia-mediated oxidative damage. Neurobiol Dis 28:206–215
Si J, Liu B, Qi K, Chen X, Li D, Yang S, Ji E (2023) Tanshinone IIA inhibited intermittent hypoxia induced neuronal injury through promoting autophagy via AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 315:116677
Zhan G, Fenik P, Pratico D, Veasey SC (2005) Inducible nitric oxide synthase in long-term intermittent hypoxia: hypersomnolence and brain injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171:1414–1420
Baker TL, Fuller DD, Zabka AG, Mitchell GS (2001) Respiratory plasticity: differential actions of continuous and episodic hypoxia and hypercapnia. Respir Physiol 129:25–35
Macey PM, Sarma MK, Nagarajan R, Aysola R, Siegel JM, Harper RM, Thomas MA (2016) Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with low GABA and high glutamate in the insular cortex. J Sleep Res 25:390–394
Eisele HJ, Markart P, Schulz R (2015) Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Oxidative Stress, and Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence from Human Studies. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015:608438
Vakulin A, Green MA, D’Rozario AL, Stevens D, Openshaw H, Bartlett D, Wong K, McEvoy RD, Grunstein RR, Rae CD (2022) Brain mitochondrial dysfunction and driving simulator performance in untreated obstructive sleep apnea. J Sleep Res 31:e13482
Ryan S, McNicholas WT, Taylor CT (2007) A critical role for p38 map kinase in NF-kappaB signaling during intermittent hypoxia/reoxygenation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 355:728–733
Deng Y, Liu K, Pan Y, Ren J, Shang J, Chen L, Liu H (2020) TLR2 antagonism attenuates the hippocampal neuronal damage in a murine model of sleep apnea via inhibiting neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Sleep Breath 24:1613–1621
Zhang P, Wang Y, Wang H, Cao J (2021) Sesamol alleviates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive deficits via inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation in rats. NeuroReport 32:105–111
Douglas RM, Ryu J, Kanaan A, Del Carmen Rivero M, Dugan LL, Haddad GG, Ali SS (2010) Neuronal death during combined intermittent hypoxia/hypercapnia is due to mitochondrial dysfunction. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 298:C1594–1602
Moya GE, Rivera PD, Dittenhafer-Reed KE (2021) Evidence for the role of mitochondrial DNA release in the inflammatory response in neurological disorders. Int J Mol Sci 22
Li W, Yang S, Yu FY, Zhao Y, Sun ZM, An JR, Ji E (2018) Hydrogen ameliorates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced neurocognitive impairment via inhibiting oxidative stress. Brain Res Bull 143:225–233
Sharma C, Kim S, Nam Y, Jung UJ, Kim SR (2021) Mitochondrial dysfunction as a driver of cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci 22:4850
Ma XM, Geng K, Law BY, Wang P, Pu YL, Chen Q, Xu HW, Tan XZ, Jiang ZZ, Xu Y (2023) Lipotoxicity-induced mtDNA release promotes diabetic cardiomyopathy by activating the cGAS-STING pathway in obesity-related diabetes. Cell Biol Toxicol 39:277–299
Yu CH, Davidson S, Harapas CR, Hilton JB, Mlodzianoski MJ, Laohamonthonkul P, Louis C, Low RRJ, Moecking J, De Nardo D, Balka KR, Calleja DJ, Moghaddas F, Ni E, McLean CA, Samson AL, Tyebji S, Tonkin CJ, Bye CR, Turner BJ, Pepin G, Gantier MP, Rogers KL, McArthur K, Crouch PJ, Masters SL (2020) TDP-43 triggers mitochondrial DNA release via mPTP to activate cGAS/STING in ALS. Cell 183:636–649 e618
Kim J, Kim HS, Chung JH (2023) Molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial DNA release and activation of the cGAS-STING pathway. Exp Mol Med 55:510–519
Xu J, Li Q, Xu CY, Mao S, ** JJ, Gu W, Shi Y, Zou CF, Ye L (2022) Obstructive sleep apnea aggravates neuroinflammation and pyroptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage via ASC/HIF-1alpha pathway. Neural Regen Res 17:2537–2543
Guo X, Shi Y, Du P, Wang J, Han Y, Sun B, Feng J (2019) HMGB1/TLR4 promotes apoptosis and reduces autophagy of hippocampal neurons in diabetes combined with OSA. Life Sci 239:117020
Zhang H, Zhou L, Zhou Y, Wang L, Jiang W, Liu L, Yue S, Zheng P, Liu H (2021) Intermittent hypoxia aggravates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via RIPK3-dependent necroptosis-modulated Nrf2/NFkappaB signaling pathway. Life Sci 285:119963
Samir P, Malireddi RKS, Kanneganti TD (2020) The PANoptosome: a deadly protein complex driving pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis). Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:238
Lee S, Karki R, Wang Y, Nguyen LN, Kalathur RC, Kanneganti TD (2021) AIM2 forms a complex with pyrin and ZBP1 to drive PANoptosis and host defence. Nature 597:415–419
Sundaram B, Pandian N, Mall R, Wang Y, Sarkar R, Kim HJ, Malireddi RKS, Karki R, Janke LJ, Vogel P, Kanneganti TD (2023) NLRP12-PANoptosome activates PANoptosis and pathology in response to heme and PAMPs. Cell 186:2783–2801 e2720
Zheng M, Kanneganti TD (2020) The regulation of the ZBP1-NLRP3 inflammasome and its implications in pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis). Immunol Rev 297:26–38
Malireddi RKS, Kesavardhana S, Kanneganti TD (2019) ZBP1 and TAK1: Master regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome/Pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PAN-optosis). Front Cell Infect Microbiol 9:406
Christgen S, Zheng M, Kesavardhana S, Karki R, Malireddi RKS, Banoth B, Place DE, Briard B, Sharma BR, Tuladhar S, Samir P, Burton A, Kanneganti TD (2020) Identification of the PANoptosome: a molecular platform triggering pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis). Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:237
Xu LH, **e H, Shi ZH, Du LD, Wing YK, Li AM, Ke Y, Yung WH (2015) Critical role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced deficits in synaptic plasticity and long-term memory. Antioxid Redox Signal 23:695–710
** W, Zhao J, Yang E, Wang Y, Wang Q, Wu Y, Tong F, Tan Y, Zhou J, Kang C (2022) Neuronal STAT3/HIF-1alpha/PTRF axis-mediated bioenergetic disturbance exacerbates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via PLA2G4A. Theranostics 12:3196–3216
Seibenhener ML, Wooten MW (2012) Isolation and culture of hippocampal neurons from prenatal mice. J Vis Exp
Oorschot DE, Jones DG (1986) Effect of cytosine arabinoside on the composition of the nonneuronal cell population in cerebral explants. Exp Neurol 92:404–412
Aminova LR, Chavez JC, Lee J, Ryu H, Kung A, Lamanna JC, Ratan RR (2005) Prosurvival and prodeath effects of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha stabilization in a murine hippocampal cell line. J Biol Chem 280:3996–4003
Zhang Y, Miao Y, **ong X, Tan J, Han Z, Chen F, Lei P, Zhang Q (2023) Microglial exosomes alleviate intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive deficits by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome. Biol Direct 18:29
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Ouyang W, Wang S, Yan D, Wu J, Zhang Y, Li W, Hu J, Liu Z (2023) The cGAS-STING pathway-dependent sensing of mitochondrial DNA mediates ocular surface inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther 8:371
Phillips NR, Sprouse ML, Roby RK (2014) Simultaneous quantification of mitochondrial DNA copy number and deletion ratio: a multiplex real-time PCR assay. Sci Rep 4:3887
Guo Y, Gu R, Gan D, Hu F, Li G, Xu G (2020) Mitochondrial DNA drives noncanonical inflammation activation via cGAS-STING signaling pathway in retinal microvascular endothelial cells. Cell Commun Signal 18:172
Shi G, Liu L, Cao Y, Ma G, Zhu Y, Xu J, Zhang X, Li T, Mi L, Jia H, Zhang Y, Liu X, Zhou Y, Li S, Yang G, Liu X, Chen F, Wang B, Deng Q, Zhang S, Zhang J (2023) Inhibition of neutrophil extracellular trap formation ameliorates neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis via STING-dependent IRE1alpha/ASK1/JNK signaling pathway in mice with traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation 20:222
Digilio L, Yap CC, Winckler B (2015) Ctip2-, Satb2-, Prox1-, and GAD65-Expressing neurons in rat cultures: preponderance of single- and double-positive cells, and cell type-specific expression of Neuron-Specific Gene Family members, Nsg-1 (NEEP21) and Nsg-2 (P19). PLoS ONE 10:e0140010
Ma J, Yang Q, Wei Y, Yang Y, Ji C, Hu X, Mai S, Kuang S, Tian X, Luo Y, Liang G, Yang J (2016) Effect of the PGD2-DP signaling pathway on primary cultured rat hippocampal neuron injury caused by aluminum overload. Sci Rep 6:24646
Perycz M, Urbanska AS, Krawczyk PS, Parobczak K, Jaworski J (2011) Zipcode binding protein 1 regulates the development of dendritic arbors in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 31:5271–5285
Casella EM, Thomas TC, Vanino DL, Fellows-Mayle W, Lifshitz J, Card JP, Adelson PD (2014) Traumatic brain injury alters long-term hippocampal neuron morphology in juvenile, but not immature, rats. Childs Nerv Syst 30:1333–1342
Messaoud-Nacer Y, Culerier E, Rose S, Maillet I, Rouxel N, Briault S, Ryffel B, Quesniaux VFJ, Togbe D (2022) STING agonist diABZI induces PANoptosis and DNA mediated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Cell Death Dis 13:269
Yan YR, Zhang L, Lin YN, Sun XW, Ding YJ, Li N, Li HP, Li SQ, Zhou JP, Li QY (2021) Chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction mediates endothelial injury via the TXNIP/NLRP3/IL-1beta signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 165:401–410
Smith JA (2020) STING, the endoplasmic reticulum, and Mitochondria: is three a crowd or a conversation? Front Immunol 11:611347
Cao Y, Shi M, Liu L, Zuo Y, Jia H, Min X, Liu X, Chen Z, Zhou Y, Li S, Yang G, Liu X, Deng Q, Chen F, Chen X, Zhang S, Zhang J (2023) Inhibition of neutrophil extracellular trap formation attenuates NLRP1-dependent neuronal pyroptosis via STING/IRE1alpha pathway after traumatic brain injury in mice. Front Immunol 14:1125759
Zhu Y, Tang Q, Wang G, Han R (2017) Tanshinone IIA protects hippocampal neuronal cells from reactive oxygen species through changes in Autophagy and activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, protein Kinas B, and mechanistic target of Rapamycin pathways. Curr Neurovasc Res 14:132–140
Klenke S, Specking C, Stegen M, Engler A, Peters J (2020) Methylation in HT22 cells and primary hippocampal neurons with and without isoflurane exposurewhether isoflurane causes. BMC Anesthesiol 20:66
Lim J, Bang Y, Kim KM, Choi HJ (2022) Differentiated HT22 cells as a novel model for in vitro screening of serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Front Pharmacol 13:1062650
Hou Y, Zhang Y, Jiang S, **e N, Zhang Y, Meng X, Wang X (2023) Salidroside intensifies mitochondrial function of CoCl(2)-damaged HT22 cells by stimulating PI3K-AKT-MAPK signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 109:154568
Chen S, Zou Q, Guo Q, Chen Y, Kuang X, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Wu W, Li G, Tu L, Tong J, Li S, Ma L, Li Q (2020) SPARC Knockdown reduces Glutamate-Induced HT22 hippocampal nerve cell damage by regulating Autophagy. Front Neurosci 14:581441
Liu Y, Tan J, Miao Y, Zhang Q (2024) Neurogenesis, a potential target for intermittent hypoxia leading to Cognitive decline. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 19:63–70
Kerner NA, Roose SP (2016) Obstructive sleep apnea is linked to Depression and Cognitive Impairment: evidence and potential mechanisms. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 24:496–508
Song S, Tan J, Miao Y, Zhang Q (2017) Effect of different levels of intermittent hypoxia on autophagy of hippocampal neurons. Sleep Breath 21:791–798
He Q, Yang QC, Zhou Q, Zhu H, Niu WY, Feng J, Wang Y, Cao J, Chen BY (2014) Effects of varying degrees of intermittent hypoxia on proinflammatory cytokines and adipokines in rats and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. PLoS ONE 9:e86326
Bertheloot D, Latz E, Franklin BS (2021) Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death. Cell Mol Immunol 18:1106–1121
Hou Y, Wei Y, Lautrup S, Yang B, Wang Y, Cordonnier S, Mattson MP, Croteau DL, Bohr VA (2021) NAD(+) supplementation reduces neuroinflammation and cell senescence in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease via cGAS-STING. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118:e2011226118
Sliter DA, Martinez J, Hao L, Chen X, Sun N, Fischer TD, Burman JL, Li Y, Zhang Z, Narendra DP, Cai H, Borsche M, Klein C, Youle RJ (2018) Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation. Nature 561:258–262
Chen C, Xu P (2023) Cellular functions of cGAS-STING signaling. Trends Cell Biol 33:630–648
Liao Y, Cheng J, Kong X, Li S, Li X, Zhang M, Zhang H, Yang T, Dong Y, Li J, Xu Y, Yuan Z (2020) HDAC3 inhibition ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury by regulating the microglial cGAS-STING pathway. Theranostics 10:9644–9662
Jiang GL, Yang XL, Zhou HJ, Long J, Liu B, Zhang LM, Lu D (2021) cGAS knockdown promotes microglial M2 polarization to alleviate neuroinflammation by inhibiting cGAS-STING signaling pathway in cerebral ischemic stroke. Brain Res Bull 171:183–195
Kong L, Li W, Chang E, Wang W, Shen N, Xu X, Wang X, Zhang Y, Sun W, Hu W, Xu P, Liu X (2022) mtDNA-STING Axis mediates microglial polarization via IRF3/NF-κB signaling after ischemic stroke. Front Immunol 13:860977
Liu M, Li Y, Han S, Wang H, Li J (2023) Activin a alleviates neuronal injury through inhibiting cGAS-STING-mediated autophagy in mice with ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 43:736–748
Marchi S, Guilbaud E, Tait SWG, Yamazaki T, Galluzzi L (2023) Mitochondrial control of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 23:159–173
Shen K, Pender CL, Bar-Ziv R, Zhang H, Wickham K, Willey E, Durieux J, Ahmad Q, Dillin A (2022) Mitochondria as Cellular and Organismal Signaling hubs. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 38:179–218
Shi M, Chen F, Chen Z, Yang W, Yue S, Zhang J, Chen X (2021) Sigma-1 receptor: a potential therapeutic target for traumatic brain Injury. Front Cell Neurosci 15:685201
Shang F, Wang SC, Gongol B, Han SY, Cho Y, Schiavon CR, Chen L, **ng Y, Zhao Y, Ning M, Guo X, He F, Lei Y, Wang L, Manor U, Marin T, Chou KT, He M, Huang PH, Shyy JY, Malhotra A (2023) Obstructive sleep apnea-induced endothelial dysfunction is mediated by miR-210. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 207:323–335
Laouafa S, Roussel D, Marcouiller F, Soliz J, Gozal D, Bairam A, Joseph V (2019) Roles of oestradiol receptor alpha and beta against hypertension and brain mitochondrial dysfunction under intermittent hypoxia in female rats. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 226:e13255
Hopfner KP, Hornung V (2020) Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21:501–521
Paul BD, Snyder SH, Bohr VA (2021) Signaling by cGAS-STING in Neurodegeneration, Neuroinflammation, and aging. Trends Neurosci 44:83–96
Bi X, Du C, Wang X, Wang XY, Han W, Wang Y, Qiao Y, Zhu Y, Ran L, Liu Y, **ong J, Huang Y, Liu M, Liu C, Zeng C, Wang J, Yang K, Zhao J (2021) Mitochondrial damage-Induced Innate Immune activation in vascular smooth muscle cells promotes chronic kidney Disease-Associated Plaque vulnerability. Adv Sci (Weinh) 8:2002738
Huang LS, Hong Z, Wu W, **ong S, Zhong M, Gao X, Rehman J, Malik AB (2020) mtDNA activates cGAS Signaling and suppresses the YAP-Mediated endothelial cell Proliferation Program to Promote Inflammatory Injury. Immunity 52:475–486 e475
Liu Z, Wang M, Wang X, Bu Q, Wang Q, Su W, Li L, Zhou H, Lu L (2022) XBP1 deficiency promotes hepatocyte pyroptosis by impairing mitophagy to activate mtDNA-cGAS-STING signaling in macrophages during acute liver injury. Redox Biol 52:102305
Zhang W, Li G, Luo R, Lei J, Song Y, Wang B, Ma L, Liao Z, Ke W, Liu H, Hua W, Zhao K, Feng X, Wu X, Zhang Y, Wang K, Yang C (2022) Cytosolic escape of mitochondrial DNA triggers cGAS-STING-NLRP3 axis-dependent nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis. Exp Mol Med 54:129–142
Zhang Q, Wei J, Liu Z, Huang X, Sun M, Lai W, Chen Z, Wu J, Chen Y, Guo X, Huang Q (2022) STING signaling sensing of DRP1-dependent mtDNA release in kupffer cells contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in mice. Redox Biol 54:102367
Zhang X, Wu J, Liu Q, Li X, Li S, Chen J, Hong Z, Wu X, Zhao Y, Ren J (2020) mtDNA-STING pathway promotes necroptosis-dependent enterocyte injury in intestinal ischemia reperfusion. Cell Death Dis 11:1050
Ding R, Li H, Liu Y, Ou W, Zhang X, Chai H, Huang X, Yang W, Wang Q (2022) Activating cGAS-STING axis contributes to neuroinflammation in CVST mouse model and induces inflammasome activation and microglia pyroptosis. J Neuroinflammation 19:137
Duan N, Zhang Y, Tan S, Sun J, Ye M, Gao H, Pu K, Wu M, Wang Q, Zhai Q (2022) Therapeutic targeting of STING-TBK1-IRF3 signalling ameliorates chronic stress induced depression-like behaviours by modulating neuroinflammation and microglia phagocytosis. Neurobiol Dis 169:105739
Zhang D, Liu Y, Zhu Y, Zhang Q, Guan H, Liu S, Chen S, Mei C, Chen C, Liao Z, ** Y, Ouyang S, Feng XH, Liang T, Shen L, Xu P (2022) A non-canonical cGAS-STING-PERK pathway facilitates the translational program critical for senescence and organ fibrosis. Nat Cell Biol 24:766–782
**e X, Wu X, Zhao D, Liu Y, Du Q, Li Y, Xu Y, Li Y, Qiu Y, Yang Y (2023) Fluvoxamine alleviates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis via regulating the cGAS-STING pathway. Pharmacol Res 187:106577
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the participants in the study.
Funding
This work was supported by Major Research Plan of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.92163213), General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81970085), Tian** science and technology plan project (Grant No. 21JCZDJC00940), Tian** health science and technology projects (Grant No. TJWJ2022XK001), and Tian** Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project (Grant No.TJYXZDXK-006 A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was collaboratively conceived and designed by all authors. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Shuying Wang and ** Tan. The initial draft of the manuscript was composed by Shuying Wang, with subsequent revisions and inputs from all authors. The final manuscript has been read and approved by every author.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Tian** Medical University Animal Care and Use Committee (IRB2022-DWFL-074, approval data: 02/21/2022).
Conflict of interest
The authors claim no relevant conflicts.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Tan, J. & Zhang, Q. Cytosolic Escape of Mitochondrial DNA Triggers cGAS-STING Pathway-Dependent Neuronal PANoptosis in Response to Intermittent Hypoxia. Neurochem Res 49, 2228–2248 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-024-04151-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-024-04151-7