Abstract
Background
Giardia duodenalis is a common parasitic protozoan causing gastrointestinal illness in humans worldwide. The genetic diversity of G. duodenalis is reflected through the identification of different assemblages. In this study, we aimed to determine the assemblages of G. duodenalis in eastern Iran using nested-PCR and high-resolution melting (HRM) real-time PCR methods.
Methods
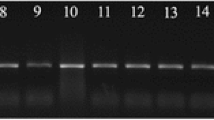
A total of 58 positive G. duodenalis, which were isolated from 1800 subjects, referred to medical center laboratories in South Khorasan province, eastern Iran, from April 2020 to March 2022, were included in this study. DNA was extracted and HRM real-time PCR was performed for assemblage characterization.
Results
HRM real-time PCR successfully characterized all samples. Accordingly, out of 58 positive samples, 53 (91.36%) and 5 (8.62%) were identified as assemblage A and B, respectively.
Conclusions
Our findings showed that HRM real-time PCR was able to characterize the assemblages of G. duodenalis. In addition, our results suggest high prevalence of assemblage A in eastern region of Iran.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All generated data from the current study are included in the article.
References
Javanmard E, Mirsamadi ES, Olfatifar M, Ghasemi E, Saki F, Mirjalali H, Zali MR, Karanis P (2020) Prevalence of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in vegetables in Iran: a nineteen-years meta-analysis review. J Environ Health Sci Engin 18(2):1629–1641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00493-w
Cai W, Ryan U, **ao L, Feng Y (2021) Zoonotic giardiasis: an update. Parasitol Res 120(12):4199–4218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07325-2
Capewell P, Krumrie S, Katzer F, Alexander CL, Weir W (2021) Molecular epidemiology of Giardia infections in the genomic era. Trend Parasitol 37(2):142–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2020.09.013
Heyworth MF (2016) Giardia duodenalis genetic assemblages and hosts. Parasite 23:13. https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2016013
Lee MF, Auer H, Lindo JF, Walochnik J (2017) Multilocus sequence analysis of Giardia spp. isolated from patients with diarrhea in Austria. Parasitol Res 116:477–481
Cacciò SM, Ryan U (2008) Molecular epidemiology of giardiasis. Mol Bioch Parasitol 160(2):75–80
Feng Y, **ao L (2011) Zoonotic potential and molecular epidemiology of Giardia species and giardiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev 24(1):110–140
Rehbein S, Klotz C, Ignatius R, Müller E, Aebischer A, Kohn B (2019) Giardia duodenalis in small animals and their owners in Germany: a pilot study. Zoonoses Public Health 66(1):117–124
Mohammad Rahimi H, Pourhosseingholi MA, Yadegar A, Mirjalali H, Zali MR (2019) High-resolution melt curve analysis: a real-time based multipurpose approach for diagnosis and epidemiological investigations of parasitic infections. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 67:101364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cimid.2019.101364
Bahramdoost Z, Mirjalali H, Yavari P, Haghighi A (2021) Development of HRM real-time PCR for assemblage characterization of Giardia lamblia. Act Trop 224:106109
Safa AH, Harandi MF, Tajaddini M, Rostami-Nejad M, Mohtashami-Pour M, Pestehchian N (2016) Rapid identification of Echinococcus granulosus and E. canadensis using high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis by focusing on a single nucleotide polymorphism. Japan J Infect Dis 69(4):300–305
Sepahvand A, Hosseini-Safa A, Yousofi HA, Tajedini MH, Gharehbabah RP, Pestehchian N (2020) Genotype characteristics of Giardia duodenalis in patients using high resolution melting analysis technique in Khorramabad. Iran Iran J Parasitol 15(2):204
Sarkari B, Ashrafmansori A, Hatam G, Motazedian M, Asgari Q, Mohammadpour I (2012) Genoty** of Giardia lamblia isolates from human in southern Iran. Trop Biomed 29(3):366–371
Pestehchian N, Rasekh H, Babaei Z, Yousefi HA, Eskandarian AA, Kazemi M, Akbari M (2012) Identification of genotypes of Giardia duodenalis human isolates in Isfahan, Iran, using polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism. Adv Biomed Res 1:84
Rafiei A, Baghlaninezhad R, Köster PC, Bailo B, Hernández de Mingo M, Carmena D, Panabad E, Beiromvand M (2020) Multilocus genoty** of Giardia duodenalis in Southwestern Iran: a community survey. PLoS ONE 15(2):e0228317
Mohammad Rahimi H, Javanmard E, Taghipour A, Haghighi A, Mirjalali H (2023) Multigene ty** of Giardia duodenalis isolated from tuberculosis and non-tuberculosis subjects. PLoS ONE 18(3):e0283515. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0283515
Pacheco FTF, Silva RKNR, de Carvalho SS, Rocha FC, das Chagas GMT, Gomes DC (2020) Predominance of Giardia duodenalis AII sub-assemblage in young children from Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Biomedica 40(3):557
Ahmad AA, El-Kady AM, Hassan TM (2020) Genoty** of Giardia duodenalis in children in upper Egypt using assemblage-specific PCR technique. PLoS ONE 15(10):e0240119
Wegayehu T, Karim MR, Li J, Adamu H, Erko B, Zhang L, Tilahun G (2016) Multilocus genoty** of Giardia duodenalis isolates from children in Oromia Special Zone, central Ethiopia. BMC Microbiol 16(1):1–10
Belkessa S, Thomas-Lopez D, Houali K, Ghalmi F, Stensvold CR (2021) Molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis in children and adults sampled in Algeria. Microorganisms 9(1):54
Hijjawi N, Yang R, Mukbel R, Yassin Y, Mharib T, Ryan U (2016) First genetic characterisation of Giardia in human isolates from Jordan. Parasitol Res 115(10):3723–3729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5132-0
Chang Y, Li J, Zhang L (2023) Genetic diversity and molecular diagnosis of Giardia. Infect Gen Evol: J Mol Epidemiol Evol Gene Infect Dis 113:105482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2023.105482
Akbarian A, Sadraie J, Forozandeh M (2012) Evaluattion of Giardia lamblia genetic differences in Khorramabad City and surrounding villages by use of PCR and sequencing. Sci J Kurdistan Univ Med Sci 17(2):61–71
Kasaei R, Carmena D, Jelowdar A, Beiromvand M (2018) Molecular genoty** of Giardia duodenalis in children from Behbahan, southwestern Iran. Parasitol Res 117(5):1425–1431
Rafiei A, Roointan ES, Samarbafzadeh AR, Shayesteh AA, Shamsizadeh A, Borujeni MP (2013) Investigation of possible correlation between Giardia duodenalis genotypes and clinical symptoms in southwest of Iran. Iran J Parasitol 8(3):389
Cacciò SM, Lalle M, Svärd SG (2018) Host specificity in the Giardia duodenalis species complex. Infect Gen Evol: J Mol Epidemiol Evol Gene Infect Dis 66:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2017.12.001
Fantinatti M, Gonçalves-Pinto M, Lopes-Oliveira LAP, Da-Cruz AM (2021) Epidemiology of Giardia duodenalis assemblages in Brazil: there is still a long way to go. Mem Instit Oswaldo Cruz 115:e200431. https://doi.org/10.1590/0074-02760200431
Ballweber LR, **ao L, Bowman DD, Kahn G, Cama VA (2010) Giardiasis in dogs and cats: update on epidemiology and public health significance. Trend Parasitol 26(4):180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2010.02.005
Seabolt MH, Roellig DM, Konstantinidis KT (2022) Genomic comparisons confirm Giardia duodenalis sub-assemblage AII as a unique species. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:1010244. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.1010244
Haque R, Roy S, Kabir M, Stroup SE, Mondal D, Houpt ER (2005) Giardia assemblage A infection and diarrhea in Bangladesh. J Infect Dis 192(12):2171–2173
Helmy MM, Abdel-Fattah HS, Rashed L (2009) Real-time PCR/RFLP assay to detect Giardia intestinalis genotypes in human isolates with diarrhea in Egypt. J Parasitol 95(4):1000–1004
Mahdy AM, Surin J, Wan K, Mohd-Adnan A, Al-Mekhlafi MH, Lim Y (2009) Giardia intestinalis genotypes: risk factors and correlation with clinical symptoms. Act Trop 112(1):67–70
Al-Mohammed HI (2011) Genotypes of Giardia intestinalis clinical isolates of gastrointestinal symptomatic and asymptomatic Saudi children. Parasitol Res 108(6):1375–1381
Zhang P, Liu Y, Alsarakibi M, Li J, Liu T, Li Y, Li G (2012) Application of HRM assays with EvaGreen dye for genoty** Giardia duodenalis zoonotic assemblages. Parasitol Res 111(5):2157–2163
Chua KH, Lim SC, Ng CC, Lee PC, Lim YAL, Lau TP, Chai HC (2015) Development of high resolution melting analysis for the diagnosis of human malaria. Sci Rep 5(1):15671
Acknowledgements
The present manuscript was a component of Mahmoodreza Behravan’s PhD thesis and Moloud Tabrizi’s MSc thesis. This research work received financial support from the Deputy Research Office of the School of Medicine at Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences. We would like to take this opportunity to express our sincere gratitude for the cooperation and support provided by all personnel of the health centers in South Khorasan Province, Iran and Foodborne and Waterborne Diseases Research Center, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Iran.
Funding
This study received support from the Research Deputy of the School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (Grant Numbers: 25680 and 33013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed: AH, HM. Sample collection and questionnaire: MB MT. Methodology and implementation: MT, ZL, HMR, SJST. Statistical analysis: MAP. Reviewing and editing the manuscript: AH, HM. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
All study participants completed a written informed consent before specimen collection. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (IR.SBMU.MSP.REC.1399.754) and (IR.SBMU.MSP.REC.1401.272).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s). All authors declare that they have seen and approved the submitted version of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tabrizi, M., Behravan, M., Seyyed Tabaei, S.J. et al. Assemblage characterization of Giardia duodenalis in South Khorasan province, eastern Iran, using HRM real-time PCR method. Mol Biol Rep 51, 127 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-09001-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-09001-3