Abstract
Background
Aberrant expression of miRNAs have been implicated in cancers, but the role of miRNAs in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains need to be elucidated. This study aimed to identify miRNAs that related to colorectal cancer (CRC) pathogenesis and determine the diagnostic value.
Methods
Three GEO datasets (GSE128449, GSE35602 and GSE49246) with 131 samples were used to screen miRNAs that differential expression between tumor and control tissues. The expression of the identified miRNAs was validated in 50 clinical tissue samples and the GSE35834 dataset. The clinical significance of these miRNAs was analyzed in the TCGA dataset and clinical tissue samples. The expression of miRNAs in tissues and plasma samples were tested by RT-PCR assay in clinical samples, and their diagnostic value was determined.
Results
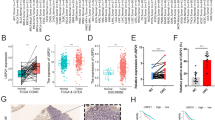
The analysis of three GEO datasets revealed that miR-595 and miR-1237 were upregulated, while miR-126, miR-139, and miR-143 were downregulated in CRC tissues compared to control tissues. The differential expression of the five miRNAs in CRC tissues was confirmed using clinical tissue samples and GEO databases. There was no significant correlation between the TNM stage and tumor stage of CRC and any of the five miRNAs. Plasma expression of the miRNAs differed significantly between CRC and non-cancer patients, and each miRNA had moderate diagnostic value for CRC. Combining the five miRNAs provided better diagnostic potential for CRC than a single miRNA.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated that five miRNAs were related to the pathogenesis of CRC, but independent of the stage of CRC; Plasma expression of these miRNAs have moderate diagnostic value, and combination of these miRNAs showed better diagnostic ability in CRC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from GEO databases (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/), with the access number as GSE128449, GSE35602, GSE49246, GSE32323, GSE35834, and GSE59856 respectively. The TCGA-COADREAD datasets was downloaded from Xena database (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/).
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- DEMs:
-
Differential expression miRNAs
- ROC:
-
Receiver Operating Characteristic
- AUC:
-
Area Under ROC Curve
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
- CEA:
-
Carcinoembryonic antigen
- CA125:
-
Carbohydrate antigen 125
- CA19-9:
-
Carbohydrate antigen 19–9
- CA153:
-
Carbohydrate antigen 153
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE (2022) Jemal A (2022) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 72(1):7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21708
Frieler M, Moore M, Longacre ML (2023) Primary and Secondary Prevention Interventions to Reduce Risk Factors Associated with Colorectal Cancer in High-Risk Groups: a Systematic Literature Review. J Cancer Educ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-023-02273-0
Fan A, Wang B, Wang X, Nie Y, Fan D, Zhao X et al (2021) Immunotherapy in colorectal cancer: current achievements and future perspective. Int J Biol Sci 17(14):3837–3849. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.64077
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Yang D, Zhang D (2021) miR-1253, a novel tumor suppressor gene in colon cancer, is associated with poor patients prognosis. Clin Exp Med 21(4):563–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-021-00706-y
Li Y, Xun J, Wang B, Ma Y, Zhang L, Yang L et al (2021) miR-3065-3p promotes stemness and metastasis by targeting CRLF1 in colorectal cancer. J Transl Med 19(1):429. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-021-03102-y
Mo WY, Cao SQ (2023) MiR-29a-3p: a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 25(3):563–577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02978-6
Bayat A, Raad M, Sharafshah A, Ahmadvand M, Aminian H (2022) Identification of miR-195-5p as a novel prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep 49(7):6453–6457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07462-6
Farouk S, El-Shenawy R, Khairy AM, Bader El-Din NG (2023) Overexpression of miRNA 26a and 26b with MMP-9 are valuable diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer patients. Biomark Med 17(3):159–169. https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm-2022-0861
Radwan E, Shaltout AS, Mansor SG, Shafik EA, Abbas WA, Shehata MR et al (2021) Evaluation of circulating microRNAs-211 and 25 as diagnostic biomarkers of colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep 48(5):4601–4610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06493-9
Nakamura K, Hernandez G, Sharma GG, Wada Y, Banwait JK, Gonzalez N et al (2022) A Liquid Biopsy Signature for the Detection of Patients With Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2022.06.089
Sur D, Advani S, Braithwaite D (2022) MicroRNA panels as diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.915226
Kent OA, Mendell JT (2006) A small piece in the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes. Oncogene 25(46):6188–6196. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209913
Li XM, Wang AM, Zhang J, Yi H (2011) Down-regulation of miR-126 expression in colorectal cancer and its clinical significance. Med Oncol 28(4):1054–1057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9637-6
Li C, Yan G, Yin L, Liu T, Li C, Wang L (2019) Prognostic roles of microRNA 143 and microRNA 145 in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Int J Biol Markers 34(1):6–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/1724600818807492
Shen K, Liang Q, Xu K, Cui D, Jiang L, Yin P et al (2012) MiR-139 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Biochem Pharmacol 84(3):320–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2012.04.017
Zou MX, Huang W, Wang XB, Li J, Lv GH, Wang B et al (2015) Reduced expression of miRNA-1237-3p associated with poor survival of spinal chordoma patients. Eur Spine J 24(8):1738–1746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3927-9
Morishita A, Nomura K, Tani J, Fujita K, Iwama H, Takuma K et al (2021) Galectin-9 suppresses the tumor growth of colon cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2021.8056
Hao Y, Zhang S, Sun S, Zhu J, **ao Y (2016) MiR-595 targeting regulation of SOX7 expression promoted cell proliferation of human glioblastoma. Biomed Pharmacother 80:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.03.008
Wang H, Jiang F, Liu W, Tian W (2020) miR-595 suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting NF-kappaB signalling pathway. Pathol Res Pract. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2020.152899
Zhou QH, Zhao YM, Jia LL, Zhang Y (2017) Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21(19):4278–4282
Liu W, Yang D, Chen L, Liu Q, Wang W, Yang Z et al (2020) Plasma Exosomal miRNA-139-3p is a Novel Biomarker of Colorectal Cancer. J Cancer 11(16):4899–4906. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.45548
Du G, Ren C, Wang J, Ma J (2022) The Clinical Value of Blood miR-654-5p, miR-126, miR-10b, and miR-144 in the Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Comput Math Methods Med 2022:8225966. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8225966
Ardila HJ, Sanabria-Salas MC, Meneses X, Rios R, Huertas-Salgado A, Serrano ML (2019) Circulating miR-141-3p, miR-143-3p and miR-200c-3p are differentially expressed in colorectal cancer and advanced adenomas. Mol Clin Oncol 11(2):201–207. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2019.1876
Todeschini P, Salviato E, Paracchini L, Ferracin M, Petrillo M, Zanotti L et al (2017) Circulating miRNA landscape identifies miR-1246 as promising diagnostic biomarker in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma: A validation across two independent cohorts. Cancer Lett 388:320–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.12.017
Fornari F, Ferracin M, Trere D, Milazzo M, Marinelli S, Galassi M et al (2015) Circulating microRNAs, miR-939, miR-595, miR-519d and miR-494. PLoS One, Identify Cirrhotic Patients with HCC. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141448
Raitoharju E, Seppala I, Oksala N, Lyytikainen LP, Raitakari O, Viikari J et al (2014) Blood microRNA profile associates with the levels of serum lipids and metabolites associated with glucose metabolism and insulin resistance and pinpoints pathways underlying metabolic syndrome: the cardiovascular risk in Young Finns Study. Mol Cell Endocrinol 391(1–2):41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2014.04.013
Luo H, Shen K, Li B, Li R, Wang Z, **e Z (2020) Clinical significance and diagnostic value of serum NSE, CEA, CA19-9, CA125 and CA242 levels in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett 20(1):742–750. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11633
Singh S, Kumar R, Kumar U, Kumari R (2020) Clinical Significance and Role of TK1, CEA, CA 19–9 and CA 72–4 levels in Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancers. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 21(11):3133–3136
Gao Y, Wang J, Zhou Y, Sheng S, Qian SY, Huo X (2018) Evaluation of Serum CEA, CA19-9, CA72-4, CA125 and Ferritin as Diagnostic Markers and Factors of Clinical Parameters for Colorectal Cancer. Sci Rep 8(1):2732. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21048-y
Li J, Feng Y, Heng D, Chen R, Wang Y, Xu Z et al (2020) Circulating non-coding RNA cluster predicted the tumorigenesis and development of colorectal carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY) 12(22):23047–23066
Peng X, Wang J, Zhang C, Liu K, Zhao L, Chen X et al (2020) A three-miRNA panel in serum as a noninvasive biomarker for colorectal cancer detection. Int J Biol Markers 35(3):74–82. https://doi.org/10.1177/1724600820950740
Maminezhad H, Ghanadian S, Pakravan K, Razmara E, Rouhollah F, Mossahebi-Mohammadi M et al (2020) A panel of six-circulating miRNA signature in serum and its potential diagnostic value in colorectal cancer. Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118226
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
This study was partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82160446 and 82260580); Guangxi Medical and health key discipline construction project; the Training Program for 1000 Young and Middle-aged Key Teachers in Guangxi; Scientific Research Project of Guangxi Health Commission (No. Z20190717).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: NSF and HBL; Collection and assembly of data: LSQ, XLY, CZM and XMZ; Performed the experiment: LSQ, XLY and CZM; Data analysis and interpretation: WHT, HBL, NSF and LSQ; Manuscript writing and review: All authors. All authors have read and approved the manuscript in its current state.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All the procedures were carried out in accordance with institutional guidelines. The study is approved by the Ethics Committee of Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital (2021-KY-NSFC-042), written informed consent was obtained from each patient. All the procedures were carried out in accordance with Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, SQ., **e, LY., Cai, ZM. et al. Systematic analyzing a five- miRNA panel and its diagnostic value of plasma expression in colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep 50, 7253–7261 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08642-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08642-8