Abstract
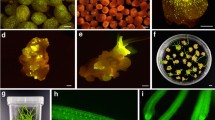
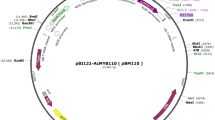
Efficiency of plant transformation is less than optimal for many important species, especially for monocots which are traditionally recalcitrant to transformation, such as wheat. And due to limited number of selectable marker genes, identification or selection of those cells that have integrated DNA into appropriate plant genome and to regenerate fully developed plants from the transformed cells, becomes even more difficult. Some of the widely used marker genes belong to the categories of herbicide or antibiotic resistance genes and flourescent protein genes. As they become an integral part of plant genome along with promoters prokaryotic or eukaryotic origin, there are certain health and environmental concerns about the use of these reporter genes. These marker genes are also inefficient with respect to time and space. In this study we have found a novel visible selection agent AtMYB12, to screen transgenic wheat, with in days after transformation. Transformed coleoptiles as well as cells regenerating from transformed cultured scutella, phenotypically exhibit purple pigmentation, making selection possible in limited and reasonable cost, time and space.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed N, Maekawa M, Utsugi S, Himi E, Ablet H, Rikiishi K, Noda K (2003) Transient expression of anthocyanin in develo** wheat coleoptile by maize C1 and B-peru regulatory genes for anthocyanin synthesis. Breed Sci 53:29–34
Arago FJL, Brasileiro ACM (2002) Positive, negative and marker-free strategies for transgenic plant selection. Braz J Plant Physiol 14:1–10
Borevitz JO, **a Y, Blount J, Dixon RA, Lamb C (2000) Activation tagging identifies a conserved MYB regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 12:2383–2394
Bovy A et al (2002) High-flavonol tomatoes resulting from the heterologous expression of the maize transcription factor genes LC and C1. Plant Cell 14:2509–2526
Casas AM, Kononowicz AK, Zehr UB, Tomes DT, Axtell JD, Butler LG, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (1993) Transgenic sorghum plants via microprojectile bombardment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:11212–11216
Chen L, Tu Z, Hussain J, Cong L, Yan Y, ** L, Yang G, He G (2010) Isolation and heterologous transformation analysis of a pollen-specific promoter from wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Biol Rep 37:737–744
Chen P, Wang C, Li K, Chang J, Wang Y, Yang G, Shewry PR, He G (2008) Cloning, expression and characterization of novel avenin-like genes in wheat and related species. J Cereal Sci 48:734–740
Daniell H, Datta R, Varma S, Gray S, Lee S-B (1998) Containment of herbicide resistance through genetic engineering of the chloroplast genome. Nat Biotechnol 16:345–348
Ding L, Li S, Gao J, Wang Y, Yang G, He G (2009) Optimization of agrobacterium-mediated transformation conditions in mature embryos of elite wheat. Mol Biol Rep 36:29–36
Elzen PJM, Townsend J, Lee KY, Bedbrook JR (1985) A chimaeric hygromycin resistance gene as a selectable marker in plant cells. Plant Mol Biol 5:299–302
Gadaleta A, Giancaspro A, Blechl A, Blanco A (2006) Phosphomannose isomerase, pmi, as a selectable marker gene for durum wheat transformation. J Cereal Sci 43:31–37
Gurskaya NG, Verkhusha VV, Shcheglov AS, Staroverov DB, Chepurnykh TV, Fradkov AF, Lukyanov S, Lukyanov KA (2006) Engineering of a monomeric green-to-red photoactivatable fluorescent protein induced by blue light. Nat Biotechnol 24:461–465
Haliloglu K (2006) Efficient regeneration system from wheat leaf base segments. Biol Plant 50:326–330
Haseloff J, Siemering KR (2005) The uses of green fluorescent protein in plants. Green fluorescent protein: properties, applications and protocols. Methods Biochem Anal 47:259
James C (2004) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops: 2004. ISAAA Briefs 32:1–12
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901
Jie Luo, Butelli E, Hill L, Parr A, Niggeweg R, Bailey P, Weisshaar B, Martin C (2008) AtMYB12 regulates caffeoyl quinic acid and flavonol synthesis in tomato: expression in fruit results in very high levels of both types of polyphenol. Plant J 56:316–326
Kunze I, Ebneth M, Heim U, Geiger M, Sonnewald U, Herbers K (2001) 2-Deoxyglucose resistance: a novel selection marker for plant transformation. Mol Breed 7:221–227
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lippincott-Schwartz J, Patterson GH (2003) Development and use of fluorescent protein markers in living cells. Science 300:87–91
Ludwig SR, Bowen B, Beach L, Wessler SR (1990) A regulatory gene as a novel visible marker for maize transformation. Science 247:449–450
McCormac A, Wu H, Bao M, Wang Y, Xu R, Elliott M, Chen D (1998) The use of visual marker genes as cell-specific reporters of Agrobacterium-mediated T-DNA delivery to wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Euphytica 99:17–25
Mehrtens F, Kranz H, Bednarek P, Weisshaar B (2005) The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB12 is a flavonol-specific regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 138:1083–1096
Philippe V (2007) Thirty years of plant transformation technology development. Plant Biotechnol J 5:221–229
Roland Bilang SZ, Leduc N, Iglesias VA, Gisel A, Simmonds J, Potrykus I, Sautter C (1993) Transient gene expression in vegetative shoot apical meristems of wheat after ballistic microtargeting. Plant J 4:735–744
Shewry PR, Tatham AS, Fido RJ (1995) Separation of plant proteins by electrophoresis. Methods in molecular biology—plant gene transfer and expression protocols, vol 49. pp 399–422
Sparkes IA, Runions J, Kearns A, Hawes C (2006) Rapid, transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in tobacco plants and generation of stably transformed plants. Nat Protoc 1:2019–2025
Stacey J, Isaac P (1994) Isolation of DNA from plants. Methods in molecular biology—protocols for nucleic acid analysis by nonradioactive probes, vol 28. pp 9–15
Stracke R, Ishihara H, Huep G, Barsch A, Mehrtens F, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B (2007) Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J 50:660–677
Sundar IK, Sakthivel N (2008) Advances in selectable marker genes for plant transformation. J Plant Physiol 165:1698–1716
Thirukkumaran G, Khan R, Chin D, Nakamura I, Mii M (2009) Isopentenyl transferase gene expression offers the positive selection of marker-free transgenic plant of Kalanchoe blossfeldiana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 97:237–242
Toshio Murashige FS (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Vain P, De Buyser J, Bui Trang V, Haicour R, Henry Y (1995) Foreign gene delivery into monocotyledonous species. Biotechnol Adv 13:653–671
Vasil I (2008) A history of plant biotechnology: from the cell theory of Schleiden and Schwann to biotech crops. Plant Cell Rep 27:1423–1440
Yao Q, Cong L, Chang JL, Li KX, Yang GX, He GY (2006) Low copy number gene transfer and stable expression in a commercial wheat cultivar via particle bombardment. J Exp Bot 57:3737
Yao Q, Cong L, He G, Chang J, Li K, Yang G (2007) Optimization of wheat co-transformation procedure with gene cassettes resulted in an improvement in transformation frequency. Mol Biol Rep 34:61–67
Acknowledgement
This work was support by the national Natural Science Foundation of China (30871524), the National S&T Major Project of the People's Republic of China (2008ZX08002004), (2008ZX08010-004), and National Science Foundation of China (2009DFB30340), (2009DFB20290).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xuan Gao and Li Zhang have contributed to this work equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Zhang, L., Zhou, S. et al. AtMYB12 gene: a novel visible marker for wheat transformation. Mol Biol Rep 38, 183–190 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0093-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0093-3