Abstract
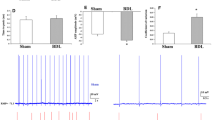
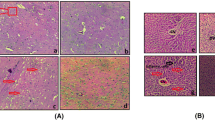
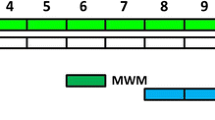
Regarding the low quality of life due to the cognitive complications in the patients with hepatic cirrhosis (HC), the goal of this study was to examine the possible neuroprotective effect of pioglitazone (PIO) on the electrophysiological alterations of hippocampus, a major area of cognition, in the experimental model of bile duct ligation (BDL). We used adult male Wistar rats in the present study to perform BDL or sham surgery. Pioglitazone was administered in BDL rats two weeks after the surgery for the next continuous four weeks. The effects of pioglitazone on BDL-induced electrophysiological alterations of the CA1 pyramidal neurons in the hippocampus were evaluated by whole-cell patch clamp recordings. Our findings demonstrated that chronic administration of PIO could not reverse the electrophysiological changes in the CA1 pyramidal neurons of the hippocampus in BDL rats but could improve the hepatic dysfunction.
Together, the results of this study suggest that PIO administration cannot counteract altered intrinsic properties of the hippocampal neurons which has been shown recently as an involved mechanism of the cognitive impairments in hepatic encephalopathy (HE).





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
All software applications used are included in this article.
References
Agarwal R (2006) Anti-inflammatory effects of short-term pioglitazone therapy in men with advanced diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiology-Renal Physiol 290:F600–F605
Aghaei I, Shabani M, Doustar N, Nazeri M, Dehpour A (2014) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activation attenuates motor and cognition impairments induced by bile duct ligation in a rat model of hepatic cirrhosis. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 120:133–139
Aghaei I, Nazeri M, Shabani M, Mossavinasab M, Mirhosseini FK, Nayebpour M, Dalili A (2015) Erythropoietin ameliorates the motor and cognitive function impairments in a rat model of hepatic cirrhosis. Metab Brain Dis 30:197–204
Aghaei I, Hajali V, Dehpour A, Haghani M, Sheibani V, Shabani M (2016) Alterations in the intrinsic electrophysiological properties of Purkinje neurons in a rat model of hepatic encephalopathy: Relative preventing effect of PPARγ agonist. Brain Res Bull 121:16–25
Aghaei I, Hajali V, Haghani M, Vaziri Z, Moosazadeh M, Shabani M (2019) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activation attenuates harmaline-induced cognitive impairments in rats. J Clin Neurosci 59:276–283
Aguilar M, Miñarro J, Felipo V (2000) Chronic moderate hyperammonemia impairs active and passive avoidance behavior and conditional discrimination learning in rats. Exp Neurol 161:704–713
Ahmadi S, Poureidi M, Rostamzadeh J (2015) Hepatic encephalopathy induces site-specific changes in gene expression of GluN1 subunit of NMDA receptor in rat brain. Metab Brain Dis 30:1035–1041
Allert N, Köller H, Siebler M (1998) Ammonia-induced depolarization of cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Brain Res 782:261–270
Arias N, Fidalgo C, Vallejo G, Arias JL (2014) Brain network function during shifts in learning strategies in portal hypertension animals. Brain Res Bull 104:52–59
Barbiero JK, Santiago RM, Lima MM, Ariza D, Morais LH, Andreatini R, Vital MA (2011) Acute but not chronic administration of pioglitazone promoted behavioral and neurochemical protective effects in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res 216:186–192
Blackburn JK, Curry DW, Thomsen AN, Roth RH, Elsworth JD (2020) Pioglitazone activates paraoxonase-2 in the brain: a novel neuroprotective mechanism. Exp Neurol 327:113234
Blackburn JK, Jamwal S, Wang W, Elsworth JD (2022) Pioglitazone transiently stimulates paraoxonase-2 expression in male nonhuman primate brain: Implications for sex-specific therapeutics in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem Int 152:105222
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361:31–39
Bonato JM, Bassani TB, Milani H, Vital MABF (2018) & R. M. W. de Oliveira Pioglitazone reduces mortality, prevents depressive-like behavior, and impacts hippocampal neurogenesis in the 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease in rats. Experimental neurology, 300, 188–200
Bordet R, Ouk T, Petrault O, Gele P, Gautier S, Laprais M, Deplanque D, Duriez P, Staels B, Fruchart J (2006) PPAR: a new pharmacological target for neuroprotection in stroke and neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem Soc Trans 34:1341–1346
Butterworth RF, Norenberg MD, Felipo V, Ferenci P, Albrecht J, Blei AT (2009) Experimental models of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN guidelines. Liver Int 29:783–788 o. E. M. o. HE]
Capano L, Dupuis A, Brian J, Mankad D, Genore L, Hastie Adams R, Smile S, Lui T, Odrobina D, Foster JA (2018) A pilot dose finding study of pioglitazone in autistic children. Mol autism 9:1–14
Cauli O, Llansola M, Erceg S, Felipo V (2006) Hypolocomotion in rats with chronic liver failure is due to increased glutamate and activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors in substantia nigra. J Hepatol 45:654–661
Cauli O, Rodrigo R, Piedrafita B, Boix J, Felipo V (2007) Inflammation and hepatic encephalopathy: ibuprofen restores learning ability in rats with portacaval shunts. Hepatology 46:514–519
Cauli O, Mansouri MT, Agusti A, Felipo V (2009) Hyperammonemia increases GABAergic tone in the cerebellum but decreases it in the rat cortex. Gastroenterology 136:1359–1367e2
Çelik T, Gören MZ, Çınar K, Gürdal H, Önder FO, Tan A, Terzioğlu B, Bozdayı AM, Bozkaya H, Uzunalimoğlu Ö (2005) Fatigue of cholestasis and the serotoninergic neurotransmitter system in the rat. Hepatology 41:731–737
Dhanda S, Sandhir R (2015) Role of dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotransmitters in behavioral alterations observed in rodent model of hepatic encephalopathy. Behav Brain Res 286:222–235
Dhanda S, Gupta S, Halder A, Sunkaria A, Sandhir R (2018) Systemic inflammation without gliosis mediates cognitive deficits through impaired BDNF expression in bile duct ligation model of hepatic encephalopathy. Brain Behav Immun 70:214–232
El Hiba O, Gamrani H, Chatoui H, Ahboucha S (2013) Loss of tyrosine hydroxylase expression within the nigro-striato-cortical pathways in the cirrhotic rat: the possible restorative effect of the neurosteroid dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate. Acta Histochem 115:637–645
El-Mlili N, Rodrigo R, Naghizadeh B, Cauli O, Felipo V (2008) Chronic hyperammonemia reduces the activity of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in cerebellum by altering its localization and increasing its phosphorylation by calcium‐calmodulin kinase II. J Neurochem 106:1440–1449
ElMlili N, Boix J, Ahabrach H, Rodrigo R, Errami M, Felipo V (2010) Chronic hyperammonemia induces tonic activation of NMDA receptors in cerebellum. J Neurochem 112:1005–1014
Erceg S, Monfort P, Hernández-Viadel M, Rodrigo R, Montoliu C, Felipo V (2005) Oral administration of sildenafil restores learning ability in rats with hyperammonemia and with portacaval shunts. Hepatology 41:299–306
Felipo V (2013) Hepatic encephalopathy: effects of liver failure on brain function. Nat Rev Neurosci 14,:851–858
Hermenegildo C, Montoliu C, Llansola M, Muñoz MD, Gaztelu JM, Miñana MD, Felipo V (1998) Chronic hyperammonemia impairs the glutamate–nitric oxide–cyclic GMP pathway in cerebellar neurons in culture and in the rat in vivo. Eur J Neurosci 10:3201–3209
Javadi-Paydar M, Ghiassy B, Ebadian S, Rahimi N, Norouzi A, Dehpour AR (2013) Nitric oxide mediates the beneficial effect of chronic naltrexone on cholestasis-induced memory impairment in male rats. Behav Pharmacol 24:195–206
Kapadia R, Yi J-H, Vemuganti R (2008) Mechanisms of anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions of PPAR-gamma agonists. Front bioscience: J virtual Libr 13:1813
Kielian T, Drew PD (2003) Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor‐γ agonists on central nervous system inflammation. J Neurosci Res 71:315–325
Kumar P, Kaundal RK, More S, Sharma SS (2009) Beneficial effects of pioglitazone on cognitive impairment in MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res 197:398–403
Leke R, Oliveira DL, Forgiarini LF, Escobar TD, Hammes TO, Meyer FS, Keiding S, Silveira TR, Schousboe A (2013) Impairment of short term memory in rats with hepatic encephalopathy due to bile duct ligation. Metab Brain Dis 28:187–192
Lizardi-Cervera J, Almeda P, Guevara L, Uribe M (2003) Hepatic encephalopathy: a review. Ann Hepatol 2:122–130
Llansola M, Montoliu C, Cauli O, Hernández-Rabaza V, Agustí A, Cabrera-Pastor A, Giménez-Garzó C, González-Usano A, Felipo V (2013) Chronic hyperammonemia, glutamatergic neurotransmission and neurological alterations. Metab Brain Dis 28:151–154
Lynch G, Kessler M, Arai A, Larson J (1990) Chapter The nature and causes of hippocampal long-term potentiation. Prog Brain Res 83:233–250
Magen I, Avraham Y, Ackerman Z, Vorobiev L, Mechoulam R, Berry EM (2009) Cannabidiol ameliorates cognitive and motor impairments in mice with bile duct ligation. J Hepatol 51:528–534
McKay B, Turner R (2004) Kv3 K + channels enable burst output in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells. Eur J Neurosci 20:729–739
Méndez M, Méndez-López M, López L, Aller M, Árias J, Cimadevilla JM, Árias JL (2008) Spatial memory alterations in three models of hepatic encephalopathy. Behav Brain Res 188:32–40
Monfort P, Corbalán R, Martinez L, López-Talavera J-C, Córdoba J, Felipo V (2001) Altered content and modulation of soluble guanylate cyclase in the cerebellum of rats with portacaval anastomosis. Neuroscience 104:1119–1125
Monfort P, Muñoz Ma-D, Felipo V (2004) Hyperammonemia impairs long-term potentiation in hippocampus by altering the modulation of cGMP-degrading phosphodiesterase by protein kinase G. Neurobiol Dis 15:1–10
Monfort P, Muñoz MD, Felipo V (2005) Chronic hyperammonemia in vivo impairs long-term potentiation in hippocampus by altering activation of cyclic GMP‐dependent‐protein kinase and of phosphodiesterase 5. J Neurochem 94:934–942
Monfort P, Erceg S, Piedrafita B, Llansola M, Felipo V (2007) Chronic liver failure in rats impairs glutamatergic synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in hippocampus and learning ability. Eur J Neurosci 25:2103–2111
Muñoz M-D, Monfort P, Gaztelu J-M, Felipo V (2000) Hyperammonemia impairs NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation in the CA1 of rat hippocampus in vitro. Neurochem Res 25:437–441
Napolitano M, Costa L, Palermo R, Giovenco A, Vacca A, Gulino A (2011) Protective effect of pioglitazone, a PPARγ ligand, in a 3 nitropropionic acid model of Huntington’s disease. Brain Res Bull 85:231–237
Park S-W, Yi J-H, Miranpuri G, Satriotomo I, Bowen K, Resnick DK, Vemuganti R (2007) Thiazolidinedione class of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonists prevents neuronal damage, motor dysfunction, myelin loss, neuropathic pain, and inflammation after spinal cord injury in adult rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:1002–1012
Patel SP, Cox DH, Gollihue JL, Bailey WM, Geldenhuys WJ, Gensel JC, Sullivan PG, Rabchevsky AG (2017) Pioglitazone treatment following spinal cord injury maintains acute mitochondrial integrity and increases chronic tissue sparing and functional recovery. Exp Neurol 293:74–82
Pflugrad H, Bronzlik P, Raab P, Tryc AB, Goldbecker A, Barg-Hock H, Strassburg CP, Ding XQ, Lanfermann H, Weissenborn K (2015) Cerebral white matter lesions in patients with cirrhosis–causative for hepatic encephalopathy or bystanders? Liver Int 35:1816–1823
Raabe W (1990) Effects of NH4 + on reflexes in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol 64:565–574
Razavinasab M, Moazzami K, Shabani M (2016) Maternal mobile phone exposure alters intrinsic electrophysiological properties of CA1 pyramidal neurons in rat offspring. Toxicol Ind Health 32:968–979
Ribeiro NQ, Santos APN, Emídio ECP, Costa MC, Freitas GJC, Carmo PHF, Silva MF, de Brito CB, de Souza DG (2019) Pioglitazone as an adjuvant of amphotericin B for the treatment of cryptococcosis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 54:301–308 & T. A. Paixão
Rodrigo R, Erceg S, Felipo V (2005) Neurons exposed to ammonia reproduce the differential alteration in nitric oxide modulation of guanylate cyclase in the cerebellum and cortex of patients with liver cirrhosis. Neurobiol Dis 19:150–161
Rodrigo R, Cauli O, Gomez–Pinedo U, Agusti A, Hernandez–Rabaza V, Garcia–Verdugo JM, Felipo V (2010) Hyperammonemia induces neuroinflammation that contributes to cognitive impairment in rats with hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 139:675–684
Rose CF, Amodio P, Bajaj JS, Dhiman RK, Montagnese S, Taylor-Robinson SD, Vilstrup H, Jalan R (2020) Hepatic encephalopathy: Novel insights into classification, pathophysiology and therapy. J Hepatol 73:1526–1547
Sauerbeck A, Gao J, Readnower R, Liu M, Pauly JR, Bing G, Sullivan PG (2011) Pioglitazone attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction, cognitive impairment, cortical tissue loss, and inflammation following traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 227:128–135
Schuppan D, Afdhal NH (2008) Liver cirrhosis. The Lancet 371:838–851
Serghides L, McDonald CR, Lu Z, Friedel M, Cui C, Ho KT, Mount HT, Sled JG, Kain KC (2014) PPARγ agonists improve survival and neurocognitive outcomes in experimental cerebral malaria and induce neuroprotective pathways in human malaria. PLoS Pathog 10:e1003980
Shafaroodi H, Moezi L, Ghorbani H, Zaeri M, Hassanpour S, Hassanipour M, Dehpour AR (2012) Sub-chronic treatment with pioglitazone exerts anti-convulsant effects in pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures of mice: The role of nitric oxide. Brain Res Bull 87:544–550
Sharma R, Kaundal RK, Sharma SS (2009) Amelioration of pulmonary dysfunction and neutrophilic inflammation by PPARγ agonist in LPS-exposed guinea pigs. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 22:183–189
Swanson CR, Joers V, Bondarenko V, Brunner K, Simmons HA, Ziegler TE, Kemnitz JW, Johnson JA, Emborg ME (2011) The PPAR-γ agonist pioglitazone modulates inflammation and induces neuroprotection in parkinsonian monkeys. J Neuroinflamm 8:1–14
Szerb JC, Butterworth RF (1992) Effect of ammonium ions on synaptic transmission in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 39:135–153
Tahamtan M, Aghaei I, Pooladvand V, Sheibani V, Khaksari M, Shabani M (2017) Characterization of the CA1 pyramidal neurons in rat model of hepatic cirrhosis: insights into their electrophysiological properties. Metab Brain Dis 32:881–889
Ulusoy GK, Celik T, Kayir H, Gürsoy M, Isik AT, Uzbay TI (2011) Effects of pioglitazone and retinoic acid in a rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res Bull 85:380–384
Weissenborn K, Bokemeyer M, Krause J, Ennen J, Ahl B (2005) Neurological and neuropsychiatric syndromes associated with liver disease. Aids 19:S93–S98
**ng B, Liu M, Bing G (2007) Neuroprotection with pioglitazone against LPS insult on dopaminergic neurons may be associated with its inhibition of NF-κB and JNK activation and suppression of COX-2 activity. J Neuroimmunol 192:89–98
Zakaria A, Rady M, Mahran L, Abou-Aisha K (2019) Pioglitazone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress, dopaminergic neuronal loss and neurobehavioral impairment by activating Nrf2/ARE/HO-1. Neurochem Res 44:2856–2868
Zhao Y, Patzer A, Gohlke P, Herdegen T, Culman J (2005) The intracerebral application of the PPARγ-ligand pioglitazone confers neuroprotection against focal ischaemia in the rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 22:278–282
Acknowledgements
Funding for this study was provided by Kerman University of Medical Sciences and Jiroft University of Medical Sciences as a grant for the PhD thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT, IA and MSH have conceived and designed the concept and road map of the study, searched the literature, designed the concept map and figures, and drafted the manuscript. VP and AN have critically reviewed the manuscript for its content, originality, usage of English language, and accuracy of interpreted data. MR designed the study, helped in manuscript preparation, and critically reviewed the manuscript. MR is the archival author and attests to the integrity of the original data and the analysis reported in this manuscript. All authors have made substantive contribution and attest to approving the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest and declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies were in accordance with the ethical standards of the ethical committee of Kerman University of Medical Sciences (Ethical approval number: IR.KMU.REC.1395.792, Reg. No. 95000573).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tahamtan, M., Aghaei, I., Shabani, M. et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ doesn’t modify altered electrophysiological properties of the CA1 pyramidal neurons in a rat model of hepatic cirrhosis. Metab Brain Dis 37, 2687–2697 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01057-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01057-7