Abstract
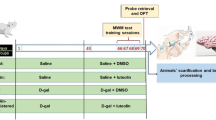
Age-related inflammation is the predominant factor for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In the present study, we examined memory performance and neuroinflammation in D-galactose (D-gal)-induced sub-acute aging model of rats. Our results demonstrated that chronic administration of D-gal (120 mg/kg) produced cognitive impairment as determined by Morris water maze (MWM) test and step-down passive avoidance test. D-gal also activated nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) p65/RelA by down-regulating the expression level of sirtuins 1 (SIRT1) in the hippocampus. Treatment with Salidroside (Sal, 20, 40 mg/kg) for 28 days ameliorated D-gal-induced memory deficits and inflammatory mediators including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β). Moreover, D-gal-induced activation of NF-κB signaling pathway in the brain was also inhibited by Sal via up-regulating SIRT1. These results suggest that D-gal-triggered memory impairment and inflammatory response may be associated with SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway, whereas treatment with Sal could positively affect these changes in hippocampus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albani D, Polito L, Batelli S, De Mauro S, Fracasso C, Martelli G, Colombo L, Manzoni C, Salmona M, Caccia S, Negro A, Forloni G (2009) The SIRT1 activator resveratrol protects SK-N-BE cells from oxidative stress and against toxicity caused by alpha-synuclein or amyloid-beta (1–42) peptide. J Neurochem 110:1445–1456
Cannizzo ES, Clement CC, Sahu R, Follo C, Santambrogio L (2011) Oxidative stress, inflammaging and immunosenescence. J Proteomics 74:2313–2323
Cao L, Liu C, Wang F, Wang H (2013) SIRT1 negatively regulates amyloid-beta-induced inflammation via the NF-κB pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res 46:659–669
Chen LF, Greene WC (2003) Regulation of distinct biological activities of the NF-kappaB transcription factor complex by acetylation. J Mol Med (Berl) 81:549–557
Chen J, Zhou Y, Mueller-Steiner S, Chen LF, Kwon H, Yi S, Mucke L, Gan L (2005) SIRT1 protects against microglia-dependent amyloid-beta toxicity through inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling. J Biol Chem 280:40364–40374
Chen X, Zhang Q, Cheng Q, Ding F (2009) Protective effect of salidroside against H2O2-induced cell apoptosis in primary culture of rat hippocampal neurons. Mol Cell Biochem 332:85–93
Chen T, Gao J, **ang P, Chen Y, Ji J, **e P, Wu H, **ao W, Wei Y, Wang S, Lan L, Ji H, Yan T (2015a) Protective effect of platycodin D on liver injury in alloxan-induced diabetic mice via regulation of Treg/Th17 balance. Int Immunopharmacol 26:338–348
Chen T, Ma Z, Zhu L, Jiang W, Wei T, Zhou R, Luo F, Zhang K, Fu Q, Ma C, Yan T (2015) Suppressing receptor-interacting protein 140: a new sight for salidroside to treat cerebral ischemia. Mol Neurobiol
Cho SH, Chen JA, Sayed F, Ward ME, Gao F, Nguyen TA, Krabbe G, Sohn PD, Lo I, Minami S, Devidze N, Zhou Y, Coppola G, Gan L (2015) SIRT1 deficiency in microglia contributes to cognitive decline in aging and neurodegeneration via epigenetic regulation of IL-1β. J Neurosci 35:807–818
Gao J, He H, Jiang W, Chang X, Zhu L, Luo F, Zhou R, Ma C, Yan T (2015) Salidroside ameliorates cognitive impairment in a d-galactose-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res 293:27–33
Gill R, Tsung A, Billiar T (2010) Linking oxidative stress to inflammation: toll-like receptors. Free Radic Biol Med 48:1121–1132
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Latz E (2014) Innate immune activation in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Immunol 14:463–477
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J (2015) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 14:388–405
Hernández-Jiménez M, Hurtado O, Cuartero MI, Ballesteros I, Moraga A, Pradillo JM, McBurney MW, Lizasoain I, Moro MA (2013) Silent information regulator 1 protects the brain against cerebral ischemic damage. Stroke 44:2333–2337
Karran E, Mercken M, De Strooper B (2011) The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: an appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:698–712
Liu Z, Li X, Simoneau AR, Jafari M, Zi X (2012) Rhodiola rosea extracts and salidroside decrease the growth of bladder cancer cell lines via inhibition of the mTOR pathway and induction of autophagy. Mol Carcinog 51:257–267
Lu T, Aron L, Zullo J, Pan Y, Kim H, Chen Y, Yang TH, Kim HM, Drake D, Liu XS, Bennett DA, Colaiácovo MP, Yankner BA (2014) REST and stress resistance in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 507:448–454
Lynch MA, Mills KH (2012) Immunology meets neuroscience--opportunities for immune intervention in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Behav Immun 26:1–10
Marchesi VT (2011) Alzheimer’s dementia begins as a disease of small blood vessels, damaged by oxidative-induced inflammation and dysregulated amyloid metabolism: implications for early detection and therapy. FASEB J 25:5–13
Michan S, Sinclair D (2007) Sirtuins in mammals: insights into their biological function. Biochem J 404:1–13
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Ng F, Wijaya L, Tang BL (2015) SIRT1 in the brain-connections with aging-associated disorders and lifespan. Front Cell Neurosci 9:64
Risitano R, Currò M, Cirmi S, Ferlazzo N, Campiglia P, Caccamo D, Ientile R, Navarra M (2014) Flavonoid fraction of Bergamot juice reduces LPS-induced inflammatory response through SIRT1-mediated NF-κB inhibition in THP-1 monocytes. PLoS ONE 9:e107431
Ruan Q, Hu X, Ao H, Ma H, Gao Z, Liu F, Kong D, Bao Z, Yu Z (2014) The neurovascular protective effects of huperzine A on D-galactose-induced inflammatory damage in the rat hippocampus. Gerontology 60:424–439
Sun Q, Jia N, Wang W, ** H, Xu J, Hu H (2014) Activation of SIRT1 by curcumin blocks the neurotoxicity of amyloid-β25-35 in rat cortical neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 448:89–94
Tan X, Gu J, Zhao B, Wang S, Yuan J, Wang C, Chen J, Liu J, Feng L, Jia X (2015) Ginseng improves cognitive deficit via the RAGE/NF-κB pathway in advanced glycation end product-induced rats. J Ginseng Res 39:116–124
Thomas J, Thomas CJ, Radcliffe J, Itsiopoulos C (2015) Omega-3 fatty acids in early prevention of inflammatory neurodegenerative disease: a focus on Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Res Int 2015:172801
von Bernhardi R, Eugenín-von Bernhardi L, Eugenín J (2015) Microglial cell dysregulation in brain aging and neurodegeneration. Front Aging Neurosci 7:124
Wang T, Di G, Yang L, Dun Y, Sun Z, Wan J, Peng B, Liu C, **ong G, Zhang C, Yuan D (2015) Saponins from Panax japonicus attenuate D-galactose-induced cognitive impairment through its anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic effects in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 67:1284–1296
Wu H, Wang H, Zhang W, Wei X, Zhao J, Yan P, Liu C (2015) rhEPO affects apoptosis in hippocampus of aging rats by upregulating SIRT1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:6870–6880
Wyss-Coray T, Rogers J (2012) Inflammation in Alzheimer disease-a brief review of the basic science and clinical literature. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a006346
**an YF, Lin ZX, Zhao M, Mao QQ, Ip SP, Che CT (2011) Uncaria rhynchophylla ameliorates cognitive deficits induced by D-galactose in mice. Planta Med 77:1977–1983
Yang H, Zhang W, Pan H, Feldser HG, Lainez E, Miller C, Leung S, Zhong Z, Zhao H, Sweitzer S, Considine T, Riera T, Suri V, White B, Ellis JL, Vlasuk GP, Loh C (2012) SIRT1 activators suppress inflammatory responses through promotion of p65 deacetylation and inhibition of NF-κB activity. PLoS ONE 7:e46364
Yeung F, Hoberg JE, Ramsey CS, Keller MD, Jones DR, Frye RA, Mayo MW (2004) Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J 23:2369–2380
Yoo DY, Kim W, Kim IH, Nam SM, Chung JY, Choi JH, Yoon YS, Won MH, Hwang IK (2012) Combination effects of sodium butyrate and pyridoxine treatment on cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the dentate gyrus of D-galactose-induced aging model mice. Neurochem Res 37:223–231
Zhang XL, Chen ML, Zhou SL (2014) Fentanyl increases colorectal carcinoma cell apoptosis by inhibition of NF-κB in a Sirt1-dependent manner. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:10015–10020
Zhu Y, Shi YP, Wu D, Ji YJ, Wang X, Chen HL, Wu SS, Huang DJ, Jiang W (2011) Salidroside protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in cardiac H9c2 cells via PI3K-Akt dependent pathway. DNA Cell Biol 30:809–819
Zhu J, Mu X, Zeng J, Xu C, Liu J, Zhang M, Li C, Chen J, Li T, Wang Y (2014) Ginsenoside Rg1 prevents cognitive impairment and hippocampus senescence in a rat model of D-galactose-induced aging. PLoS ONE 9:e101291
Zhu L, Wang J, Wei T, Gao J, He H, Chang X, Yan T (2015) Effects of Naringenin on inflammation in complete freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis by regulating Bax/Bcl-2 balance. Inflammation 38:245–251
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National twelve five major drug discovery project (2011ZX09102-002-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Zhou, R., You, X. et al. Salidroside suppresses inflammation in a D-galactose-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease via SIRT1/NF-κB pathway. Metab Brain Dis 31, 771–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9813-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9813-2