Abstract
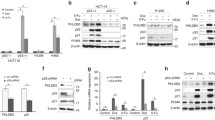
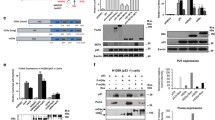
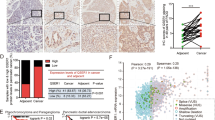
Pleckstrin homeolike domain, family A, member 1 (PHLDA1) is a multifunctional protein that plays diverse roles in A variety of biological processes, including cell death, and hence its altered expression has been found in different types of cancer. Although studies have shown a regulatory relationship between p53 and PHLDA1, the molecular mechanism is still unclear. Especially, the role of PHLDA1 in the process of apoptosis is still controversial. In this study, we found that the expression of PHLDA1 in human cervical cancer cell lines was correlated with the up-expression of p53 after treatment with apoptosis-inducing factors. Subsequently, the binding site and the binding effect of p53 on the promoter region of PHLDA1 were verified by our bioinformatics data analysis and luciferase reporter assay. Indeed, we used CRISPR-Cas9 to knockout the p53 gene in HeLa cells and further confirmed that p53 can bind to the promoter region of PHLDA1 gene, and then directly regulate the expression of PHLDA1 by recruiting P300 and CBP to change the acetylation and methylation levels in the promoter region. Finally, a series of gain–of–function experiments further confirmed that p53 re-expression in HeLap53-/- cell can up-regulate the reduction of PHLDA1 caused by p53 knockout, and affect cell apoptosis and proliferation. Our study is the first to explore the regulatory mechanism of p53 on PHLDA1 by using the p53 gene knockout cell model, which further proves that PHLDA1 is a target-gene in p53-mediated apoptosis, and reveals the important role of PHLDA1 in cell fate determination.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Abbreviations
- PHLDA1:
-
Pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 1
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- UV:
-
Ultra violet irradiation
- 5-FU:
-
5-Fluorouracil
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay
- OE:
-
Over expression
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
References
Park CG, Lee SY, Kandala G, Choi Y (1996) A novel gene product that couples TCR signaling to Fas(CD95) expression in activation-induced cell death. Immunity 4:583–591
Gomes I, **ong W, Miki T, Rosner MR (1999) A proline- and glutamine-rich protein promotes apoptosis in neuronal cells. J Neurochem 73:612–622
Kuske MD, Johnson JP (2000) Assignment of the human PHLDA1 gene to chromosome 12q15 by radiation hybrid map**. Cytogenet Cell Genet 89:1
Chen Y, Takikawa M, Tsutsumi S, Yamaguchi Y, Okabe A, Shimada M, Kawase T, Sada A, Ezawa I, Takano Y, Nagata K, Suzuki Y, Semba K, Aburatani H, Ohki R (2018) PHLDA1, another PHLDA family protein that inhibits Akt. Cancer Sci 109:3532–3542
Nagai MA, Fregnani JH, Netto MM, Brentani MM, Soares FA (2007) Down-regulation of PHLDA1 gene expression is associated with breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 106:49–56
Neef R, Kuske MA, Prols E, Johnson JP (2002) Identification of the human PHLDA1/TDAG51 gene: down-regulation in metastatic melanoma contributes to apoptosis resistance and growth deregulation. Cancer Res 62:5920–5929
Nagai MA (2016) Pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A, member 1 (PHLDA1) and cancer. Biomed Rep 4:275–281
Kastrati I, Canestrari E, Frasor J (2015) PHLDA1 expression is controlled by an estrogen receptor-NFkappaB-miR-181 regulatory loop and is essential for formation of ER+ mammospheres. Oncogene 34:2309–2316
Murohashi M, Hinohara K, Kuroda M, Isagawa T, Tsuji S, Kobayashi S, Umezawa K, Tojo A, Aburatani H, Gotoh N (2010) Gene set enrichment analysis provides insight into novel signalling pathways in breast cancer stem cells. Br J Cancer 102:206–212
Joo JH, Liao G, Collins JB, Grissom SF, Jetten AM (2007) Farnesol-induced apoptosis in human lung carcinoma cells is coupled to the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Cancer Res 67:7929–7936
Xu J, Bi G, Luo Q, Liu Y, Liu T, Li L, Zeng Q, Wang Q, Wang Y, Yu J, Yi P (2021) PHLDA1 modulates the endoplasmic reticulum stress response and is required for resistance to oxidative stress-induced cell death in human ovarian cancer cells. J Cancer 12:5486–5493
Hossain GS, van Thienen JV, Werstuck GH, Zhou J, Sood SK, Dickhout JG, de Koning AB, Tang D, Wu D, Falk E, Poddar R, Jacobsen DW, Zhang K, Kaufman RJ, Austin RC (2003) TDAG51 is induced by homocysteine, promotes detachment-mediated programmed cell death, and contributes to the cevelopment of atherosclerosis in hyperhomocysteinemia. J Biol Chem 278:30317–30327
Coutinho-Camillo CM, Lourenco SV, Nonogaki S, Vartanian JG, Nagai MA, Kowalski LP, Soares FA (2013) Expression of PAR-4 and PHLDA1 is prognostic for overall and disease-free survival in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Virchows Arch 463:31–39
Zhao P, Lu Y, Liu L (2015) Correlation of decreased expression of PHLDA1 protein with malignant phenotype of gastric adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:5230–5235
Zhao PO, Li X, Lu Y, Liu L (2015) Downregulated expression of PHLDA1 protein is associated with a malignant phenotype of cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Lett 10:895–900
Johnson EO, Chang KH, de Pablo Y, Ghosh S, Mehta R, Badve S, Shah K (2011) PHLDA1 is a crucial negative regulator and effector of Aurora A kinase in breast cancer. J Cell Sci 124:2711–2722
Li G, Wang X, Hibshoosh H, ** C, Halmos B (2014) Modulation of ErbB2 blockade in ErbB2-positive cancers: the role of ErbB2 Mutations and PHLDA1. PLoS ONE 9:e106349
Fearon AE, Carter EP, Clayton NS, Wilkes EH, Baker AM, Kapitonova E, Bakhouche BA, Tanner Y, Wang J, Gadaleta E, Chelala C, Moore KM, Marshall JF, Chupin J, Schmid P, Jones JL, Lockley M, Cutillas PR, Grose RP (2018) PHLDA1 mediates drug resistance in receptor tyrosine kinase-driven cancer. Cell Rep 22:2469–2481
Ma M, Hua S, Min X, Wang L, Li J, Wu P, Liang H, Zhang B, Chen X, **ang S (2022) p53 positively regulates the proliferation of hepatic progenitor cells promoted by laminin-521. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:290–307
Zhang N, Jiang T, Wang Y, Wang S, Hu L, Bu Y (2020) BTG4 is a novel p53 target gene that inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis. Genes (Basel) 11:217–230
El-Deiry WS, Kern SE, Pietenpol JA, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1992) Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet 1:45–49
Wang J, Wang F, Zhu J, Song M, An J, Li W (2018) Transcriptome profiling reveals PHLDA1 as a novel molecular marker for ischemic cardiomyopathy. J Mol Neurosci 65:102–109
Zanconato F, Forcato M, Battilana G, Azzolin L, Quaranta E, Bodega B, Rosato A, Bicciato S, Cordenonsi M, Piccol S (2015) Genome-wide association between YAP/TAZ/TEAD and AP-1 at enhancers drives oncogenic growth. Nat Cell Biol 17:1218–1227
Liang B, Song X, Liu G, Li R, **e J, **ao L, Du M, Zhang Q, Xu X, Gan X, Huang D (2007) Involvement of TR3/Nur77 translocation to the endoplasmic reticulum in ER stress-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 313:2833–2844
Watts GS, Oshiro MM, Junk DJ, Wozniak RJ, Watterson S, Domann FE, Futscher BW (2004) The acetyltransferase p300/CBP-associated factor is a p53 target gene in breast tumor cells. Neoplasia 6:187–194
Grossman SR (2001) p300/CBP/p53 interaction and regulation of the p53 response. Eur J Biochem 268:2773–2778
Hogg SJ, Motorna O, Cluse LA, Johanson TM, Coughlan HD, Raviram R, Myers RM, Costacurta M, Todorovski I, Pijpers L, Bjelosevic S, Williams T, Huskins SN, Kearney CJ, Devlin JR, Fan Z, Jabbari JS, Martin BP, Fareh M, Kelly MJ, Dupere-Richer D, Sandow JJ, Feran B, Knight D, Khong T, Spencer A, Harrison SJ, Gregory G, Wickramasinghe VO, Webb AI, Taberlay PC, Bromberg KD, Lai A, Papenfuss AT, Smyth GK, Allan RS, Licht JD, Landau DA, Abdel-Wahab O, Shortt J, Vervoort SJ, Johnstone RW (2021) Targeting histone acetylation dynamics and oncogenic transcription by catalytic P300/CBP inhibition. Mol Cell 81(2183–2200):e13
Hsu E, Zemke NR, Berk AJ (2021) Promoter-specific changes in initiation, elongation, and homeostasis of histone H3 acetylation during CBP/p300 inhibition. Elife 10:e63512-63533
Durbas M, Horwacik I, Boratyn E, Rokita H (2016) Downregulation of the PHLDA1 gene in IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells increases levels of Aurora A, TRKB and affects proteins involved in apoptosis and autophagy pathways. Int J Oncol 49:823–837
Rho J, Gong S, Kim N, Choi Y (2001) TDAG51 is not essential for Fas/CD95 regulation and apoptosis in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 21:8365–8370
Durbas M, Pabisz P, Wawak K, Wisniewska A, Boratyn E, Nowak I, Horwacik I, Woznicka O, Rokita H (2018) GD2 ganglioside-binding antibody 14G2a and specific aurora A kinase inhibitor MK-5108 induce autophagy in IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells. Apoptosis 23:492–511
Murata T, Sato T, Kamoda T, Moriyama H, Kumazawa Y, Hanada N (2014) Differential susceptibility to hydrogen sulfide-induced apoptosis between PHLDA1-overexpressing oral cancer cell lines and oral keratinocytes: role of PHLDA1 as an apoptosis suppressor. Exp Cell Res 320:247–257
Aubrey BJ, Kelly GL, Janic A, Herold MJ, Strasser A (2018) How does p53 induce apoptosis and how does this relate to p53-mediated tumour suppression? Cell Death Differ 25:104–113
Funding
This work was supported by the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (2020A1515010174), the Distinctive Innovation Grant of Guangdong Department of Education (2020KTSCX035), and Provincial Natural Science Foundation cultivation special project (210719166884337, 210719166884340).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XS, DH and BL conceived the research and designed the experiments. LZ, WY, XL, JM, KQ, RL, ML, LX and TS performed the experiments. BL wrote the manuscript. BL, XS and DH analyzed the data. All authors revised the manuscript and approved its final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Zhou, L., Yang, W. et al. PHLDA1 is a P53 target gene involved in P53-mediated cell apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 479, 653–664 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04752-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04752-w