Abstract
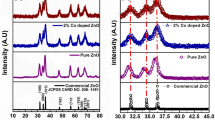
Cobalt-doped zinc sulfide quantum dots with different cobalt concentrations were prepared by the solution route. Structural, optical, morphological, and magnetic responses of the prepared quantum dots were analyzed. X-ray diffraction study confirmed that cubic (zinc blende) structure is the dominant structure of synthesized samples. Crystallite size and lattice constant were found to decrease with cobalt dopant. Transmission electron microscope analysis shows that the mean size of the particles lies in the range of 7–10 nm. The absorption edge of cobalt-doped zinc sulfide nanoparticles is shifted to lower wavelength as compared to that of bulk zinc sulfide which confirmed the quantum confinement effect. The bandgap variation was observed with do**, and it varied from 4.3 to 5.6 eV. The emission spectrum reveals that the cobalt dopant suppresses the ultraviolet emission and enhances the visible emission. Fourier-transform infrared spectrum confirmed the formation of zinc sulfide and the substitution of cobalt ion. Magnetization versus magnetic field result demonstrates that the zinc sulfide and cobalt-doped zinc sulfides are superparamagnetic. Electron spin resonance spectra also confirmed the superparamagnetic nature of zinc sulfide and cobalt-doped zinc sulfide samples. Micro-Raman study also confirmed the incorporation of cobalt in the lattice and the size of the order of the exciton Bohr radius for ZnS.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Poornaprakash, B., Chalapathi, U., Poojitha, P.T., Prabhakar Vattikuti, S.V., Park, S.H.: Co-doped ZnS quantum dots: structural, optical, photoluminescence, magnetic, and photocatalytic properties. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 539–544 (2020)
Pham, M.T., Ca, N.X., Loan, P.N., Tran, N., Huy, B.T., Dang, N.T., Phan, T.L.: Electronic structure and ferromagnetism in zinc blende Zn1−xCoxS nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 32, 1761–1768 (2019)
Manojkumar, K., Prasad, B., Kranthi, Y., Varma, J.S.K., Vinay, K., Amaranatha Reddy, D., Subramanyam, K.: Benchmark analysis on magnetic and photoluminescence properties of selective metal ions doped ZnS nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 32, 2489–2500 (2019)
Bhargava, R.N., Gallagher, D.: Optical properties of manganese-doped nanocrystals of ZnS. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 416 (1994)
Lin, K.B., Su, Y.H.: Photoluminescence of Cu:ZnS, Ag:ZnS, and Au:ZnS nanoparticles applied in bio-LED. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 113, 351–359 (2013)
Sapra, S., Prakash, A., Ghangrekar, A., Periasamy, N.: Emission properties of manganese-doped ZnS nanocrystals. J. Phy. Chem. B. 109, 1663–1668 (2005)
Corrado, C., Cooper, J.K., Zhang, J.Z.: Cu-doped ZnS nanocrystals: synthesis, structure, and optical properties. Sci. Adv. Mater. 4, 254–265 (2012)
Rivera-Medina, M.J., Hernandez-Torres, J., Boldu-Olaizola, J.L., Barreto-Renteria, J., Hernandez-Alcantara, J.M., Jancik, V., Alonso-Huitron, J.C.: Synthesis of europium-doped ZnS nano-crystalline thin films with strong blue photoluminescence. RSC Adv. 6, 07613–107621 (2016)
Yamamoto, S.: Photoluminescence quenching in cobalt doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 094310 (2012)
Akhtar, M.S., Alghamdi, Y.G., Malik, M.A., Arif Khalil, R.M., Riaz, S., Naseem, S.: Structural, optical, magnetic and half-metallic studies of cobalt doped ZnS thin films deposited via chemical bath deposition. J. Mater. Chem. C. 3, 6755–6733 (2015)
Salem, J.K., Hammad, T.M., Kuhn, S., Draaz, M.A., Hejazy, N.K., Hempelmann, R.: Structural and optical properties of Co-doped ZnS nanoparticles synthesized by a cap** agent. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 2177–2182 (2014)
Bi, C., Pan, L., Xu, M., Yin, J., Qin, L., Liu, J., Zhu, H., **ao, J.Q.: Synthesis and characterization of Co-doped wurtzite ZnS nanocrystals. Mater. Chem. Phys. 116, 363–367 (2009)
Ashok Kumar, R., Geetha, K., Prabukanthan, P.: Synthesis of Co2+ ions doped ZnS nanoparticles by chemical precipitation method and their characterization. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 8, 286–294 (2015)
Poornaprakash, B., Amaranatha Reddy, D., Murali, G., Madhusudhana Rao, N., Vijayalakshmi, R.P., Reddy, B.K.: Composition dependent room temperature ferromagnetism and PL intensity of cobalt doped ZnS nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 577, 79–85 (2013)
Ibrahim, R.M., Markom, M., Abd Razak, K.F.: Optical properties of CO2+-doped ZnS nanoparticles synthesized using reverse micelle method. J. Tech. 79, 15 (2017)
Sharma, R.K., Kumar, A., Gautam, S., Goyal, N.: Synthesis and characterization of cobalt doped ZnS nanoparticles. Int. Res. Adv. 3, 26 (2016)
Chen, K., Hou, Q., Dong, X., Zhang, H., Li, Y., Liu, H., Huang, Y., Li, Q.: Structural transformation in Co-doped ZnS nanoparticles. J. Phys. 430, 012077 (2013)
Vijay Anand, K., Vinitha, G., Gautam, S., Chae, K.H., Mohan, R., Asokan, K., Ravindran, T.R., Jayavel, R.: Enhancement of third-order nonlinear optical properties of HMTA stabilized pure and doped ZnS nanoparticles and their electronic structures. J. Nonlin. Opt. Phys & Mater. 27, 1850016 (2018)
Manivannan, N., Chandarshekar, B., SenthilKumaran, C.K.: Punicagranatum flower extract mediated synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticle and evolution of its antibacterial activity. Inter. J. Appl. Pure Sci. Agri. 04, 7–12 (2018)
**, Z., Fukumura, T., Kawasaki, M., Ando, K., Saito, H., Sekiguchi, T., Yoo, Y.Z., Murakami, M., Matsumoto, Y., Hasegawa, T., Koinuma, H.: High throughput fabrication of transition-metal-doped epitaxial ZnO thin films: a series of oxide-diluted magnetic semiconductors and their properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 3824–3826 (2001)
Liu, L., Yang, L., Pu, Y., **ao, D., Zhu, J.: Optical properties of water-soluble Co2+:ZnS semiconductor nanocrystals synthesized by a hydrothermal process. Mater. Lett. 66, 121–124 (2012)
Sarkar, R., Tiwary, C.S., Kumbhakar, P., Mitra, A.K.: Yellow-orange light emission from Mn2+ doped ZnS nanoparticles. Physica B: Conden. Mater. 404, 3855–3858 (2009)
Zhang, H., Chen, Q., Zhang, H., Rui, W., Ding, Q., Cao, Y., Zhong, W., Shen, K., Du, J., **ang, D., Xu, Q.: Interstitial H+-mediated ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnS. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28, 1389–1393 (2015)
Shannon, R.D.: Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta.Cryst. A. 32, 751–767 (1976)
Benyahia, K., Benhaya, A., Aida, M.S.: ZnS thin films deposition by thermal evaporation for photovoltaic applications. J. Semicond. 36, 103001 (2015)
Kuhs, J., Dobbelaere, T.: Plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition of zinc sulfide thin films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 35, 01B111 (2017)
Senados, K.M., Vequizo, R.M.: Effects of thermal annealing on the diode properties and space charge limited conduction of the physical vapor-deposited n-ZnS/p-Si (100) heterojunctions. Mater. Today. 5, 15174–15179 (2018)
Shanmugam, N., Cholan, S., Kannadasan, N., Sathishkumar, K., Viruthagiri, G.: Effect of annealing on the ZnS nanocrystals prepared by chemical precipitation method. J. Nanomater. 7, 351798 (2013)
Reddy, D.A., Murali, G., Poornaprakash, B., Vijayalakshmi, R.P., Reddy, B.K.: Effect of annealing temperature on optical and magnetic properties of Cr doped ZnS nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 152, 596–602 (2012)
Wahab, R., Ansari, S.G., Kim, Y.S., Dhage, M.S., Seo, H.K., Song, M., Shin, H.S.: Effect of annealing on the conversion of ZnS to ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by the sol-gel method using zinc acetate and thiourea. Met. Mater. Int. 15, 453 (2009)
Patel, P.C., Ghosh, S., Srivastava, P.C.: Structural, magnetic and optical properties of ZnO nanostructures converted from ZnS nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 81, 85–92 (2016)
Mahmood, K., Asghar, M., Amin, N., Ali, A.: Phase transformation from cubic ZnS to hexagonal ZnO by thermal annealing. J. Semicond. 36, 033001 (2015)
Akhtar, M.S., Malik, M.A., Riaz, S., Naseem, S., Brien, P.O.: Optimizing conditions for the growth of nanocrystalline ZnS thin films from acidic chemical baths. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 30, 292–297 (2015)
Williamson, G.K., Hall, W.H.: X-ray line broadening from filed aluminum and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1, 22–31 (1953)
Pathak, C.S., Mandal, M.K., Agarwala, V.: Optical properties of undoped and cobalt doped ZnS nanophosphor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 467–471 (2013)
Tauc, J., Menth, A.: States in the gap. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 8, 569–585 (1972)
Joshi, G.P., Saxena, N.S., Sharma, T.P., Dixit, V., Mishra, S.C.K.: Bandgap determination of chemically doped polyaniline materials from reflectance measurements. Ind. J. Pure. Appl. Phys. 41, 462–446 (2003)
Chattopadhyay, M., Kumbhakar, P., Chatterjee, U.: Observation of two-photon absorption at UV radiation in ZnS quantum dots. Pramana. 82, 327–330 (2014)
Kumar, S., Verma, N.K.: Room temperature magnetism in cobalt-doped ZnS nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28, 137–142 (2015)
Nguyen, T.P., Lam, Q.V., Vu, T.B.: Effects of precursor molar ratio and annealing temperature on structure and photoluminescence characteristics of Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots. J. Lumin. 196, 359–367 (2018)
Tamrakar, R., Ramrakhiani, M., Chandra, B.P.: Effect of cap** agent concentration on photophysical properties of zinc sulfide nanocrystals. The Open Nanoscience J. 2, 12–16 (2008)
Viswanath, R., Bhojya Naik, H.S., Yashavanth Kumar, G.S., Prashanth Kumar, P.N., Arun Kumar, G., Praveen, R.: EDTA-assisted hydrothermal synthesis, characterization and photoluminescent properties of Mn2+ doped ZnS. J. Lumin. 153, 446–452 (2014)
Kaur, J., Sharma, M., Pandey, O.P.: Photoluminescence and photocatalytic studies of metal ions (Mn and Ni) doped ZnS nanoparticles. Opt. Mater.(Amst). 47, 7–17 (2015)
Ghosh, P.K., Ahmed, S.F., Jana, S., Chattopadhyay, K.K.: Photoluminescence and field emission properties of ZnS: Mn nanoparticles synthesized by rf-magnetron sputtering technique. Opt. Mater. (Amst). 29, 1584–1590 (2007)
Brus, L.: Electronic wave functions in semiconductor clusters: experiment and theory. J. Phys. Chem. 90, 2555–2560 (1986)
Sathya, M., Pushpanathan, K.: Synthesis and optical properties of Pb doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl.Surf. Sci. 449, 346–357 (2018)
Jay Chithra, M., Pushpanathan, K.: Thermal, structural and optical investigation of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mod. Phys. Lett. B. 30, 1650406 (2016)
Shionoya, S., Goldberg, P.: Luminescence of inorganic solids, vol. 114, p. 206. Academic, New York (1966)
Mandal, A., Mitra, S., Datta, A., Banerjee, S., Dhara, S., Chakravorty, D.: Multiphonon scattering and photoluminescence of two dimensional ZnS nanosheets grown within Na-4 mica. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 074321 (2012)
Becker, W.G., Bard, A.J.: Photoluminescence and photoinduced oxygen adsorption of colloidal zinc sulfide dispersions. J. Phys. Chem. 87, 4888–4893 (1983)
Kasai, P.H., Otomo, Y.: Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of the ZnS-A and -B centers. J. Chem. Phys. 37, 1262 (1962)
Biswas, S., Kar, S., Chaudhuri, S.: Optical and magnetic properties of manganese-incorporated zinc sulfide nanorods synthesized by a solvothermal process. J. Phys. Chem. B. 19, 17526–17530 (2005)
Ye, C., Fang, X., Li, G.L., Zhang, L.: Temperature-dependent photoluminescence from elemental sulfur species on ZnS nanobelts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 3035–3037 (2004)
Jiang, Y., Meng, X.M., Liu, J., **e, Z.Y., Lee, C.S., Lee, S.T.: ZnS nanowires with wurtzite polytype modulated structure. Adv. Mater. 15, 1195–1198 (2003)
Chen, W., Zhang, J.Z., Joly, A.G.: Optical properties and potential applications of doped semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 4, 919–947 (2004)
Kim, J.S., Kim, J., Kim, T.W., Kim, S.M., Park, H.L.: Critical thickness of ultrathin ferroelectric BaTiO3 films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 102907 (2005)
Chitkara, M., Singh, K., Sandhu, I.S., Bhatti, H.S.: Photo-catalytic activity of Zn1-xMnxS nanocrystals synthesized by wet chemical technique. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 438 (2011)
Brafman, O., Mitra, S.S.: Raman effect in wurtzite- and zinc-blende-type ZnS single crystals. Phys. Rev. 171, 931 (1968)
Nilsen, W.G.: Raman spectrum of cubic ZnS. Phys. Rev. 182, 838 (1969)
Panda, S.K., Dutta, A., Chowdhuri, S.: Nearly monodispersed ZnS nanospheres: synthesis and optical properties. Chem. Phys. Lett. 440, 235–238 (2007)
Bruchhausen, A., Fainstein, A., Jusserand, B., Andre, R.: Universal aspects of nonequilibrium currents in a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B. 73, 85305 (2006)
Dhara, S., Arora, A.K., Bera, S., Ghatak, J.: Multiphonon probe in ZnS quantum dots. J. Raman Spectrosc. 41, 1102–1105 (2010)
Pal, M., Mathews, N.R., Morales, E.R., Graciay Jiménez, J.M., Mathew, X.: Synthesis of Eu+3 doped ZnS nanoparticles by a wet chemical route and its characterization. Opt. Mater. 35, 2664–2669 (2013)
Schmidt, R.L., Kunc, K., Cardona, M., Bilz, H.: Second-order Raman scattering in II-VI semiconductors: relative intensities and trends. Phys. Rev. B. 20, 3345 (1979)
**ong, Q., Wang, J., Reese, O., Voon, L.Y., Eklund, P.C.: Raman scattering from surface phonons in rectangular cross-sectional w-ZnS nanowires. Nano Lett. 4, 1991–1996 (2004)
Lide, D.R.: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 83rd edn, pp. 4–146 (2002)
Zhao, W., Wei, Z., Zhang, L., Wu, X., Wang, X.J., Jiang, J.: Room temperature ferromagnetic and optical properties of chrome doped ZnS nanorods prepared by hydrothermal method. J. Nanomater. 8, 9378349 (2017)
Patel, P.C., Ghosh, S., Srivastava, P.C.: Effect of impurity concentration on optical and magnetic properties in ZnS:Cu nanoparticles. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 93, 148–152 (2017)
Kumar, S., Verma, N.K.: Ferromagnetic and weak superparamagnetic like behavior of Ni-doped ZnS nanocrystals synthesized by reflux method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 1132–1137 (2014)
Shobana, M., Meher, S.R.: Effect of cobalt do** on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of sol-gel derived ZnS nanocrystalline thin films and ab initio studies. Thin Solid Films. 683, 97–110 (2019)
Bi, C., Pan, L.Q., Xu, M., Qin, L.Q., Yin, J.H.: 9th IEEE Conference on Nanotechnology. 874, 26–30 (2009)
Sambasivam, S., Joseph, D.P., Lin, J.G., Venkateswaran, C.: Synthesis and characterization of thiophenol passivated Fe-doped ZnS nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 150, 125 (2008)
Eryong, N., Donglai, L., Yunsen, Z., Xue, B., Liang, Y., Yong, J., Zhifeng, J., **aosong, S.: Photoluminescence and magnetic properties of Fe-doped ZnS nano-particles synthesized by chemical co-precipitation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 8762–8766 (2011)
Chawla, S., Sharma, S., Shah, J.: Fabrication of ZnS:Cr nanoparticles with superparamagnetism and fluorescence properties. Mater. Lett. 108, 189–192 (2012)
Patel, S.P., Pivin, J.C., Patel, M.K., Won, J., Chandra, R., Kanjilal, D., Kumar, L.: Defects induced magnetic transition in Co doped ZnS thin films: effects of swift heavy ion irradiations. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 2136–2141 (2012)
Rashad, M.M., Rayan, D.A., El-Barawy, K.: Hydrothermal synthesis and magnetic properties of Mn doped ZnS nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 200, 072077 (2010)
Sanchez-Lopez, J.C., Reddy, E.P., Rojas, T.C., Sayagues, M.J., Justo, A., Femandez, A.: Preparation and characterization of CdS and ZnS nanosized particles obtained by the inert gas evaporation method. Nanostruct. Mater. 12, 459–462 (1999)
Dantas, N.O., Damigo, L., Fanyao, Q.U., Silva, R.S., Sartoratto, P.P.C., Miranda, K.L., Vilela, E.C., Pelegrini, F., Morais, P.C.: Structural and magnetic properties of ZnO and Zn1−xMnxO nanocrystals. J. Non-Crys. Solids. 354, 4727–4729 (2008)
Pivin, J.C., Socol, G., Mihailescu, I., Berthet, P., Singh, F., Patel, M.K., Vincent, L.: Structure and magnetic properties of ZnO films doped with Co, Ni or Mn synthesized by pulsed laser deposition under low and high oxygen partial pressures. Thin Solid Films. 517, 916–922 (2008)
Jayakumar, O.D., Salunke, H.G., Kadam, R.M., Mohapatra, M., Yaswant, G., Kulshreshtha, S.K.: Magnetism in Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by a co-precipitation method. Nanotechnol. 17, 1278 (2006)
Srinivas, K., Rao, S.M., Reddy, P.V.: Preparation and properties of Zn0.9Ni0.1O diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Nano Part. Res. 13, 817–837 (2011)
Acknowledgement
Authors thank SAIF IIT(M) for providing VSM analysis and STIC−Cochin for providing TEM experimental facilities to carry out the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elsi, S., Mohanapriya, S. & Pushpanathan, K. Observation of Novel Superparamagnetism in ZnS:Co Quantum Dots. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 3223–3240 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05573-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05573-4