Abstract
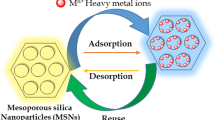
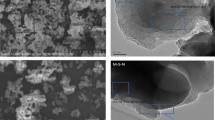
This study describes the total removal of multiple heavy metal ions from wastewater using organo-functionalized ordered mesoporous silica MCM-41. Hydrothermal synthesis of siliceous MCM-41 was done using sodium silicate as precursor through a new cost-effective and environmentally friendly silica precipitation method. Functionalization of siliceous MCM-41 by thiol-containing organosilane was done through a post-synthesis grafting route at room temperature. Physicochemical characterization reveals that the resultant materials have highly ordered hexagonal mesoporous structure and high BET surface area in the range of 1000‒1200 m2/g, before and after organo-functionalization. The organo-functionalized mesoporous materials have been applied for adsorption of a mixture of heavy metal ions from wastewater at room temperature, where the heavy metal ions covalently bind non-selectively with the pendant thiol moieties inside the mesopores. As envisaged from elemental analyses using atomic emission spectroscopy, high efficiency of heavy metal ion adsorption from wastewater was observed, which was significantly better than that of standard adsorbents.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
HB Bradl Heavy Metals in the Environment, Origin, Interaction and Remediation (Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, 2005)
A.T. Paulino, L.B. Santos, J. Nozaki, Removal of Pb2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+ from battery manufacture wastewater by chitosan produced from silkworm chrysalides as a low-cost adsorbent. React. Funct. Polym. 68, 634–642 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2007.10.028
T. Inaba, E. Kobayashi, Y. Suwazono, M. Uetani, M. Oishi, H. Nakagawa, K. Nogawa, Estimation of cumulative cadmium intake causing Itai–itai disease. Toxicol. Lett. 159, 192–201 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2005.05.011
D.W. O’Connell, C. Birkinshaw, T.F. O’Dwyer, Heavy metal adsorbents prepared from the modification of cellulose: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 6709–6724 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.01.036
F. Fu, Q. Wang, Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J. Environ. Manag. 92, 407–418 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011
E.S. Abdel-Halim, S.S. Al-Deyab, Removal of heavy metals from their aqueous solutions through adsorption onto natural polymers. Carbohydr. Polym. 84, 454–458 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.12.001
E. Mahmoudi, S. Azizkhani, A.W. Mohammad, L.Y. Ng, A. Benamor, W.L. Ang, M. Ba-Abbad, Simultaneous removal of Congo red and cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions using graphene oxide–silica composite as a multifunctional adsorbent. J. Environ. Sci. 98, 151–160 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.05.013
J. Wei, L. Duan, J. Wei, E. Hoffmann, Y. Song, X. Meng, Lead removal from water using organic acrylic amine fiber (AAF) and inorganic-organic P-AAF, fixed bed filtration and surface-induced precipitation. J. Environ. Sci. 101, 135–144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.08.009
C.T. Kresge, M.E. Leonowicz, W.J. Roth, J.C. Vartuli, J.S. Beck, Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 359, 710–712 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/359710a0
J.S. Beck, J.C. Vartuli, W.J. Roth, M.E. Leonowicz, C.T. Kresge, K.D. Schmitt, C.T.-W. Chu, D.H. Olson, E.W. Sheppard, S.B. McCullen, J.B. Higgins, J.L. Schlenker, A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114, 10834–10843 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00053a020
D. Rautaray, P.K. Parida, M. Lolage, Precipitated silica. US Patent 10981795 B2 (2021). https://patents.google.com/patent/US10981795B2/en
A. Stein, B.J. Melde, R.C. Schroden, Hybrid inorganic–organic mesoporous silicates—Nanoscopic reactors coming of age. Adv. Mater. 12, 1403–1419 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-4095(200010)12:19%3C1403::AID-ADMA1403%3E3.0.CO;2-X
A.P. Wight, M.E. Davis, Design and preparation of organic-inorganic hybrid catalysts. Chem. Rev. 102, 3589–3614 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr010334m
K. Moller, T. Bein, Inclusion chemistry in periodic mesoporous hosts. Chem. Mater. 10, 2950–2963 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm980243e
A. Ghosh, R. Kumar, Efficient heterogeneous catalytic systems for enantioselective hydrogenation of prochiral carbonyl compounds. J. Catal. 228, 386–396 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2004.08.040
A. Ghosh, C.R. Patra, P. Mukherjee, M. Sastry, R. Kumar, Preparation and stabilization of gold nanoparticles formed by in situ reduction of aqueous chloroaurate ions within surface-modified mesoporous silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 58, 201–211 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(02)00626-1
B. Lee, Y. Kim, H. Lee, J. Yi, Synthesis of functionalized porous silicas via templating method as heavy metal ion adsorbents: the introduction of surface hydrophilicity onto the surface the adsorbents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 50, 77–90 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(01)00437-1
E. Da’na, Adsorption of heavy metals on functionalized-mesoporous silica: A review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 247, 145–157 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.03.050
Y. Li, J. He, K. Zhang, T. Liu, Y. Hu, X. Chen, C. Wang, X. Huang, L. Kong, J. Liu, Super rapid removal of copper, cadmium and lead ions from water by NTA-silica gel. RSC Adv. 9, 397–407 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA08638A
M.A.A. Zaini, Y. Amano, M. Machida, Adsorption of heavy metals onto activated carbons derived from polyacrylonitrile fiber. J. Hazard. Mater. 180, 552–560 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.069
N. Wahab, M. Saeed, M. Ibrahim, A. Munir, M. Saleem, M. Zahra, A. Waseem, Synthesis, characterization and applications of silk/Bentonite clay composite for heavy metal removal from aqueous solution. Front. Chem. 7, 654 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00654
S. Chella, P. Kollu, E.V.P.R. Komarala, S. Doshic, M. Saranya, S. Felix, R. Ramachandran, P. Saravanan, V.L. Koneru, V. Venugopal, S.K. Jeong, A.N. Grace, Solvothermal synthesis of MnFe2O4-graphenecomposite – Investigation of its adsorption and antimicrobial properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 327, 27–36 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.11.096
J. He, Y. Li, C. Wang, K. Zhang, D. Lina, L. Kong, J. Liu, Rapid adsorption of Pb, Cu and Cd from aqueous solutions by β-cyclodextrin polymers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 426, 29–39 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.103
L. Pan, Z. Wang, Q. Yang, R. Huang, Efficient removal of lead, copper and cadmium ions from water by a porous calcium alginate/graphene oxide composite aerogel. Nanomaterials 8, 957 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8110957
J. Xu, Z. Luan, H. He, W. Zhou, L. Kevan, A reliable synthesis of cubic mesoporous MCM-48 molecular sieve. Chem. Mater. 10, 3690–3698 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm980440d
K. Mukhopadhyay, A. Ghosh, R. Kumar, Heteropolyacids aided rapid and convenient syntheses of highly ordered MCM-41 and MCM-48: exploring the accelerated process by 29Si MAS NMR and powder X-ray diffraction studies. Chem. Commun. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1039/b206482k
S.J. Gregg, K.S.W. Sing, Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity (Academic Press, London, 1967), pp. 121–194
C.-Y. Chen, H.-X. Li, M.E. Davis, Studies on mesoporous materials. I. Synthesis and characterization of MCM-41. Microporous Mater. 2, 17–26 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-6513(93)80058-3
X. Chen, L. Huang, Q. Li, Hydrothermal transformation and characterization of porous silica templated by surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 8460–8467 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9705333
K. Bandyopadhyay, K.S. Mayya, K. Vijayamohanan, M. Sastry, Spontaneously organized molecular assembly of an aromatic organic disulfide on silver/platinum alloy surfaces: an angle dependent X-ray photoemission investigation. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Related Phenomena 87, 101–107 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0368-2048(97)00090-X
Funding
Funding provided by Head, Innovation Centre, Tata Chemicals Limited is gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank Dr. Debabrata Rautaray for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lolage, M., Chaskar, M. & Ghosh, A. Synthesis, characterization and application development of ordered mesoporous silica in wastewater remediation. J Porous Mater 28, 1867–1879 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-021-01126-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-021-01126-9