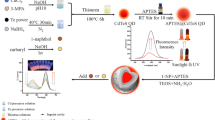
Abstract
Molecular imprinted polymers (MIPs) are sort of custom-made material that can recognize the compounds selectively. Due to its unique qualities such as low cost, resilience and high selectivity, MIPs have sparked tremendous research interest in Photocatalysis, Extraction and sensing applications. The MIPs were developed using [6]-gingerol as template molecule Itaconic acid as monomer, EGDMA as crosslinker and the reaction was proceeded through Exsitu polymerization method using AIBN as initiator to prepare MIPs. The CdS Quantum Dots (QDs) was also employed in the synthesis to develop MIPs hybrid nanocomposite. The physicochemical properties of the MIPs polymer nano catalyst were investigated using a variety of spectroscopic and microscopic techniques. XRD, FESEM, were employed to analyze crystalline size and morphology of synthesized QDs and MIPs hybrid composite and the size of the QDs was found to be 6 nm. Thermogravimetric and differential scanning calorimeter were used to study thermal properties of the composite. Electrochemical study was also performed by using cyclic voltammetry and impedance spectroscopy. The energetic features of hybrid organic inorganic composites of CdS with Molecular imprinted polymers based on gingerol extract is presented using a DFT approach. Results demonstrate that the addition of MIPs contribute to stabilization of occupied states at Valence band which may enhance the photocatalytic properties by stabilization of freshly formed exciton due to light excitation. The composite was employed to investigate the photodegradation of imidacloprid and Buprofezin under visible light source and the highest degradation efficiency was found to be 84%(Imidacloprid) and 80%(Buprofezin) with varying amount of catalyst.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Wang, C. Zhang, G. Yang, Y. Yang, Biological properties of 6-gingerol: a brief review. Nat. Product Commun. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X1400900736
R. Pai Jakribettu, R. Boloor, H. Bhat, A. Thaliath, R. Haniadka, M. Rai, T. George, S. Baliga, Ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) Oils, in: 2016: pp. 447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-416641-7.00050-X.
S.H. Hassan Ahmed, T. Gonda, A. Hunyadi, Medicinal chemistry inspired by ginger: exploring the chemical space around 6-gingerol. RSC Adv. 11, 26687–26699 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA04227K
S.A. Waly, M.M. Shehata, H.H. Mahmoud, Synthesis and characterization of CdS nanoparticles prepared by precipitation in the presence of span 20 as surfactant. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 90, 292–297 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427217020203
R. Balu, A. Dakshanamoorthy, A simple hydrothermal synthesis of cadmium sulfide wrapped on graphene nanocomposite for supercapacitor applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 21, 5835–5845 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2021.19503
X. Liu, A facile route to preparation of sea-urchinlike cadmium sulfide nanorod-based materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 91, 212–216 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2004.11.015
B. Srinivasa Goud, Y. Suresh, S. Annapurna, A.K. Singh, G. Bhikshamaiah, Green Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide Nanoparticles, Materials Today: Proceedings. 3 (2016) 4003–4008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2016.11.064.
M. Pattabi, J. Uchil, Synthesis of cadmium sulphide nanoparticles. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 63, 309–314 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-0248(00)00050-7
P.S. Sharma, Z. Iskierko, A. Pietrzyk-Le, F. D’Souza, W. Kutner, Bioinspired intelligent molecularly imprinted polymers for chemosensing: A mini review. Electrochem. Commun. 50, 81–87 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2014.11.019
M. Fizir, A. Richa, H. He, S. Touil, M. Brada, L. Fizir, A mini review on molecularly imprinted polymer based halloysite nanotubes composites: innovative materials for analytical and environmental applications. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 19, 241–258 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09537-x
M. Gao, Y. Gao, G. Chen, X. Huang, X. Xu, J. Lv, J. Wang, D. Xu, G. Liu, Recent advances and future trends in the detection of contaminants by molecularly imprinted polymers in food samples. Front. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.616326
S. Basak, R. Venkatram, R.S. Singhal, Recent advances in the application of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) in food analysis. Food Control 139, 109074 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109074
L. Spanhel, M.A. Anderson, Synthesis of porous quantum-size cadmium sulfide membranes: photoluminescence phase shift and demodulation measurements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 2278–2284 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00162a031
S. Mathew, S. Ani Joseph, P. Radhakrishnan, V.P.N. Nampoori, C.P.G. Vallabhan, Shifting of fluorescence peak in CdS nanoparticles by excitation wavelength change. J Fluoresc. 21, 1479–1484 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-011-0833-3
A.M.E. Nahrawy, A.B.A. Hammad, A.M. Mansour, Structural investigation and optical properties of Fe, Al, Si, and Cu–ZnTiO nanocrystals. Phys. Scr. 96, 115801 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ac119e
A. el-fattah Mansour, M. Nasr, H. Saleh, G. Mahmoud, Physical characterization of 5′,5″-dibromo-o-cresolsulfophthalein (BCP) spin-coated thin films and BCP/p-Si based diode. Appl. Phys. A (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2920-2
A.M. El Nahrawy, A.M. Mansour, A.B. Abou Hammad, Spectroscopic study of Eu3+-doped magnesium lanthanum phosphate (MLPO) films on SiO2 substrate. SILICON 14, 1227–1234 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00855-x
T.F. Retajczyk, D.K. Roe, Phase selective sampling in a.c. polarography and application to direct measurement of double-layer capacity. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 16, 21–32 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(68)80273-6
A.M. Bond, Modern polarographic methods in analytical chemistry (M. Dekker, New York, 1980)
L. Saikia, D. Bhuyan, M. Saikia, B. Malakar, D. Dutta, P. Sengupta, Photocatalytic performance of ZnO nanomaterials for self sensitized degradation of Malachite Green dye under solar light. Appl. Catal. A (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.10.053
A. Derbalah, M. Sunday, R. Chidya, W. Jadoon, H. Sakugawa, Kinetics of photocatalytic removal of imidacloprid from water by advanced oxidation processes with respect to nanotechnology. J. Water Health 17, 254–265 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2019.259
Z. Akbari, M. Montazerozohori, S.J. Hoseini, R. Naghiha, P. Hayati, G. Bruno, A. Santoro, J.M. White, Synthesis, crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analyses, antimicrobial activity, and thermal behavior of some novel nanostructure hexa-coordinated Cd(II) complexes: Precursors for CdO nanostructure. Appl. Organometallic Chem. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.6181
K.A. Adegoke, M. Iqbal, H. Louis, S.U. Jan, M. Anam, O.S. Bello, Photocatalytic conversion of CO2 using ZnO semiconductor by hydrothermal method. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 19, 1–27 (2018). https://doi.org/10.21743/pjaec/2018.06.01
Q. Shi, Y. Wang, H. Zhao, F. Zhang, Y. Ma, Y. Yuan, C. Pei, B. Liu, L. Ning, C. Zhang, H. Yang, Spatial charge separation between wurtzite CdS polar (0001) and (000 1 ¯) facets and their enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. J. Alloy. Compd. 700, 138–148 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.049
C. Zheng, Y.-P. Huang, Z.-S. Liu, Recent developments and applications of molecularly imprinted monolithic column for HPLC and CEC. J. Sep. Sci. 34, 1988–2002 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201100164
A. Yuan, H. Lei, Z. Wang, X. Dong, Improved photocatalytic performance for selective oxidation of amines to imines on graphitic carbon nitride/bismuth tungstate heterojunctions. J Colloid Interface Sci. 560, 40–49 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.10.060
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Investigation. B.C.D. Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. E.F.G. I. Formal analysis, Investigation. H.J. I. Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflcit of interest
The authors declare no Conflcit of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Malik, A.Q., Tabasum, S., Rani, S. et al. Fluorescent CdS QDs Modified With Molecular Imprinted Polymer for the Photodegradation of Imidacloprid and Buprofezin Pesticides Under Visible Light. J Inorg Organomet Polym 33, 3468–3484 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02753-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02753-2