Abstract
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammation disease that may involve extra-articular organs in addition to joints. Many proinflammatory cytokines are involved in the inflammatory process of RA. IκBα conjugates with NF-κB and is a key player in regulation of the inflammatory process. We carried out experiments to define the effect of different promoter polymorphisms on the transcriptional activities of IκBα promoter and the development of RA.
Methods
Different IκBα promoter reporters were constructed and were examined in human mononuclear cells, THP-1 cells. One hundred forty patients and 115 healthy controls were recruited from the Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital.
Results
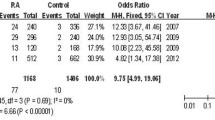
The activities of IκBα promoter constructs with -826C, -550A, -519T, and -826T, -550A, -519T genotypes were expressed at one half the activity level of other constructs. Promoter constructs containing the sites -550A/T and -519T had a reduced risk of rheumatoid arthritis. The odds ratio of -826C/T genotype was significantly associated with an increase of risk in causing rheumatoid arthritis, whereas -826T/T genotype was associated only with a slightly increased risk of RA, but without statistical significance (odds ratio = 1.2; 95% confidence interval, 0.4–3.8).
Conclusion
The increase of T allele was associated with a significant increased risk and the tendency to the pathogenesis of RA. The association between IκBα promoter polymorphisms and disease severity of rheumatoid arthritis is partly due to different transcriptional activities of IκBα promoter and the activation of NF-κB.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–61.
Bingham CO 3rd. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: pivotal cytokines involved in bone degradation and inflammation. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2002;65:3–9.
Brennan FM, Hayes AL, Ciesielski CJ, Green P, Foxwell BM, Feldmann M. Evidence that rheumatoid arthritis synovial T cells are similar to cytokine-activated T cells: involvement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and nuclear factor kappaB pathways in tumor necrosis factor alpha production in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:31–41.
Dai SM, Shan ZZ, Xu H, Nishioka K. Cellular targets of interleukin-18 in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:1411–8.
McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:429–42.
Barnes PJ, Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1066–71.
Campbell IK, Gerondakis S, O'Donnell K, Wicks IP. Distinct roles for the NF-kappaB1 (p50) and c-Rel transcription factors in inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2000;105:1799–806.
Makarov SS. NF-kappaB as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammation: recent advances. Mol Med Today. 2000;6:441–8.
Tak PP, Firestein GS. NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 2001;107:7–11.
Wang T, Zhang X, Li JJ. The role of NF-kappaB in the regulation of cell stress responses. Int Immunopharmacol. 2002;2:1509–20.
Chen LF, Greene WC. Sha** the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:392–401.
Li Q, Verma IM. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:725–34.
Emmerich F, Meiser M, Hummel M, Demel G, Foss HD, Jundt F, et al. Overexpression of I kappa B alpha without inhibition of NF-kappaB activity and mutations in the I kappa B alpha gene in Reed-Sternberg cells. Blood. 1999;94:3129–34.
Iwai K, Lee BR, Hashiguchi M, Fukushima A, Iwashima M. IkB-alpha-specific transcript regulation by the C-terminal end of c-Rel. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:141–4.
Ortutay C, Vihinen M. Immunome knowledge base (IKB): an integrated service for immunome research. BMC Immunol. 2009;10:3.
Whiteside ST, Israel A. I kappa B proteins: structure, function and regulation. Semin Cancer Biol. 1997;8:75–82.
Cheon H, Sun YK, Yu SJ, Lee YH, Ji JD, Song GG, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-AA increases IL-1beta and IL-8 expression and activates NF-kappaB in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Scand J Immunol. 2004;60:455–62.
Lin CH, Ou TT, Wu CC, Tsai WC, Liu HW, Yen JH. IkappaBalpha promoter polymorphisms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Immunogenet. 2007;34:51–4.
Okazaki Y, Sawada T, Nagatani K, Komagata Y, Inoue T, Muto S, et al. Effect of nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition on rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes and collagen induced arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:1440–7.
Abdallah A, Sato H, Grutters JC, Veeraraghavan S, Lympany PA, Ruven HJ, et al. Inhibitor kappa B-alpha (IkappaB-alpha) promoter polymorphisms in UK and Dutch sarcoidosis. Genes Immun. 2003;4:450–4.
Hung YH, Ou TT, Lin CH, Li RN, Lin YC, Tsai WC, et al. IkBalpha promoter polymorphisms in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int. 2009.
Mozzato-Chamay N, Corbett EL, Bailey RL, Mabey DC, Raynes J, Conway DJ. Polymorphisms in the IkappaB-alpha promoter region and risk of diseases involving inflammation and fibrosis. Genes Immun. 2001;2:153–5.
Tak PP, Gerlag DM, Aupperle KR, van de Geest DA, Overbeek M, Bennett BL, et al. Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappaB kinase beta is a key regulator of synovial inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:1897–907.
Lin CH, Wang SC, Ou TT, Li RN, Tsai WC, Liu HW, et al. I kappa B alpha promoter polymorphisms in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol. 2008;28:207–13.
Ou TT, Lin CH, Lin YC, Li RN, Tsai WC, Liu HW, et al. IkappaBalpha promoter polymorphisms in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. J Clin Immunol. 2008;28:440–4.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the grants from the National Science Council (NSC 94-2314-B-037-057, NSC 95-2314-B-037-007) and the Center of Excellence for Environmental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University.
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, RN., Hung, YH., Lin, CH. et al. Inhibitor IκBα Promoter Functional Polymorphisms in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Clin Immunol 30, 676–680 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-010-9439-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-010-9439-9