Abstract
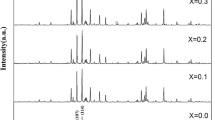
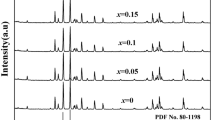
M-type hexaferrite substituted with cobalt and lanthanum [\({\text{SrCo}}_{1.5z} {\text{La}}_{0.5z} {\text{Fe}}_{12 - 2z} {\text{O}}_{19}\) (SCLF; 0.0 \(\le z \le 0.5)\)] was synthesized by auto-combustion Sol–gel methodology. XRD study indicated that prepared specimens exhibit a hexagonal magnetoplumbite phase without any secondary peak. The crystallite size decreases from 48.94 to 28.82 nm as the level of substitution increases in SrM hexaferrite. The micrographs showed an enhancement in the inter-grain connectivity of grains with substitution. Mössbauer spectra revealed the variation observed in hyperfine interactions, isomer shift, quadrupole splitting, and relative area of five sextets of Fe3+ ions. Analysis of Mössbauer depicted that the substituents tend to occupy spin-up 12k-2a sites of crystal lattice from z = 0.0 to z = 0.3, which elucidated the diminution observed in magnetization. The coercivity gradually decreased from z = 0.0 (5026.54 Oe) to z = 0.5 (862.47 Oe). The saturation magnetization initially decreased with substitution from z = 0.0 to 0.3 and then increased for z = 0.4 and 0.5 samples. The magnetic susceptibility (dM/dH) of samples derived from magnetic parameters is high for z = 0.0, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4. Both Ms with tunable Hc and magnetic susceptibility results make them considerable materials for recording applications.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
H. Bayrakdar, Fabrication, magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of Ba2Co2Cr2Fe12O22 hexagonal ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 674, 185–188 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.055
A. Sharbati, J. Mola-Verdi-Khani, G.R. Amiri, Microwave absorption studies of nanocrystalline SrMnx/2(TiSn)x/4 Fe12−xO19 prepared by the citrate sol-gel method. Solid State Commun. 152(3), 199–203 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2011.11.009
A.D. Deshpande, K.G. Rewatkar, V.M. Nanoti, Study of morphology and magnetic properties of nanosized particles of Zirconium—Cobalt substituted calcium hexaferrites. Mater. Today Proc. 4(11), 12174–12179 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.09.147
G. Feng et al., Co substituted BaFe12O19 ceramics with enhanced magnetic resonance behavior and microwave absorption properties in 2.6–18 GHz. Ceram. Int. 45(11), 13859–13864 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.083
B. Zong, X. Niu, Analysis of structure and magnetic behavior in M-type hexaferrite compounds Sr1−xYxFe10CoTiO19. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(7), 5290–5297 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03089-0
Y. Feng, S. Li, Y. Zheng, Z. Yi, Y. He, Y. Xu, Preparation and characterization of MgFe2O4 nanocrystallites via PVA sol–gel route. J. Alloys Compd. 699, 521–525 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.432
S.K. Durrani, S. Naz, M. Mehmood, M. Nadeem, M. Siddique, Structural, impedance and Mössbauer studies of magnesium ferrite synthesized via sol–gel auto-combustion process. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 21(8), 899–910 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2015.12.006
S.V. Trukhanov et al., Magnetic and dipole moments in indium doped barium hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 457, 83–96 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.02.078
R.B. Jotania, R.B. Khomane, C.C. Chauhan, S.K. Menon, B.D. Kulkarni, Synthesis and magnetic properties of barium-calcium hexaferrite particles prepared by sol-gel and microemulsion techniques. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320(6), 1095–1101 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2007.10.032
C. Singh, S. Bindra Narang, I.S. Hudiara, K.C. James Raju, K. Sudheendran, Microwave and electrical properties of Co–Zr substituted Ba–Sr ferrite. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 11(6), 692–697 (2010)
T. Giannakopoulou, L. Kompotiatis, A. Kontogeorgakos, G. Kordas, Microwave behavior of ferrites prepared via sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 246(3), 360–365 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00106-3
N. Tran, Y.J. Choi, T.L. Phan, D.S. Yang, B.W. Lee, Electronic structure and magnetic and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of BaFe12−xCoxO19 M-type hexaferrites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 19(12), 1343–1348 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2019.08.023
G. Sriramulu, N. Maramu, K. Praveena, S. Katlakunta, Effect of Cr3+–Al3+ cosubstitution on structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Srhexaferrites. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 33(35), 26113–26123 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09298-z
J. Du, L. Lian, Y. Liu, Y. Du, Effect of Zn substitution on the structure and magnetic properties of Sr0.1La0.45Ca0.45Fe11.7−xZnxCo0.3O19 hexagonal ferrites. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 30(21), 19618–19624 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02335-4
X. Suo, J. Li, W. Zhang, P. Li, Effect of La3+ Substitution on the Structure and Magnetic Properties of M-type Sr Hexaferrites. J Supercond Nov Magn. 36(1) 197–206 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-022-06450-y
R.A. Nandotaria et al., Magnetic interactions and dielectric dispersion in Mg substituted M-type Sr–Cu hexaferrite nanoparticles prepared using one step solvent free synthesis technique. Ceram. Int. 44(4), 4426–4435 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.043
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, H. Güngüneş, A. Baykal, S.V. Trukhanov, A.V. Trukhanov, Manganese/yttrium codoped strontium nanohexaferrites: evaluation of magnetic susceptibility and mossbauer spectra. Nanomaterials (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010024
B.K. Rai, S.R. Mishra, V.V. Nguyen, J.P. Liu, Synthesis and characterization of high coercivity rare-earth ion doped Sr0.9RE0.1Fe10Al2O19 (RE: Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, and Gd). J. Alloys Compd. 550, 198–203 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.09.021
C.C. Chauhan, T. Gupta, A.A. Gor, K.R. Jotania, R.B. Jotania, Effect of calcination temperature on structural and magnetic properties of lightly lanthanum substituted M-type strontium cobalt hexaferrites. Mater. Today Proc. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.1184
M.M. Hessien, N. El-Bagoury, M.H.H. Mahmoud, M. Alsawat, A.K. Alanazi, M.M. Rashad, Implementation of La3+ ion substituted M-type strontium hexaferrite powders for enhancement of magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166187
C. Rambabu et al., Effect of La3+ and Ni2+ substitution on Sr1−xLaxFe12−yNiyO19 hexaferrite structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2022.116257
C. Stergiou, Magnetic, dielectric and microwave absorption properties of rare earth doped Ni–Co and Ni–Co–Zn spinel ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.11.001
M. Ayub, I.H. Gul, K. Nawaz, K. Yaqoob, Effect of rare earth and transition metal La-Mn substitution on electrical properties of co-precipitated M-type Ba-ferrites nanoparticles. J. Rare Earths 37(2), 193–197 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2018.08.005
G. Feng et al., Lanthanum-substituted Ba0.4Ca0.6Fe11.4Co0.6O19 ceramics with enhanced microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(1), 621–627 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02567-4
M. Augustin, T. Balu, Estimation of lattice stress and strain in zinc and manganese ferrite nanoparticles by williamson-hall and size-strain plot methods. Int. J. Nanosci. 16(3), 1–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219581X16500356
J. Mohammed et al., Structural, dielectric, and magneto-optical properties of Cu2+–Er3+ substituted nanocrystalline strontium hexaferrite. Mater. Res. Express (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab063b
H. Mahajan, S.K. Godara, A.K. Srivastava, Synthesis and investigation of structural, morphological, and magnetic properties of the manganese doped cobalt-zinc spinel ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 896, 162966 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162966
H. Moradmard, S. Farjami Shayesteh, P. Tohidi, Z. Abbas, M. Khaleghi, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of magnesium doped nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 650, 116–122 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.07.269
H. Kaur et al., Elucidation of microwave absorption mechanisms in Co–Ga substituted Ba–Sr hexaferrites in X-band. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(17), 14995–15005 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9638-3
S. Bindra Narang, K. Pubby, Nickel spinel ferrites: a review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167163
S.K. Chawla, S.S. Meena, P. Kaur, R.K. Mudsainiyan, S.M. Yusuf, Effect of site preferences on structural and magnetic switching properties of CO–Zr doped strontium hexaferrite SrCoxZrxFe(12–2x)O19. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 378, 84–91 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.10.168
T.T. Carol, J. Mohammed, B.H. Bhat, S. Mishra, S.K. Godara, A.K. Srivastava, Effect of Cr–Bi substitution on the structural, optical, electrical and magnetic properties of strontium hexaferrites. Physica B 575, 411681 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.411681
T. Kaur, S. Kumar, B.H. Bhat, B. Want, A.K. Srivastava, Effect on dielectric, magnetic, optical and structural properties of Nd–Co substituted barium hexaferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 119(4), 1531–1540 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9134-z
T.M. Meaz, C.B. Koch, An investigation of trivalent substituted M-type hexagonal ferrite using X-ray and Mössbauer spectroscopy. Hyperfine Interact. 166(1–4), 455–463 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-006-9308-3
G.A. Ashraf, L. Zhang, W. Abbas, G. Murtaza, Synthesis and characterizations of Al-Sm substituted Ba-Sr M-type hexagonal ferrite nanoparticles via sol–gel route. Ceram. Int. 44(15), 18678–18685 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.096
J. Xu, H. Zou, H. Li, G. Li, S. Gan, G. Hong, Influence of Nd3+ substitution on the microstructure and electromagnetic properties of barium W-type hexaferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 490(1–2), 552–556 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.10.079
J.H. De Araújo, J.M. Soares, M.F. Ginani, F.L.A. Machado, J.B.M. Cunha, Mössbauer and magnetic study of nanocrystalline strontium hexaferrite prepared by an ionic coordination reaction technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 343(3), 203–207 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.04.077
I.A. Auwal et al., Mössbauer analysis and cation distribution of Zn substituted BaFe12O19 Hexaferrites. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 31(1), 151–156 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4170-x
G.D. Soria, P. Jenus, J.F. Marco, A. Mandziak, F. Moutinho, Strontium hexaferrite platelets: a comprehensive soft X-ray absorption and Mössbauer spectroscopy study. Sci. Rep. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48010-w
M. Awawdeh, I. Bsoul, S.H. Mahmood, Magnetic properties and Mossbauer spectroscopy on Ga, Al, and Cr substituted hexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 585, 465–473 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.09.174
S.C. Bhandari, D. Guragain, J. Mohapatra, S. Yoon, J.P. Liu, S.R. Mishra, Magnetic and Mössbauer effect study of Ca–Sc Co-doped M-type strontium hexaferrite. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05882-2
C. Liu et al., Microstructure and magnetic properties of M-type strontium hexagonal ferrites with Y-Co substitution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 436, 126–129 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.04.040
H.S. Mund, B.L. Ahuja, Structural and magnetic properties of Mg doped cobalt ferrite nano particles prepared by sol-gel method. Mater. Res. Bull. 85, 228–233 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.09.027
C.C. Chauhan, T. Gupta, A.A. Gor, K.R. Jotania, R.B. Jotania, Effect of calcination temperature on structural and magnetic properties of lightly lanthanum substituted M-type strontium cobalt hexaferrites. Mater. Today Proc. 47, 715–718 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.1184
R. Nongjai, S. Khan, K. Asokan, H. Ahmed, I. Khan, Magnetic and electrical properties of in doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4759436
M.V. Rane, D. Bahadur, A.K. Nigam, C.M. Srivastava, Mössbauer and FT-IR studies on non-stoichiometric barium hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 192(2), 288–296 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(98)00533-2
C. Singh, S.B. Narang, I.S. Hudiara, Y. Bai, K. Marina, Hysteresis analysis of Co–Ti substituted M-type Ba–Sr hexagonal ferrite. Mater. Lett. 63(22), 1921–1924 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.06.002
S. Kumar, M. Kumar Manglam, S. Supriya, H. Kumar Satyapal, R. Kumar Singh, M. Kar, Lattice strain mediated dielectric and magnetic properties in La doped barium hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 473, 312–319 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.10.085
R. Grössinger, Correlation between the inhomogeneity and the magnetic anisotropy in polycrystalline ferromagnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 28(1–2), 137–142 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(82)90037-3
T. Ben Ghzaiel, W. Dhaoui, A. Pasko, F. Mazaleyrat, Effect of non-magnetic and magnetic trivalent ion substitutions on BaM-ferrite properties synthesized by hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 671, 245–253 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.02.071
A. Ghasemi, A. Morisako, Static and high frequency magnetic properties of Mn–Co–Zr substituted Ba-ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 456(1–2), 485–491 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.02.101
A. Kara, Effect of rare-earth co-do** on the microstructural and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19. Adv. Mater. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.2478/adms-2020-0014
N. Sivakumar, A. Narayanasamy, K. Shinoda, C.N. Chinnasamy, B. Jeyadevan, J.M. Greneche, Electrical and magnetic properties of chemically derived nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 102(1), 8 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2752098
D. Shekhawat, P.K. Roy, Impact of yttrium on the physical, electro-magnetic and dielectric properties of auto-combustion synthesized nanocrystalline strontium hexaferrite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30(2), 1187–1198 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0387-0
J. Yang, W. Yang, F. Li, Y. Yang, Research and development of high-performance new microwave absorbers based on rare earth transition metal compounds: a review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 497, 165961 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165961
C. Liu et al., Influence of the Eu substitution on the structure and magnetic properties of the Sr-hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 46(1), 171–179 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.08.245
R. Srivastava, B.C. Yadav, Ferrite materials: Introduction, synthesis techniques, and applications as sensors. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. Biomed. 4(2), 141–154 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/19430892.2012.676918
R. Shams Alam, M. Moradi, H. Nikmanesh, J. Ventura, M. Rostami, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of BaMgx/2Mnx/2CoxTi2xFe12–4xO19 hexaferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 402, 20–27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.11.038
J. Singh et al., Elucidation of phase evolution, microstructural, Mössbauer and magnetic properties of Co2+[sbnd]Al3+doped M-type Ba[sbnd]Sr hexaferrites synthesized by a ceramic method. J. Alloys Compd. 695, 1112–1121 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.10.237
A. Baykal, S. Yokuş, S. Güner, H. Güngüneş, H. Sözeri, M. Amir, Magneto-optical properties and Mössbauer Investigation of BaxSryPbzFe12O19 Hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 43(4), 3475–3482 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.10.013
V. Dixit, D. Thapa, B. Lamichhane, C.N. Nandadasa, Y.K. Hong, S.G. Kim, Site preference and magnetic properties of Zn–Sn-substituted strontium hexaferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 125(17), 6–13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5084762
A. Awadallah, S.H. Mahmood, Y. Maswadeh, I. Bsoul, A. Aloqaily, Structural and magnetic properties of vanadium doped M-type barium hexaferrite (BaFe12−xVxO19). IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/92/1/012006
V. Pop et al., Structural and magnetic behaviour of SmCo5/α-Fe nanocomposites obtained by mechanical milling and subsequent annealing. Rom. Rep. Phys. 55(1–2), 127–136 (2010)
I. Panneer Muthuselvam, R.N. Bhowmik, Mechanical alloyed Ho3+ do** in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite and understanding of magnetic nanodomains. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322(7), 767–776 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.10.057
J.N. Dahal, D. Neupane, T.P. Poudel, Synthesis and magnetic properties of 4:1 hard-soft SrFe12O19-La1–xSrxMnO3 nanocomposite prepared by auto-combustion method. AIP Adv. 9(7), 7 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5096530
D.N. Dipesh, L. Wang, H. Adhikari, J. Alam, S.R. Mishra, Influence of Al3+do** on structural and magnetic properties of CoFe2–xAlxO4 Ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 688, 413–421 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.030
W. Zhang, A. Sun, X. Zhao, N. Suo, L. Yu, Z. Zuo, Structural and magnetic properties of La3+ ion doped Ni–Cu–Co nano ferrites prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 90(3), 599–610 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-04941-4
A. Thakur, R. R. Singh, P. B. Barman, Structural and magnetic properties of La3+ substituted strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles prepared by citrate precursor method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 326, 35–40 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.08.038
S. W. Lee, S. Y. An, I. B. Shim, C. S. Kim, Mössbauer studies of La-Zn substitution effect in strontium ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 290, 231–233 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2004.11.190
J. Lee, E.J. Lee, T.Y. Hwang, J. Kim, Y.H. Choa, Anisotropic characteristics and improved magnetic performance of Ca–La–Co-substituted strontium hexaferrite nanomagnets. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72608-0
B. H. Bhat B. Want, Magnetic, dielectric and complex impedance properties of lanthanum and magnesium substituted strontium hexaferrite. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 27(12), 12582–12590 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5389-1
Funding
There are not any financial and personal relationships with other people or organisations that could be viewed as inappropriately influencing (bias) their work. Funding source(s) had no such involvement in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT: Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Data analysis and Curation, Software, Original Drafting. CS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Data Curation, Writing—review and editing. AKS: Investigation, Data Analysis. SRM and MFA: Performed XRD and FTIR Characterization. KDM, IVB, VGS, VIP: Performed SEM, Mössbauer and VSM Measurements.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, M., Singh, C., Martinson, K.D. et al. Significantly improved magnetic parameters of Co–La co-doped strontium hexagonal ferrites for recording applications: structural, hysteresis, and mössbauer performance metrics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 2002 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11328-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11328-3