Abstract
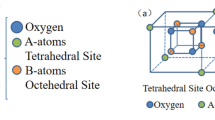
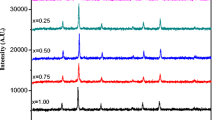
In this paper, magnesium substitute cobalt ferrite with chemical formula Co1−xMgxFe2O4 (x = 0.0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0) was prepared by sol–gel method. The prepared ferrite powder was characterized in a series of ways. X-ray diffraction (XRD) shows that the samples have a single-phase cubic spinel structure, and the structural parameters of the samples are different with the ion distribution. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) can further verify the spinel structure of ferrite and analyze the elastic modulus of the prepared material. Beyond that, the completeness of chemical reactions can be determined by the information of functional groups. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used to monitor the morphology of the sample, which also showed that the samples were evenly distributed and agglomerated due to magnetic influence. Energy dispersive spectrometers (EDS) show that the elemental composition of the substance corresponds to a chemical formula and is free of other impurities. Vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) shows that non-magnetic Mg2+ can replace magnetic Co2+, which changes the interaction intensity and magnetic order between sites, thus changing the magnetic properties of samples, and realizing the magnetic transition from ferromagnetism to superparamagnetism.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Data sharing and data citation is encouraged.
References
D.R. Mane, U.N. Devatwal, K.M. Jadhav, Structural and magnetic properties of aluminum and chromium co-substituted cobalt ferrite. Mater. Lett. 91, 44 (2000)
L.B. Kong, Z.W. Li, G.Q. Lin, Y.B. Gan, Magneto-dielectric properties of Mg–Cu–Co ferrite ceramics: I. Densification behavior and microstructure development. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 3106, 90 (2007)
Y. Konseoglu, H. Kavas, B. Aktas, Surface effects on magnetic properties of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles. Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 1595, 203 (2006)
W. Zhang, H. Wang, F. Zhang, Z. Qian, W. Su, Effect of surface modifications on the magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 547, 6 (2010)
M. Siva Ram Prasad, B.B.V.S.V. Prasad, B. Rajesh, K.H. Rao, K.V. Ramesh, Magnetic properties and DC electrical resistivity studies on cadmium substituted nickel-zinc ferrite system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2115, 323 (2011)
S. Singhal, S.K. Barthwal, K. Chandra, Structural, magnetic and Mössbauer spectral studies of nano size aluminum substituted nickel zinc ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 94, 296 (2006)
K.R. Krishna, D. Ravinder, K.V. Kumar, ACh. Lincon, Synthesis, XRD & SEM studies of zinc substitution in nickel ferrites by citrate gel technique. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 153, 2 (2012)
J.L. Dormann, M. Nogues, Magnetic structures of substituted ferrites. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 1223, 2 (1990)
L. Wang, B.K. Rai, S.R. Mishra, Structural and magnetic study of Al3+ doped Ni0.75Zn0.25Fe2−xAlxO4 nanoferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 183, 65 (2015)
A.A. Ati, Z. Othaman, A. Samavati, F.Y. Doust, Structural and magnetic properties of Co–Al substituted Ni ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Mol. Struct. 1058, 136–141 (2014)
V. Sepelak, K.D. Becker, Mössbauer studies in the mechanochemistry of spinel ferrites. J. Mater. Synth. Process. 155–166, 8 (2000)
Y. Köseoğlu, M. Bay, M. Tan, A. Baykal, H. Sözeri, R. Topkaya, N. Akdoğan, Magnetic and dielectric properties of Mn0.2Ni0.8Fe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by PEG-assisted hydrothermal method. J. Nanopart. Res. 2235, 13 (2011)
A. Goldman, Modern Ferrite Technology (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1993)
M. Pardavi-Horvath, Microwave applications of soft ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 171, 215 (2000)
K. Rathod, P. Kamble, K. Sanadi, G. Kamble, M. Guar, K. Garadkar, Photovoltaic application study of zinc telluride thin films grown by chemical bath deposition method. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 11, 131–144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.4236/ampc.2021.118013
K.C. Rathod, K.R. Sanadi, P.D. Kamble, G.S. Kamble, M.L. Gaur, K.M. Garadkar, Photovoltaic solar application study of Cu0.5Zn0.5Se thin films by chemical bath deposition method. Mater. Res. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2021-0259
S. Pavithradevi, N. Suriyanarayanan, T. Boobalan, Synthesis and characterization of polyol-assisted nano Cu0.2Ni0.2Sn0.2Ba0.4Fe2O4 by a wet hydroxyl route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 137–143 (2017)
A.T. Raghavender, K.M. Jadhav, Dielectric properties of Al-substituted Co ferrite nanoparticles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 32, 575–578 (2009)
G. Aravind, M. Raghasudha, D. Ravinder, Synthesis, characterization and FC–ZFC magnetization studies of cobalt substituted lithium nano ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 378, 278–284 (2015)
M. Mozaffari, V. Amighian, V. Darsheshdar, The effect of cobalt substitution magnetic hardening of magnetite. J. Mag. Magn. Mater. 350, 119–124 (2014)
Qu. Yuqiu, H. Yang, N. Yang, Y. Fan, H. Zhu, G. Zou, The effect of reaction temperature on the particle size, structure and magnetic properties of coprecipitated CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 60, 3548 (2006)
Z. Ahmad et al., Structural and complex impedance spectroscopic studies of Mg-substituted CoFe2O4. Ceram. Int. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.08.154
V. Kuncser, G. Schinteie, B. Sahoo, W. Keune, D. Bica, L. Vekas, G. Filoti, Magnetic interactions in water based ferrofluids studied by Mössbauer spectroscopy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 016205, 19 (2007)
V.D. Sudheesh, N. Thomas, N. Roona, H. Choudhary, B. Sahoo, N. Lakshmi, V. Sebastian, Synthesis of nanocrystalline spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M=Zn and Mg) by solution combustion method: influence of fuel to oxidizer ratio. J. Alloys. Compd. 577, 742 (2018)
S.A. Oliver, R.J. Willey, H.H. Hamdeh, G. Oliveri, G. Busca, Structure and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite fine powders. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1695, 33 (1995)
G. Busca, E. Finocchio, V. Lorenzelli, M. Trombetta, S.A. Rossini, IR study of alkene allylic activation on magnesium ferrite and alumina catalysts. Faraday Trans. 4687, 92 (1996)
A. Franco, M.S. Silva, High temperature magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 10, 109 (2011)
R. Ali, A. Mahmood, M.A. Khan, A.H. Chughtai, M. Shahid, I. Shakir, M.F. Warsi, Impacts of Ni-Co substitution on the structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of magnesium nano-ferrites fabricated by micro-emulsion method. J. Alloys. Compd. 363, 584 (2014)
M.J. Iqbal, Z. Ahmad, T. Meydan, I.C. Nlebedim, Influence of Ni–Cr substitution on the magnetic and electric properties of magnesium ferrite nanomaterials. Mater. Res. Bull. 344, 47 (2012)
A.A. Ati, Z. Othaman, A. Samavati, F.Y. Doust, Structural and magnetic properties of Co–Al substituted Ni ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Mol. Struct. 136, 1058 (2014)
M.A. Ahmed, E. Ateia, S.I. El-Dek, Spectroscopic analysis of ferrite doped with different rare earth elements. Vib. Spectrosc. 69, 30 (2002)
E. Ateia, M.A. Ahmed, A.K. El-Aziz, Effect of rare earth radius and concentration on the structural and transport properties of doped Mn–Zn ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 545, 311 (2007)
T. Ramachandran, K. Vishista, Combustion synthesis of Mg–Er ferrite nanoparticles:cation distribution and structural, optical, and magnetic properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 631, 40 (2015)
A. Manikandan, J. Judith Vijaya, L. John Kennedy, M. Bououdina, Microwave combustion synthesis, structural, optical and magnetic properties of Zn1−xSrxFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 5910, 39 (2013)
J. Sharma, N. Sharma, J. Parashar, V.K. Saxena, D. Bhatnagar, K.B. Sharma, Dielectric properties of nanocrystalline Co-Mg ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 649, 362–367 (2015)
P. Jadoun, J. Sharma, S. Kumar, S.N. Dolia, D. Bhatnagar, V.K. Saxena, Structural and magnetic behavior of nanocrystalline Cr doped Co-Mg ferrite. Ceram. Int. 6748, 44 (2018)
A. Franco Jr., F.C. e Silva, V.S. Zapf, High temperature magnetic properties of Co1−xMgxFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by forced hydrolysis method. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 07B530 (2012)
H.S. Mund, B.L. Ahuja, Structural and magnetic properties of Mg doped cobalt ferrite nano particles prepared by sol-gel method. Mater. Res. Bull. 228, 85 (2017)
S.V. Bhandare, R. Kumar, A.V. Anupama, M. Mishra, R. Vijaya Kumar, V.M. Jali, B. Sahoo, Effect of Mg-substitution in Co–Ni-Ferrites: cation distribution and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 3, 251 (2020)
K. Krieble, T. Schaefer, J.A. Paulsen et al., Mössbauer spectroscopy investigation of Mn-substituted Co-ferrite (CoMnxFe2−xO4). J. Appl. Phys. 97, 10F101-12 (2005)
R.V. Kumar, A.V. Anupama, R. Kumar, H.K. Choudhary, V.B. Khopkar, G. Aravind, B. Sahoo, Cation distributions and magnetism of Al-substituted CoFe2O4-NiFe2O4 solid solutions synthesized by sol-gel auto-combustion method. Ceram. Int. 20709, 44 (2018)
N. Thomas, P.V. Jithinb, V.D. Sudheesh, V. Sebastian, Magnetic and dielectric properties of magnesium substituted cobalt ferrite samples synthesized via one step calcination free solution combustion method. Ceram. Int. 7306, 43 (2017)
L. George, C. Viji, M. Maheen, E.M. Mohammed, Enhanced magnetic properties at low temperature of Mn substituted Ni-Zn mixed ferrite doped with Gd ions for magnetoresistive applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 3, 110833 (2020)
M. Arunabha, Roy, Formation and stability of nanosized, undercooled propagating intermediate melt during β→δ phase transformation in HMX. Nanocrystal. 1, 56001 (2021)
V.G. Patil, S.E. Shirsath, S.D. More, S.J. Shuklac, K.M. Jadhav, Effect of zinc substitution on structural and elastic properties of cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 200, 488 (2009)
A.M. Roy, Energetics and kinematics of undercooled nonequilibrium interfacial molten layer in cyclotetramethylene-tetranitramine crystal. Physica B 1, 412986 (2021)
W.R. Agami, Effect of neodymium substitution on the electric and dielectric propertiesof Mn-Ni-Zn ferrite. Physica B 534, 17–21 (2018)
M.A. Khan, M.U. Islam, M. Ishaque, I.Z. Rahman, A. Genson, S. Hampshire, Structural and physical properties of Ni-Tb-Fe-O system. Mater. Charact. 60, 73–78 (2009)
S.S. Jadhav, S.E. Shirsath, B.G. Toksha, S.M. Patange, S.J. Shukla, K.M. Jadhav, Structural properties and cation distribution of Co-Zn nanoferrites. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 23, 5629–5638 (2009)
P. Scherrer, Göttinger Nachrichten Gesell, vol. 2 (Springer, Berlin, 1918), pp. 98–100
M. Anis-ur-Rehman, M.A. Malik, K. Khan, A. Maqsood, Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Mg–Co ferrites. J. Nano Res. 14, 1–9 (2011)
H.M. Zaki, S. Al-Heniti, T.A. Elmosalami, Structural, magnetic and dielectric studies of copper substituted nano-crystalline spinel magnesium zinc ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.01.304
K.B. Modi, J.D. Gajera, M.C. Chhantbar, K.G. Saija, G.J. Baldha, H.H. Joshi, Structural properties of magnesium and aluminium co-substituted lithium ferrite. Mater. Lett. 4053, 4049–4053 (2003)
M. Kaur, P. Jain, M. Singh, Studies on structural and magnetic properties of ternary cobalt magnesium zinc (CMZ) Co0.6−xMgxZn0.4Fe2O4 (x=0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 335, 332–339 (2015)
R.M. Rosnan, Z. Othaman, R. Hussin, A.A. Ati, A. Samavati, S. Dabagh, S. Zare, Effects of Mg substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Co0.5Ni0.5−xMgxFe2O4 nanoparticle ferrites. Chin. Phys. B 5, 047501 (2016)
R.D. Waldron, Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. 99, 1727–1735 (1955)
O.L. Anderson, in Physics Acoustics, vol. 3BC, ed. by W.P. Mason (Academic Press, New York, 1965), p.45
C.N.R. Rao, J. Gopalkrishnan, New Directions in Solid State Chemistry (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1997)
M. Kurian, S. Thankachan, D.S. Nair, A. E. K., A. Babu, A. Thomas, B. Krishna K. T., Structural, magnetic, and acidic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesised by wet chemical methods. J. Adv. Ceram. 4(3), 199–205 (2015)
E.E. Ateia, A.A.H. El-Bassuony, G. Abdellatif, A.T. Mohamed, The impact of Ni substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Mg nano-ferrite. J. Silicon 10, 1687 (2018)
Hu. **, H.-b Yang, D.-a Pan, H. Wang, J.-J. Tian, S.-G. Zhang, X.-F. Wang, A.A. Volinsky, Heat treatment effects on microstructure and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrite powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 176, 322 (2010)
P.A. Shaikh, R.C. Kambale, A.V. Rao, Y.D. Kolekar, Effect of Ni do** on structural and magnetic properties of Co1–xNixFe1.9Mn0.1O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 718–726 (2010)
J.M.D. Coey, Rare-Earth Iron Permanent Magnets, vol. 45 (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1996), p.5526
J.M.D. Coey, Rare earth-iron permanent magnets. J. Cheminformatics. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.199211311
J. Park, K. An, Y. Hwang, J.G. Park, H.J. Noh, J.Y. Kim et al., Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 3, 891 (2004)
S. Bhukal, T. Namgyal, S. Mor, S. Bansal, S. Singhal, Structural, electrical, optical and magnetic properties of chromium substituted Co-Zn nanoferrites Cu0.6Zn0.4CrxFe2−xO4 (0≤x≤1.0) prepared via sol-gel Au-to-combustion method. J. Mol Struct. 1012, 12–167 (2012)
I. Panneer Muthuselvam, R.N. Bhowmik, Mechanical alloyed Ho3+ do** in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite and understanding of magnetic nanodomains. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 774, 322 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XH contributed to experiment, conceptualization, investigation, writing-original draft, and visualization; AS checked the manuscript; JW and YJ helped checking the tables and figures.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author states that there is no conflict of interest with other institutions (financial or non-financial, directly or indirectly related to work, in all scientific fields).
Ethical approval
The author states that the manuscript complies with the ethical rules applicable to the journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Sun, A., Wang, J. et al. Study on the structure and magnetic transformation of magnesium substituted cobalt spinel-type ferrite. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 190 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09401-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09401-4