Abstract
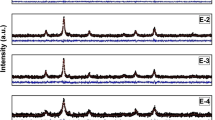
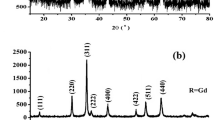
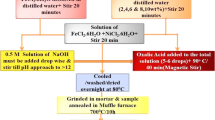
This research is the basic study of temperature-sensitive ferrite characteristics prepared by coprecipitation with do** different sizes of rare earth elements. Ni0.5Zn0.5RExFe2-xO4 (NZRF) (x = 0.02, 0.05, 0.07, and 0.09) nanoparticles (NPs) doped by Sc, Dy, and Gd prepared by chemical coprecipitation method. XRD results show that the grain size of Ni0.5Zn0.5RExFe2-xO4 is from 10.6 to 12.4 nm, which is close to the average grain size of 13.9 nm observed on TEM images. It is also found that the ferrite particles are spherical and slightly agglomerated in TEM images. FTIR results show that the NZRF has the characteristic stretching of tetrahedral and octahedral sites in spinel ferrite near 580 cm−1 and 418 cm−1. The concentrations of nickel, zinc, iron, and rare earth elements have been determined by ICP-AES, and all ions have participated in the reaction. The magnetic properties of Sc3+, Dy3+, and Gd3+-doped NZRF NPs at room temperature are recorded by a physical property measurement system (PPMS-9). It is found that the magnetization can be changed by adding rare-earth ions. All the samples exhibit very small coercivity and almost zero remanences, which indicates the superparamagnetism of the synthesized nanoparticles at room temperature (RT). When x = 0.07, Gd3+-doped Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 (NZF) exhibits the highest saturation magnetization. Magnetic properties of NZGd0.07 vary the most with temperature. The thermomagnetic coefficient of NZGd0.07 nanoparticles stabilized to 0.18 emu/gK at 0–100 °C. Hence, NZGd0.07 with low Curie temperature and the high thermomagnetic coefficient can be used to prepare temperature-sensitive ferrofluid for hyperthermia.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.C.F.M. Costa, E. Tortella, M.R. Morelli, R.H.G.A. Kiminami, Synthesis, microstructure and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn ferrites—ScienceDirect. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 256, 174–182 (2003)
A. Manohar, C. Krishnamoorthi, Structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of CaFe2O4nanocrystals prepared by solvothermal reflux method. J. Alloy. Compd. 722, 818–827 (2017)
G.V.M. Williams, T. Prakash, J. Kennedy, S.V. Chong, S. Rubanov, Spin-dependent tunnelling in magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 460, 229–233 (2018)
A. Manohar, C. Krishnamoorthi, Low Curie-transition temperature and superparamagnetic nature of Fe3O4 nanoparticles prepared by colloidal nanocrystal synthesis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 192, 235–243 (2017)
N. Raghuram, T.S. Rao, N.S. Kumar, K.C.B. Naidu, H. Manjunatha, B.R. Rao, A. Khan, A.M. Asiri, BaSrLaFe12O19 nanorods: optical and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 8022–8032 (2020)
A. Manohar, D.D. Geleta, C. Krishnamoorthi, J. Lee, Synthesis, characterization and magnetic hyperthermia properties of nearly monodisperse CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 46, 28035–28041 (2020)
A. Manohar, C. Krishnamoorthi, C. Pavithra, N. Thota, Magnetic hyperthermia and photocatalytic properties of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by solvothermal reflux method. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 34, 251–259 (2020)
K.T. Arul, E. Manikandan, P.P. Murmu, J. Kennedy, M. Henini, Enhanced magnetic properties of polymer-magnetic nanostructures synthesized by ultrasonication. J. Alloy Compd. 720, 395–400 (2017)
A. Jordan, R. Scholz, P. Wust, H. Fahling, R. Felix, Magnetic fluid hyperthermia (MFH): cancer treatment with AC magnetic field induced excitation of biocompatible superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 201, 413–419 (1999)
A. Manohar, C. Krishnamoorthi, K.C.B. Naidu, C. Pavithra, Dielectric, magnetic hyperthermia, and photocatalytic properties of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by solvothermal reflux method. Appl. Phys. A (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2760-0
A. Manohar, K. Chintagumpala, K.H. Kim, Mixed Zn–Ni spinel ferrites: Structure, magnetic hyperthermia and photocatalytic properties. Ceram. Int. 47, 7052–7061 (2021)
S.I. Ahmad, S.A. Ansari, D. Ravi Kumar, Structural, morphological, magnetic properties and cation distribution of Ce and Sm co-substituted nano crystalline cobalt ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 208, 248–257 (2018)
S.M. Ognjanovic, I. Tokic, Z. Cvejic, S. Rakic, V.V. Srdic, Structural and dielectric properties of yttrium substituted nickel ferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 49, 259–264 (2014)
A. Mallikarjuna, S. Ramesh, N.S. Kumar, K.C.B. Naidu, K.V. Ratnam, H. Manjunatha, Photocatalytic activity, negative AC-electrical conductivity, dielectric modulus, and impedance properties in 0.6 (Al0.2La0.8TiO3) + 0.4 (BiFeO3) nanocomposite. Cryst. Res. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.202000068
N.I. Abu-Elsaad, A.S. Nawara, S.A. Mazen, Synthesis, structural characterization, and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn nanoferrites substituted with different metal ions (Mn2+, Co2+, and Cu2+). J. Phys. Chem. Solids (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109620
M.A. Almessiere, A.D. Korkmaz, Y. Slimani, M. Nawaz, S. Ali, A. Baykal, Magneto-optical properties of rare earth metals substituted Co-Zn spinel nanoferrites. Ceram. Int. 45, 3449–3458 (2019)
R.K. Singh, J. Shah, R.K. Kotnala, Magnetic and dielectric properties of rare earth substituted Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe1.95R0.05O4 (R = Pr, Sm and La) ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 210, 64–69 (2016)
S.E. Jacobo, M. Arana, P.G. Bercoff, Gadolinium substitution effect on the thermomagnetic properties of Ni ferrite ferrofluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 415, 30–34 (2016)
K.K. Bamzai, G. Kour, B. Kaur, S.D. Kulkarni, Effect of cation distribution on structural and magnetic properties of Dy substituted magnesium ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 327, 159–166 (2013)
R.A. Pawar, S.M. Patange, A.R. Shitre, S.K. Gore, S.S. Jadhav, S.E. Shirsath, Crystal chemistry and single-phase synthesis of Gd3+substituted Co–Zn ferrite nanoparticles for enhanced magnetic properties. RSC Adv. 8, 25258–25267 (2018)
T.J. Shinde, A.B. Gadkari, P.N. Vasambekar, Effect of Nd3+ substitution on structural and electrical properties of nanocrystalline zinc ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2777–2781 (2010)
N. Hamdaoui, Y. Azizian-Kalandaragh, M. Khlifi, L. Beji, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Ni0.6Mg0.4Fe2O4 ferromagnetic ferrite prepared by sol gel method. Ceram. Int. 45, 16458–16465 (2019)
R. RaeisiShahraki, M. Ebrahimi, S.A. SeyyedEbrahimi, S.M. Masoudpanah, Structural characterization and magnetic properties of superparamagnetic zinc ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by the coprecipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3762–3765 (2012)
R. Kesavamoorthi, C.R. Raja, Substitution effects on rare-earth ions-doped nickel-zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 30, 1207–1212 (2016)
I. Soibam, S. Phanjoubam, H.B. Sharma, H.N.K. Sarma, C. Prakash, Magnetic studies of Li–Zn ferrites prepared by citrate precursor method. Phys. B 404, 3839–3841 (2009)
D. Makovec, A. Košak, A. Žnidaršič, M. Drofenik, The synthesis of spinel–ferrite nanoparticles using precipitation in microemulsions for ferrofluid applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 289, 32–35 (2005)
P. Pahuja, R.K. Kotnala, R.P. Tandon, Effect of rare earth substitution on properties of barium strontium titanate ceramic and its multiferroic composite with nickel cobalt ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 617, 140–148 (2014)
L.B. de Mello, L.C. Varanda, F.A. Sigoli, I.O. Mazali, Co-precipitation synthesis of (Zn-Mn)-co-doped magnetite nanoparticles and their application in magnetic hyperthermia. J. Alloy. Compd. 779, 698–705 (2019)
P. Thakur, S. Taneja, D. Sindhu, U. Lüders, A. Sharma, B. Ravelo, A. Thakur, Manganese zinc ferrites: a short review on synthesis and characterization. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 33, 1569–1584 (2020)
S. Amiri, H. Shokrollahi, Magnetic and structural properties of RE doped Co-ferrite (REåNd, Eu, and Gd) nano-particles synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 345, 18–23 (2013)
X. Wu, Z. Ding, N. Song, L. Li, W. Wang, Effect of the rare-earth substitution on the structural, magnetic and adsorption properties in cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 42, 4246–4255 (2016)
P. Scherrer, Bestimmung der Grösse und der innerenStruktur von KolloidteilchenmittelsRöntgenstrahlen. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen 26, 98 (1918)
X. Zhou, Y. Zhou, L. Zhou, J. Wei, J. Wu, D. Yao, Effect of Gd and La do** on the structure, optical and magnetic properties of NiZnCo ferrites. Ceram. Int. 45, 6236–6242 (2019)
S. Ikram, F. Ashraf, M. Alzaid, K. Mahmood, N. Amin, S.A. Haider, Role of nature of rare earth ion dopants on structural, spectral, and magnetic properties in spinel ferrites. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05723-8
Z. Liu, Z. Peng, C. Lv, X. Fu, Do** effect of Sm 3+ on magnetic and dielectric properties of Ni-Zn ferrites. Ceram. Int. 43, 1449–1454 (2017)
C.C. Naik, A.V. Salker, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Dy3+ and Sm3+ substituted Co–Cu ferrite. Mater. Res. Express (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab0dd0
Z. Bitar, W. Abdeen, R. Awad, Effect of Er~(3+) and Pr~(3+) on the structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Zn-Co ferrite synthesised via co-precipitation method. Mater. Res. Innov. 24, 104–112 (2020)
M. Sertkol, Y. Köseoğlu, A. Baykal, H. Kavas, A. Bozkurt, M.S. Toprak, Microwave synthesis and characterization of Zn-doped nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 486, 325–329 (2009)
F. Moravvej-Farshi, M. Amishi, K.A. Nekouee, Influence of different milling time on synthesized Ni–Zn ferrite properties by mechanical alloying method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 13610–13619 (2020)
M. Kumari, M.C. Bhatnagar, Study of the effect of Pr do** on structural, morphological and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 32, 1027–1033 (2018)
G. Umapathy, G. Senguttuvan, L.J. Berchmans, V. Sivakumar, P. Jegatheesan, Influence of cerium substitution on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrites synthesized by combustion method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 17505–17515 (2017)
V. JagadeeshaAngadi, B. Rudraswamy, K. Sadhana, S.R. Murthy, K. Praveena, Effect of Sm3+ –Gd3+ on structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrites synthesized via combustion route. J. Alloy. Compd. 656, 5–12 (2016)
X. Zhao, A. Sun, W. Zhang, Y. Han, X. Pan, Effects of Mg substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Ni0.2MgxCo0.8−xFe2O4 nanoparticle ferrites. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 32, 2589–2598 (2019)
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A. DemirKorkmaz, S. Guner, A. Baykal, S.E. Shirsath, I. Ercan, P. Kogerler, Sonochemical synthesis of Dy3+ substituted Mn0.5Zn0.5Fe2-xO4 nanoparticles: structural, magnetic and optical characterizations. Ultrason. Sonochem. 61, 104836–104836 (2019)
A. Kumar, P.S. Rana, M.S. Yadav, R.P. Pant, Effect of Gd3+ ion distribution on structural and magnetic properties in nano-sized Mn–Zn ferrite particles. Ceram. Int. 41, 1297–1302 (2015)
V. Verma, R.K. Kotnala, V. Pandey, P.C. Kothari, L. Radhapiyari, B.S. Matheru, The effect on dielectric losses in lithium ferrite by cerium substitution. J. Alloy. Compd. 466, 404–407 (2008)
S. Joshi, M. Kumar, H. Pandey, M. Singh, P. Pal, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Gd3+ substituted NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 768, 287–297 (2018)
S. Aslam, M.S. Shifa, Z.A. Gilani, H.M. Noor ul Huda Khan Asghar, M.N. Usmani, J.U. Rehman, M. Azhar Khan, A. Perveen, M. Khalid, Structural, optical and magnetic elucidation of co-do** of Nd3+ and Pr3+ on lithium nanoferrite and its technological application. Results Phys. 12, 1334–1339 (2019)
J. Hu, Y. Ma, X. Kan, C. Liu, X. Zhang, R. Rao, M. Wang, G. Zheng, Investigations of Co substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Ni-Zn spinel ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167200
C.C. Chauhan, A.R. Kagdi, R.B. Jotania, A. Upadhyay, C.S. Sandhu, S.E. Shirsath, S.S. Meena, Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Co-Zr substituted M-type calcium hexagonal ferrite nanoparticles in the presence of α-Fe2O3 phase. Ceram. Int. 44, 17812–17823 (2018)
T.A. Nhlapo, T. Moyo, The effect of particle size on structural and magnetic properties of Sm3+ ion substituted Zn-Mnnanoferrites synthesized by glycol-thermal method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167096
S. Urcia-Romero, O. Perales-Pérez, G. Gutiérrez, Effect of Dy-do** on the structural and magnetic properties of Co–Zn ferrite nanocrystals for magnetocaloric applications. J. Appl. Phys. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3338847
Acknowledgements
One part of this work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China [NSFC 21976039].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Analysis, Data curation, Writing, JP: data curation, FG, DZ, FQ and CH: Discussion of the experiment, GD: Correction of writing, YW: Conceptualization, TF: Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Pan, J., Gao, F. et al. Structure and magnetic properties of coprecipitated nickel-zinc ferrite-doped rare earth elements of Sc, Dy, and Gd. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 13511–13526 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05928-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05928-0