Abstract
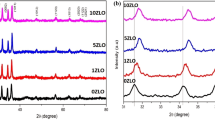
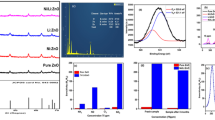
The present work focuses on the deposition of ZnO thin films on crystalline and porous Germanium substrates for hazardous gas detection. The porous Ge substrates were obtained by means of surface exfoliation by using H+ implantation and subsequent annealing. Morphological analysis revealed the formation of pores in the range between 1 and 5 µm. The deposition of ZnO thin films has been made on crystalline and porous Ge substrates utilizing the dip coating method. Structural and morphological characterizations confirmed the formation of highly porous polycrystalline ZnO film exclusively on porous Ge substrates. All the obtained samples were tested for their sensitivities at 0.1, 0.5, 1 and 2% of CO2 concentrations. The ZnO films deposited on porous Ge exhibited an increment of sensing response by a factor of 2, which is correlated to the increment of the superficial area induced by the substrate. Maximum sensing response ~ 50% was achieved for 2% of CO2 when measured at 300 °C. ZnO over porous Ge films showed complete resistance recovery, whereas ZnO over crystalline Ge showed a drift in the recovery resistance. ZnO deposited porous Ge showed the fastest response and recovery time ~ 25 and 10 s, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
I.J. Church, A.L. Parsons, Modified atmosphere packaging technology: a review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 67(2), 143–152 (1995)
Dansk geologisk forening, Bulletin of the Geological Society of Denmark. Geological Society of Denmark
J. Etoh, S. Taguchi, E. Izawa, Gas measurement of fluid inclusions from the Hishikari epithermal gold deposit, Southern Kyushu, Japan, Using Laser Raman Microprobe. Resour. Geol. 52(4), 405–408 (2002)
J.G. Allen, P. MacNaughton, U. Satish, S. Santanam, J. Vallarino, J.D. Spengler, Associations of cognitive function scores with carbon dioxide, ventilation, and volatile organic compound exposures in office workers: a controlled exposure study of green and conventional office environments. Environ. Health Perspect. 124, 6 (2015)
W.J. Fisk, A.H. Rosenfeld, Estimates of improved productivity and health from better indoor environments. Indoor Air 7(3), 158–172, (1997)
K. Küsel, T. Dorsch, Effect of supplemental electron donors on the microbial reduction of Fe(III), sulfate, and CO2 in coal mining–impacted freshwater lake sediments. Microb. Ecol. 40(3), 238–249
I. Chemistry, C. Division, Chemo—resistive CO2 gas sensor based on CuO–SnO2 heterojunction nanocomposite material, pp. 8–10, 2015
P.M. Shirage, K. Rana, Y. Kumar, S. Sen, RSC Advances a simple wet chemical method as excellent materials for CO and CO2 gas sensing. RSC Adv. 6, 82733–82742 (2016)
T. Wagner, S. Haffer, C. Weinberger, D. Klaus, M. Tiemann, Mesoporous materials as gas sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. Chem. Soc. Rev 42(42), 4036–4053 (2013)
T.V.K. Karthik, M. De La, L. Olvera, A. Maldonado, V. Velumurugan, Sensing properties of undoped and Pt-doped SnO2 thin films deposited by chemical spray. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 37, 143–150 (2015)
T.V.K. Karthik, A. Maldonado, Manufacturing of tin oxide pellets and their application for CO and C3H8 gas sensors.
A.P. Rambu, L. Ursu, N. Iftimie, V. Nica, M. Dobromir, F. Iacomi, Study on Ni-doped ZnO films as gas sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 280, 598–604 (2013)
G.F. Fine, L.M. Cavanagh, A. Afonja, R. Binions, Metal oxide semi-conductor gas sensors in environmental monitoring. Sensors 10(6), 5469–5502 (2010)
H. Shokry Hassan, A.B. Kashyout, I. Morsi, A.A.A. Nasser, I. Ali, Synthesis, characterization and fabrication of gas sensor devices using ZnO and ZnO: In nanomaterials. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 3(3), 216–221 (2014)
A. Gankanda, D.M. Cwiertny, V.H. Grassian, Role of atmospheric CO2 and H2O adsorption on ZnO and CuO nanoparticle aging: formation of new surface phases and the impact on nanoparticle dissolution. J. Phys. Chem. C 120(34), 19195–19203 (2016)
H. Shokry Hassan, A.B. Kashyout, H.M.A. Soliman, M.A. Uosif, N. Afify, Effect of reaction time and Sb do** ratios on the architecturing of ZnO nanomaterials for gas sensor applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 277, 73–82 (2013)
N. Van Hieu, N.D. Khoang, D.D. Trung, L.D. Toan, N. Van Duy, N.D. Hoa, Comparative study on CO2 and CO sensing performance of LaOCl-coated ZnO nanowires. J. Hazard. Mater. 244, 209–216 (2013)
D.H. Kim, J.Y. Yoon, H.C. Park, K.H. Kim, CO2-sensing characteristics of SnO2 thick film by coating lanthanum oxide. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 62(1), 61–66 (2000)
L. Martínez, J.T. Holguín-Momaca, T.V.K. Karthik, S.F. Olive-Méndez, J. Campos-Alvarez, V. Agarwal, Sputtering temperature dependent growth kinetics and CO2 sensing properties of ZnO deposited over porous silicon. Superlattices Microstruct. 98, 8–17 (2016)
J.M. Zahler, A. Fontcuberta i Morral, M.J. Griggs, H.A. Atwater, Y.J. Chabal, Role of hydrogen in hydrogen-induced layer exfoliation of germanium. Phys. Rev. B 75(3), 35309 (2007)
S. Hayashi, D. Bruno, M.S. Goorsky, Temperature dependence of hydrogen-induced exfoliation of InP. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(2), 236–238 (2004)
J. Lee, C. Lee, H.-E. Song, B.-Y. Jang, W. Yoon, Acoustic emission characterization of hydrogen-induced exfoliation of silicon. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 8(1), 62–65 (2016)
A.J. Pitera, E.A. Fitzgerald, Hydrogen gettering and strain-induced platelet nucleation in tensilely strained Si0.4Ge0.6/Ge for layer exfoliation applications. J. Appl. Phys. 97(10), 104511 (2005)
C.M. Varma, Hydrogen-implant induced exfoliation of silicon and other crystals. App. Phys. Letters 71, 3419 (1998)
J.M. Zahler, C.-G. Ahn, S. Zaghi, H.A. Atwater, C. Chu, P. Iles, Ge layer transfer to Si for photovoltaic applications. Thin Solid Films 403–404, 558–562 (2002)
X. **a, J. Tu, Y. Zhang, X. Wang, C. Gu, X.B. Zhao, H.J. Fan, High-quality metal oxide core/shell nanowire arrays on conductive substrates for electrochemical energy storage. ACS Nano 6(6), 5531–5538 (2012)
M. Balucani, P. Nenzi, E. Chubenko, A. Klyshko, V. Bondarenko, Electrochemical and hydrothermal deposition of ZnO on silicon: from continuous films to nanocrystals. J. Nanoparticle Res. 13(11), 5985–5997 (2011)
Q. Ma, B. Zhai, Y.M. Huang, Sol–gel derived ZnO/porous silicon composites for tunable photoluminescence. J. Sol–Gel Sci. Technol. 64(1), 110–116 (2012)
N. Rusli, M. Tanikawa, M. Mahmood, K. Yasui, A. Hashim, Growth of high-density zinc oxide nanorods on porous silicon by thermal evaporation. Materials (Basel) 5(12), 2817–2832 (2012)
T. Prakash, G. Neri, A. Bonavita, E. Ranjith Kumar, K. Gnanamoorthi, Structural, morphological and optical properties of Bi-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by microwave irradiation method. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 4913 (2015)
S.M. Pawar, B.S. Pawar, J.H. Kim, O.S. Joo, C.D. Lokhande, Recent status of chemical bath deposited metal chalcogenide and metal oxide thin films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11(2), 117–161 (2011)
P. O’Brien, T. Saeed, J. Knowles, Speciation and the nature of ZnO thin films from chemical bath deposition J. Mater. Chem. 6(7), 1135–1139, 1996
S. Dalui, S.N. Das, R.K. Roy, R.N. Gayen, A.K. Pal, Aligned zinc oxide nanorods by hybrid wet chemical route and their field emission properties. Thin Solid Films 516(23), 8219–8226 (2008)
D. harvey, Chapter 8 Gravimetric Methods 8A Overview of Gravimetric Methods 8B Precipitation Gravimetry 8C Volatilization Gravimetry 8D Particulate Gravimetry 8E Key Terms 8F Chapter Summary 8G Problems 8H Solutions to Practice Exercises.
T.V.K. Karthik, M. de la L. Olvera, A. Maldonado, Sensors based on tin oxide pellets. Sens. Lett. 12(10), 1513–1518 (2014)
U. Dadwal, M. Reiche, R. Singh (2012). Ion implantation-induced layer splitting of semiconductors, ion implantation, Mark Goorsky (Ed.), InTech, 10.5772/35956. https://mts.intechopen.com/books/ion-implantation/ion-implantation-induced-layer-splitting-of-semiconductors
S.O. Kucheyev, J.S. Williams, S.J. Pearton, Ion implantation into GaN, Mater. Sci. Eng. 33(2–3), 51–108, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-796X(01)00028-6 (2001)
G. Angélica, A. Hernández, White luminescence emission from silicon implanted germanium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 428, 1098–1105 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.09.234. ISSN 0169–4332
Q.-Y. Tong, K. Gutjahr, S. Hopfe, U. Gösele, T.-H. Lee, Layer splitting process in hydrogen-implanted Si, Ge, SiC, and diamond substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 1390 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.118586
M.L. David, F. Pailloux, M. Drouet, M.F. Beaufort, J.F. Barbot, E. Simoen, C. Claeys, Solid State Phenomena 131–133, 101–106 (2008)
C. **g, C. Zhang, X. Zang, W. Zhou, W. Bai, T. Lin, J. Chu, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 10, 065001 (2009)
D.N. Montenegro, V. Hortelano, O. Martíınez, M.C. Martíez-Tomas, V. Sallet, V. Muñoz-Sanjosé, J. Jiménez. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 46, 235302 (2013)
C. Bundesmann, N. Ashkenov, M. Schubert, D. Spemann, T. Butz, E.M. Kaidashev, M. Lorenz, M. Grundmann, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83(10), 8 (2003)
K. Prashant, R.K. Sharma, R.J. Dutta, A. C. Pandey, CrystEngComm 15, 4438 (2013)
X.-B. Leah Bergman, J. Chen, J.L. Huso, Morrison, H. Hoeck, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 093507 (2005)
S. Kuriakose, B. Satpati, S. Mohapatra, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 12741 (2014)
R. Cuscó, B. Wang, M.J. Callahan, E. Alarcón-Lladó, J. Ibáñez, L. Artús, J. Jiménez. Phys. Rev. B 75, 165202 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Mexican National Council for Science and Technology (CONACYT), Project No. CB-254903. Authors would like to thank to PRODEP for their financial support by the project UAEH-PTC-801 No. 511-6/18-8661. A special thanks to Ph.D student Cecilia Salinas-Fuentes for her assistance in SEM measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernandez, A.G., Kudriavtsev, Y., Karthik, T.V.K. et al. Optimization of Ge substrates for ZnO deposition and their application for CO2 detection. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 6660–6668 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00975-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00975-0