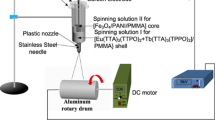
Abstract
At present, the nanobelts with coaxial or Janus structure, which provide at most two subareas, have been reported. The nanobelts with more than two subareas have not been proposed. Here, we report the flexible, especial-structured Janus nanobelts array pellicle that has three functions of anisotropically electrical conduction, superparamagnetism and photoluminescence. Each especial-structured Janus nanobelt comprises a photoluminescent-superparamagnetic dual functional [Fe3O4/polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)]@[Tb(BA)3phen/PMMA] co-axis nanobelt and an adjacent conductive polyaniline (PANI)/PMMA nanobelt. In addition, all the especial-structured Janus nanobelts are ordered in the same orientation to form a two-dimensional (2D) array pellicle. The conduction along the length orientation can reach 108 higher than that in the width orientation (two vertical orientations), and thus, the array pellicle has outstanding anisotropically electric conductance. Moreover, we can adjust the degree of electroconductive anisotropy of the specimens by changing the amount of PANI. Under the 281-nm excitation, the main green light emission at 545 nm was clearly observed in the Janus nanobelts array pellicle. Furthermore, the Janus nanobelts array pellicle also combines with excellent tunable superparamagnetism. The concept and manufacturing technology of the novel Janus nanobelts array pellicle provide a simple method to preparing multifunctional pellicle.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.M. Zhang, J. Yang, Z.W. Quan, P.P. Yang, C.X. Li, Z.Y. Hou, J. Lin, Cryst. Growth Des. 9, 2725–2733 (2009)
R. Bhandari, M.R. Knecht, Langmuir 28, 8110–8119 (2012)
M.J. Yim, K.W. Paik, IEEE T. Comp. Pack. Man. 21, 233–242 (1997)
J.H. Liu, R. Yang, S.M. Li, J. Environ. Sci. 18, 979–982 (2006)
N.I. Kovtyukhova, T.E. Mallouk, J. Phys. Chem. B. 109, 2540–2545 (2005)
C. Feng, K. Liu, J.S. Wu, L. Liu, J.S. Cheng, Y.Y. Zhang, Y.H. Sun, Q.Q. Li, S.S. Fan, K.L. Jiang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 885–891 (2010)
J.R. Huang, Y.T. Zhu, W. Jiang, Q.X. Tang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 1754–1758 (2014)
W.A.D. Heer, A. Chatelain, D. Ugarte, Science 270, 1179–1181 (1995)
Q.L. Ma, J.X. Wang, X.T. Dong, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 2436–2443 (2015)
Q.L. Ma, W.S. Yu, X.T. Dong, M. Yang, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, Sci. Rep. 5, 14583 (2015)
L. Han, M.M. Pan, Y. Lv, Y.T. Gu, X.F. Wang, D. Li, Q.L. Kong, X.T. Dong, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Eletron. 26, 677–684 (2015)
X. **, Q.L. Ma, M. Yang, X.T. Dong, J.X. Wang, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Eletron. 25, 4024–4032 (2014)
J. Tian, Q.L. Ma, W.S. Yu, X.T. Dong, Y. Yang, B. Zhao, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, New J. Chem. 41, 13983–13992 (2017)
Y.T. Geng, P. Zhang, Q.T. Wang, Y.X. Liu, K. Pan, J. Mater. Chem. B 5, 5390–5396 (2017)
C. Luo, X.X. Wang, J.Q. Wang, K. Pan, Compos. Sci. Technol. 133, 97–103 (2016)
X.B. Li, Q.L. Ma, J. Tian, X. **, D. Li, X.T. Dong, W.S. Yu, X.L. Wang, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, Nanoscale 9, 18918–18930 (2017)
N. Lv, Z.G. Wang, W.Z. Bi, G.M. Li, J.L. Zhang, J.Z. Ni, J. Mater. Chem. B 4, 4402–4409 (2016)
N. Lv, G.M. Li, X. Wang, J.L. Zhang, J.Z. Ni, J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 11926–11931 (2017)
P. Zhang, C.L. Shao, X.H. Li, M.Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, C.Y. Su, N. Lu, K.X. Wang, Y.C. Liu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 25, 10453–10458 (2013)
Y.C. Chou, C.L. Shao, X.H. Li, C.Y. Su, H.C. Xu, M.Y. Zhang, P. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y.C. Liu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 285, 509–516 (2013)
K. Lun, Q.L. Ma, M. Yang, X.T. Dong, Y. Yang, J.X. Wang, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Eletron. 26, 5994–6003 (2015)
Q.L. Ma, J.X. Wang, X.T. Dong, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, Chem. Eng. J. 222, 16–22 (2013)
H. Shao, Q.L. Ma, X.T. Dong, W.S. Yu, M. Yang, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 21845–21855 (2015)
Q.L. Ma, J.X. Wang, X.T. Dong, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, Nanoscale 6, 2945–2952 (2014)
X. **, J.X. Wang, X.T. Dong, Q.L. Ma, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, Chem. Eng. J. 254, 259–267 (2014)
X. **, Q.L. Ma, X.T. Dong, D. Li, W.S. Yu, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Eletron. 29, 7119–7129 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51573023, 50972020), Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (20170101101JC, 20180520011JH), Industrial Technology Research and Development Project of Jilin Province Development and Reform Commission (2017C052-4), Science and Technology Research Planning Project of the Education Department of Jilin Province during the 13th 5-year plan period (JJKH20170608KJ, JJKH20181122KJ), and Innovative Foundation (XJJLG-2017-04) and Youth Foundation (XQNJJ-2016-01, XQNJJ-2017-17) of Changchun University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
**, X., Yu, W., Li, D. et al. Employing novel Janus nanobelts to achieve anisotropic conductive array pellicle functionalized by superparamagnetism and green fluorescence. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 4219–4230 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00713-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00713-6