Abstract
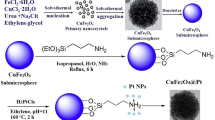
We have developed a facile three-step fabricating procedure whereby uniformly dispersed and highly catalytically active PtPd bimetal nanoparticles (NPs) were tightly tethered to the catalytically active and superparamagnetic CuFe2O4 submicrospheres. The obtained CuFe2O4@PtPd composite catalyst with core-satellite structure was characterized by TEM, HAADF-STEM, XRD and XPS. For comparison, structurally similar CuFe2O4@Pt and CuFe2O4@Pd were also prepared by the same method. Their catalytic properties for reduction of p-nitrothiophenol (p-NTP) by NaBH4 were comparatively studied and the enhanced catalytic mechanism was tentatively explained. The results indicate that the inherent catalytic activity of CuFe2O4 can be obviously heightened when Pt, Pd and PtPd alloy NPs are attached to its surface, respectively. However, the catalytic performance of CuFe2O4@PtPd is enhanced more prominently than that of CuFe2O4@Pt and CuFe2O4@Pd. The significantly enhanced activity by loading PtPd NPs compared to that by loading Pt or Pd NPs is mainly attributed to: (1) PtPd NPs with smaller size are uniformly and strongly bound to the CuFe2O4 and effectively boost their synergistic catalysis. (2) The electronic coupling effect in PtPd alloy NPs may play a more important part in enhancing the catalytic activity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hudson R, Feng Y, Varma R, Moores A (2014) Bare magnetic nanoparticles: sustainable synthesis and applications in catalytic organic transformations. Green Chem 16:4493–4505
Bai S, Shen X, Zhong X, Liu Y, Zhu G, Xu X, Chen K (2012) One-pot solvothermal preparation of magnetic reduced graphene oxide-ferrite hybrids for organic dye removal. Carbon 50:2337–2346
Li M, **ong Y, Liu X, Bo X, Zhang Y, Han C, Guo L (2015) Facile synthesis of electrospun MFe2O4 (M = Co, Ni, Cu, Mn) spinel nanofibers with excellent electro-catalytic properties for oxygen evolution and hydrogen peroxide reduction. Nanoscale 7:8920–8930
Ren Y, Lin L, Ma J, Yang J, Feng J, Fan Z (2015) Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by magnetic ferrospinel MFe2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn) as heterogeneous catalysts in the water. Appl Catal B 165:572–578
Chen M, Mo L, Cui Z, Zhang Z (2019) Magnetic nanocatalysts: synthesis and application in multicomponent reactions. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 15:27–37
Zhang Q, Yang X, Guan J (2019) Applications of magnetic nanomaterials in heterogeneous catalysis. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:4681–4697
Baruwati B, Guin D, Manorama S (2007) Pd on surface-modified NiFe2O4 nanoparticles: a magnetically recoverable catalyst for Suzuki and Heck reactions. Org Lett 9:5377–5380
Demirelli M, Karaoğlu E, Baykal A, Sözeri H, Uysal E (2014) Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of CoFe2O4-APTES-Pd magnetic recyclable catalyst. J Alloys Comp, 582201−582207
Saire-Saire S, Barbosa E, Garcia D, Andrade L, Garcia-Segura S, Camargo P, Alarcon H (2019) Green synthesis of Au decorated CoFe2O4 nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and dimethylphenylsilane oxidation. RSC Adv 9:22116–22123
Sun W, Qiao K, Liu J, Cao L, Gong X, Yang J (2016) Pt-doped NiFe2O4 spinel as a highly efficient catalyst for H2 selective catalytic reduction of NO at room temperature. ACS Comb Sci 18:195–202
Chen Z, Wang L, Xu H, Wen Q (2020) Efficient heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by modified CuFe2O4 for degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A. Chem Eng J 389:124345
Gholinejad M, Aminianfar A (2015) Palladium nanoparticles supported on magnetic copper ferrite nanoparticles: the synergistic effect of palladium and copper for cyanation of aryl halides with K4[Fe(CN)6]. J Mol Catal A 397:106–113
Goyal A, Bansal S, Singhal S (2014) Facile reduction of nitrophenols: comparative catalytic efficiency of MFe2O4 (M = Ni, Cu, Zn) nano ferrites. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:4895–4908
Li Y, Shen J, Hu Y, Qiu S, Min G, Song Z, Sun Z, Li C (2015) General flame approach to chainlike MFe2O4 spinel (M = Cu, Ni Co, Zn) nanoaggregates for reduction of nitroaromatic compounds. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:9750–9757
Dey C, De D, Nandi M, Goswami M (2020) A high performance recyclable magnetic CuFe2O4 nanocatalyst for facile reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Mater Chem Phy 242:122237
Amini M, Kafshdouzsani M, Akbari A, Gautam S, Shim C, Chae K (2018) Spinel copper ferrite nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and catalytic activity. Appl Organomet Chem 32:e4470
Zarei M (2020) CuFe2O4 nanoparticles catalyze the reaction of alkynes and nitrones for the synthesis of 2-azetidinones. New J Chem 44:17341–17345
Wang L, Hu G, Wang Z, Wang B, Song Y, Tang H (2015) Highly efficient and selective degradation of methylene blue from mixed aqueous solution by using monodisperse CuFe2O4 nanoparticles. RSC Adv 5:73327–73332
Feng J, Su L, Ma Y, Ren C, Guo Q, Chen X (2013) CuFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles: a simple and efficient catalyst for the reduction of nitrophenol. Chem Eng J 221:16–24
Jiang HL, Xu Q (2011) Recent progress in synergistic catalysis over heterometallic nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 21:13705–13725
Guo Y, Zhang L, Liu X, Li B, Tang D, Liu W, Qin W (2016) Synthesis of magnetic core-shell carbon dots@MFe2O4 (M = Mn, Zn and Cu) hybrid materials and their catalytic properties. J Mater Chem A 4:4044–4055
Wang J, Yu B, Wang W, Cai X (2019) Facile synthesis of carbon dots-coated CuFe2O4 nanocomposites as a reusable catalyst for highly efficient reduction of organic pollutants. Catal Commun 126:35–39
Zhao Y, He G, Dai W, Chen H (2014) High catalytic activity in the phenol hydroxylation of magnetically separable CuFe2O4-reduced graphene oxide. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:12566–12574
Guo X, Wang K, Li D, Qin J (2017) Heterogeneous photo-Fenton processes using graphite carbon coating hollow CuFe2O4 spheres for the degradation of methylene blue. Appl Sur Sci 420:792–801
Wang L, Bock D, Li J, Stach E, Marschilok A, Takeuchi K, Takeuch E (2018) Synthesis and characterization of CuFe2O4 nano/submicron wire-carbon nanotube composites as binder-free anodes for Li-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:8770–8785
Ma S, Feng J, Qin W, Ju Y, Chen X (2015) CuFe2O4@PDA magnetic nanomaterials with a core-shell structure: synthesis and catalytic application in the degradation of methylene blue in water. RSC Adv 5:53514–53523
Manikandan V, Mirzaei A, Sikarwar S, Yadav B, Vigneselvan S, Vanitha A, Chandrasekaran J (2020) The rapid response and high sensitivity of a ruthenium-doped copper ferrite thin film (Ru-CuFe2O4) sensor. RSC Adv 10:13611–13615
Zhao C, Lan W, Gong H, Bai J, Ramachandran R, Liu S, Wang F (2018) Highly sensitive acetone-sensing properties of Pt-decorated CuFe2O4 nanotubes prepared by electrospinning. Ceram Int 44:2856–2863
Kumar A, Srivastava R (2020) Pd-decorated magnetic spinels for selective catalytic reduction of furfural: interplay of a framework-substituted transition metal and solvent in selective reduction. ACS Appl Energy Mater 3:9928–9939
Lin L, Cui H, Zeng G, Chen M, Zhang H, Xu M, Shen X, Bortolini C, Dong M (2013) Ag-CuFe2O4 magnetic hollow fibers for recyclable antibacterial materials. J Mater Chem B 1:2719–2723
Li Z, Guo C, Lyu J, Hu Z, Ge M (2019) Tetracycline degradation by persulfate activated with magnetic Cu/CuFe2O4 composite: efficiency, stability, mechanism and degradation pathway. J Hazard Mater 373:85–96
Gu Z, Li S, **ong Z, Xu H, Gao F, Du Y (2018) Rapid synthesis of platinum-ruthenium bimetallic nanoparticles dispersed on carbon support as improved electrocatalysts for ethanol oxidation. J Colloid Interface Sci 521:111–118
Ye W, Yu J, Zhou Y, Gao D, Wang D, Wang C, Xue D (2016) Green synthesis of Pt-Au dendrimer-like nanoparticles supported on polydopamine-functionalized graphene and their high performance toward 4-nitrophenol reduction. Appl Catal B 181:371–378
Rong H, Cai S, Niu Z, Li Y (2013) Composition-dependent catalytic activity of bimetallic nanocrystals: AgPd-catalyzed hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. ACS Catal 3:1560–1563
Censabella M, Torrisi V, Boninelli S, Bongiorno C, Grimaldi MG, Ruffino F (2019) Laser ablation synthesis of mono- and bimetallic Pt and Pd nanoparticles and fabrication of Pt-Pd/Graphene nanocomposites. Appl Surf Sci 475:494–503
Zhang H, Xu L, Tian Y, Jiao A, Li S, Liu X, Chen M, Chen F (2019) Convenient synthesis of 3D fluffy PtPd nanocorals loaded on 2D h-BN supports as highly efficient and stable electrocatalysts for alcohol oxidation reaction. ACS Omega 4:11163–11172
Zhang P, Li R, Huang Y, Chen Q (2014) A novel approach for the in situ synthesis of Pt-Pd nanoalloys supported on Fe3O4@C core-shell nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic activity for reduction reactions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:2671–2678
Cheng C, Wen Y, Xu X, Gu H (2009) Tunable synthesis of carboxyl-functionalized magnetite nanocrystal clusters with uniform size. J Mater Chem 19:8782–8788
Guo S, Dong S, Wang E (2009) A general route to construct diverse multifunctional Fe3O4/metal hybrid nanostructures. Chem Eur J 15:2416–2424
Du X, Luo S, Du H, Tang M, Huang X, Shen P (2016) Monodisperse and self-assembled Pt-Cu nanoparticles as an efficient electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation reaction. J Mater Chem A 4:1579–1585
Yuan M, Liu A, Zhao M, Dong W, Zhao T, Wang J, Tang W (2014) Bimetallic PdCu nanoparticle decorated three-dimensional grapheme hydrogel for non-enzymatic amperometric glucose sensor. Sens Actuators B 190:707–714
Pan Y, Guo X, Li M, Liang Y, Wu Y, Wen Y, Yang H (2015) Construction of dandelion-like clusters by PtPd nanoseeds for elevating ethanol eletrocatalytic oxidation. Electrochim Acta 159:40–45
Yao K, Zhao C, Wang N, Li T, Lu W, Wang J (2020) An aqueous synthesis of porous PtPd nanoparticles with reversed bimetallic structures for highly efficient hydrogen generation from ammonia borane hydrolysis. Nanoscale 12:638–647
Wu J, Shan S, Cronk H, Chang F, Kareem H, Zhao Y, Luo J, Petkov V, Zhong C (2017) Understanding composition-dependent synergy of PtPd alloy nanoparticles in electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reaction. J Phys Chem C 121:14128–14136
Zheng Y, Qiao J, Yuan J, Shen J, Wang A, Huang S (2018) Controllable synthesis of PtPd nanocubes on grapheme as advanced catalysts for ethanol oxidation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43:4902–4911
Zhang Y, Bu L, Jiang K, Guo S, Huang X (2016) Concave Pd-Pt core-shell nanocrystals with ultrathin Pt shell feature and enhanced catalytic performance. Small 12:706–712
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2018JM2032) and the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (No. 2020ZDLGY11-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Dale Huber.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Liu, Y., Du, Q. et al. PtPd alloy nanoparticles supported on CuFe2O4 submicrospheres with enhanced synergistic catalysis for reduction of p-nitrothiophenol. J Mater Sci 57, 18827–18838 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07770-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07770-z