Abstract
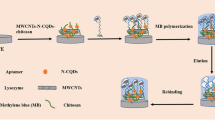
This paper demonstrated a new method for preparing fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) for specific recognition of a target protein. The MIP-based fluorescent receptor was developed by coating MIP layer on the surface of l-cysteine modified Mn2+-doped ZnS quantum dots (QDs) using the surface molecular imprinting process. These MIP-QDs composites demonstrated fast adsorption kinetics, high stability, and good dispersibility in aqueous media. Since the fluorescence quenching of MIP-QDs composites is proportional to the concentration of the lysozyme, the MIP-based fluorescent receptor was successfully applied to the direct fluorescence quantification of lysozyme without further pretreatment. The MIP-based fluorescent receptor exhibited good selectivity and sensitivity for lysozyme detection. The optimum fluorescence intensity of the MIP-QDs was found to be at pH 6.0, and the linear range of lysozyme was from 0.1 to 2.0 μM with the detection limit of 25.2 nM. Moreover, the proposed fluorescent receptor was satisfactorily applied to the determination of lysozyme in real samples. This study provides a new approach for recognizing and detecting of specific proteins in biological samples.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harrison JF, Lunt GS, Scott P, Blainey JD (1968) Urinary lysozyme, ribonuclease, and low-molecular-weight protein in renal disease. Lancet 1:371–375
Cheng AKH, Ge B, Yu HZ (2007) Aptamer-based biosensors for label-free voltammetric detection of lysozyme. Anal Chem 79:5158–5164
Levinson SS, Elin RJ, Yam L (2002) Light chain proteinuria and lysozymuria in a patient with acute monocytic leukemia. Clin Chem 48:1131–1132
Carstens C, Deckwart M, Webber-Witt M, Schäfer V, Eichhorn L, Brockow K, Fischer M, Christmann M, Paschke-Kratzin A (2014) Evaluation of the efficiency of enological procedures on lysozyme depletion in wine by an indirect ELISA method. J Agric Food Chem 62:6247–6253
Viadl ML, Gautron J, Nys Y (2005) Development of an ELISA for quantifying lysozyme in hen egg white. J Agric Food Chem 53:2379–2385
Cai Z, Chen G, Huang X, Ma M (2011) Determination of lysozyme at the nanogram level in chicken egg white using Resonance Rayleigh-scattering method with Cd-doped ZnSe quantum dots as probe. Sensor Actuat B Chem 157:368–373
Lu X, Luo Z, Liu C, Zhao S (2008) Resonance Rayleigh scattering for detection of proteins in HPLC. J Sep Sci 31:2988–2993
Sener G, Ozgur E, Yilmaz E, Uzun L, Say R, Denizli A (2010) Quartz crystal microbalance based nanosensor for lysozyme detection with lysozyme imprinted nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 26:815–821
Mihai I, Vezeanu A, Polonschii C, Albu C, Radu G-L, Vasilescu A (2015) Label-free detection of lysozyme in wines using an aptamer based biosensor and SPR detection. Sensors Actuat B Chem 206:198–204
Chen YM, Yu CJ, Cheng TL, Tseng WL (2008) Colorimetric detection of lysozyme based on electrostatic interaction with human serum albumin-modified gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 24:3654–3660
Liu S, Na W, Pang S, Shi F, Su X (2014) A label-free fluorescence detection strategy for lysozyme assay using CuInS(2) quantum dots. Analyst 139:3048–3054
Li S, Gao Z, Shao N (2014) Non-covalent conjugation of CdTe QDs with lysozyme binding DNA for fluorescent sensing of lysozyme in complex biological sample. Talanta 129:86–92
Kondekova M, Maier V, Ginterova P, Marak J, Sevcik J (2014) Analysis of lysozyme in cheese samples by on-line combination of capillary zone electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Food Chem 153:398–440
Liao YH, Brown MB, Martin GP (2001) Turbidimetric and HPLC assays for the determination of formulated lysozyme activity. J Pharmacy and Pharmacology 53:549–554
Rodriguez MC, Rivas GA (2009) Label-free electrochemical aptasensor for the detection of lysozyme. Talanta 78:212–216
Rohrbach F, Karadeniz H, Erdem A, Famulok M, Mayer G (2012) Label-free impedimetric aptasensor for lysozyme detection based on carbon nanotube-modified screen-printed electrodes. Anal Biochem 421:454–459
Vasilescu A, Gaspar S, Mihai I, Tache A, Litescu SC (2013) Development of a label-free aptasensor for monitoring the self-association of lysozyme. Analyst 138:3530–3537
Wang J, Liu B (2009) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer between an anionic conjugated polymer and a dye-labeled lysozyme aptamer for specific lysozyme detection. Chem Commun 17:2284–2286. doi:10.1039/B820001G
Pellegrino L, Tirelli A (2000) A sensitive HPLC method to detect hen’s egg white lysozyme in milk and dairy products. Int Dairy J 10:435–442
Kondeková M, Maierb V, Ginterováb P, Marák J (2014) Analysis of lysozyme in cheese samples by on-line combination of capillary zone electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Food Chem 153:398–404
Erdema A, Eksina E, Mutia M (2014) Chitosan–graphene oxide based aptasensor for the impedimetric detection of lysozyme. Colloid Surfaces B 115:205–211
Haupt K (2003) Peer reviewed: molecularly imprinted polymers: the next generation. Anal Chem 75:376A–383A
Gn Wulff (2002) Enzyme-like catalysis by molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem Rev 102:1–28
Haupt K, Mosbac K (2000) Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem Rev 100:2495–2504
Lin CI, Joseph AK, Chang CK, Lee YD (2004) Molecularly imprinted polymeric film on semiconductor nanoparticles: analyte detection by quantum dot photoluminescence. J Chromatogr A 1027:259–262
Bossi A, Bonini F, Turner AP, Piletsky SA (2007) Molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of proteins: the state of the art. Biosens Bioelectron 22:1131–1137
Janiak DS, Kofinas P (2007) Molecular imprinting of peptides and proteins in aqueous media. Anal Bioanal Chem 389:399–404
Ge Y, Turner AP (2008) Too large to fit? Recent developments in macromolecular imprinting, Trends Biotechnol 26:218–224
Díaz-Díaz G, Antuña-Jiménez D, Carmen Blanco-López M, Jesús Lobo-Castañón M, Jand Miranda-Ordieres A, Tuñón-Blanco P (2012) New materials for analytical biomimetic assays based on affinity and catalytic receptors prepared by molecular imprinting. Trend Anal Chem 33:68–80
Ding Z, Annie Bligh SW, Tao L et al (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymer based on MWCNT-QDs as fluorescent biomimetic sensor for specific recognition of target protein. Mat Sci Eng C 48:469–479
Alivisatos AP (1996) Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science 271:933
Resch-Genger U, Grabolle M, Cavaliere-Jaricot S, Nitschke R, Nann T (2008) Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat Methods 5:763–775
Algar WR, Massey M, Krull UJ (2009) The application of quantum dots, gold nanoparticles and molecular switches to optical nucleic-acid diagnostics. Trends Anal Chem 28:292–306
Basabe-Desmonts L, Reinhoudt DN, Crego-Calama M (2007) Design of fluorescent materials for chemical sensing. Chem Soc Rev 36:993–1017
Wei X, Zhou Z, Hao T, Li H, Yan Y (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymer nanospheres based on Mn-doped ZnS QDs via precipitation polymerization for room-temperature phosphorescence probing of 2,6-dichlorophenol. RSC Adv 5:19799–19806
Zhang W, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK (2012) Thermo-sensitive imprinted polymer coating CdTe quantum dots for target protein specific recognition. Chem Commun 48:1757–1759
You CC, Miranda OR, Gider B, Ghosh PS, Kim I, Erdogan B, Krovi SA, Bunz UHF, Rotello VM (2007) Detection and identification of proteins using nanoparticle-fluorescent polymer ‘chemical nose’ sensors. Nat Nanotechnol 2:318–323
Koneswaran M, Narayanaswamy R (2009) l-cysteine-capped ZnS quantum dots based fluorescence sensor for Cu2+ ion. Sensor Actuat B Chem 139:104–109
Bian W, Wang F, Wei Y, Wang L, Liu Q, Dong W, Shuang S, Choi MMF (2015) Doped zinc sulfide quantum dots based phosphorescence turn-off/on probe for detecting histidine in biological fluid. Anal Chim Acta 856:82–89
Tan L, Huang C, Peng R, Tang Y, Li W (2014) Development of hybrid organic-inorganic surface imprinted Mn-doped ZnS QDs and their application as a sensing material for target proteins. Biosens Bioelectron 61:506–511
Wang HF, He Y, Ji TR, Yan XP (2009) Surface molecular imprinting on Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots for room-temperature phosphorescence optosensing of pentachlorophenol in water. Anal Chem 81:1615–1621
Gattás-Asfura KM, Leblanc RM (2003) Peptide-coated CdS quantum dots for the optical detection of copper(ii) and silver(i). Chem Commun 21:2684–2685
Tan L, Kang C, Xu S, Tang Y (2013) Selective room temperature phosphorescence sensing of target protein using Mn-doped ZnS QDs-embedded molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens Bioelectron 48:216–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Yang, S., Sun, L. et al. Surface-imprinted polymer coating l-cysteine-capped ZnS quantum dots for target protein specific recognition. J Mater Sci 51, 6075–6085 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9914-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9914-7