Abstract
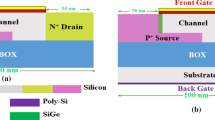
A two-dimensional (2-D) technology computer-aided design (TCAD)-based simulation study of the back bias in the ultrathin silicon-on-insulator (SOI) tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) is presented. The transfer characteristics of a conventional TFET called the back-bias TFET (BB-TFET) depend on the back bias and the oxide thickness below the TFET epitaxial layer. The back bias affects the electric field at the source/channel and drain/channel junctions, hence both the ON-state current (\(I_{\mathrm{ON}}\)) and the ambipolar current (\(I_{\mathrm{AMB}}\)) reduce with a negative back-bias voltage. This reduction in \(I_{\mathrm{ON}}\) is not desirable in a TFET, hence a modified TFET structure called the back-bias underdrain TFET (BBUD-TFET) is proposed. In the BBUD-TFET, the back bias is applied on a p-Si pocket placed under the drain region, which is isolated using an ultrathin oxide. The back bias in the proposed BBUD-TFET mainly affects the electric field at the drain/channel interface, having a negligible impact on the source/channel interface. The BBUD-TFET structure is analyzed with \({\mathrm{SiO}}_2\) or \({\mathrm{HfO}}_2\) as the gate oxide. In the BBUD-TFET with \({\mathrm{HfO}}_2\) as the gate oxide, the back bias completely suppresses the ambipolar current without reducing \(I_{\mathrm{ON}}\). Furthermore, the oxide thickness and back-bias voltage are optimized for the BBUD-TFET structure. In this study, 2-D TCAD simulations are carried out to investigate and analyze the performance of the BB-TFET and BBUD-TFET.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi, W.Y., Park, B.G., Lee, J.D., Liu, T.J.K.: Tunneling field-effect transistors (TFETs) with subthreshold swing (SS) less than 60 mV/dec. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 28(8), 743 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/LED.2007.901273
Ionescu, A.M., Riel, H.: Tunnel field-effect transistors as energy-efficient electronic switches. Nature 479(7373), 329 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10679
Seabaugh, A.C., Zhang, Q.: Low-voltage tunnel transistors for beyond CMOS logic. Proc. IEEE 98(12), 2095 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2010.2070470
Krishnamohan, T., Kim, D., Raghunathan, S., Saraswat, K.: Double-gate strained-Ge heterostructure tunneling FET (TFET) with record high drive currents and \(<\)60 mV/dec subthreshold slope. In: 2008 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEEE, 2008), pp. 1–3 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEDM.2008.4796839
Hraziia, A., Vladimirescu, A., Amara, A., Anghel, C.: An analysis on the ambipolar current in Si double-gate tunnel FETs. Solid State Electron. 70, 67 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sse.2011.11.009
Abdi, D.B., Kumar, M.J.: Controlling ambipolar current in tunneling FETs using overlap** gate-on-drain. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2(6), 187 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/JEDS.2014.2327626
Kondekar, P., Sharma, D., Nigam, K., Raad, B.: Dielectric and work function engineered TFET for ambipolar suppression and RF performance enhancement. Electron. Lett. 52(9), 770 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2015.4348
Narang, R., Saxena, M., Gupta, R.S., Gupta, M.: Assessment of ambipolar behavior of a tunnel FET and influence of structural modifications. J. Semicond. Technol. Sci. 12(4), 482 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5573/JSTS.2012.12.4.482
Nigam, K., Kondekar, P., Sharma, D.: Approach for ambipolar behaviour suppression in tunnel FET by workfunction engineering. Micro Nano Lett. 11(8), 460 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2016.0178
Shaker, A., El Sabbagh, M., El-Banna, M.M.: Influence of drain do** engineering on the ambipolar conduction and high-frequency performance of TFETs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2017.2724560
Singh, S., Kondekar, P.N.: A novel electrostatically doped ferroelectric Schottky barrier tunnel FET: process resilient design. J. Comput. Electron. 16(3), 685 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-017-0987-6
Rahimian, M., Fathipour, M.: Asymmetric junctionless nanowire TFET with built-in n+ source pocket emphasizing on energy band modification. J. Comput. Electron. 15(4), 1297 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-016-0895-1
Loan, S.A., Alharbi, A.G., Rafat, M.: Ambipolar leakage suppression in electron-hole bilayer TFET: investigation and analysis. J. Comput. Electron. 17(3), 977 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-018-1184-y
Bal, P., Ghosh, B., Mondal, P., Akram, M.W., Tripathi, B.M.M.: Dual material gate junctionless tunnel field effect transistor. J. Comput. Electron. 13(1), 230 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-013-0505-4
Guo, A., Matheu, P., Liu, T.J.K.: SOI TFET ION/IOFF enhancement via back biasing. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58(10), 3283 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2011.2161480
Matheu, P., Ho, B., Jacobson, Z.A., Liu, T.K.: Planar GeOI TFET performance improvement with back biasing. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59(6), 1629 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2012.2191410
Sahay, S., Kumar, M.J.: Controlling the drain side tunneling width to reduce ambipolar current in tunnel FETs using heterodielectric BOX. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 62(11), 3882 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2015.2478955
Wang, H., Han, G., Liu, Y., Zhang, J., Hao, Y., Jiang, X.: Theoretical investigation of backgate-biasing effects on ultrathin-body GeSn based tunneling FET. In: 2017 IEEE SOI-3D-Subthreshold Microelectronics Unified Conference, S3S 2017, pp. 1–3 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/S3S.2017.8309214
Silvaco Inc., Atlas User’s Manual. Silvaco Inc. (2016)
Boucart, K., Ionescu, A.M.: Double-gate tunnel FET with high-\(\kappa\) gate dielectric. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 54(7), 1725 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2007.899389
Shih, C.H., Chien, N.D.: Bandgap-dependent onset behavior of output characteristics in line-tunneling field-effect transistors. J. Comput. Electron. 16(3), 696 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-017-1020-9
Adell, P.C., Barnaby, H.J., Member, S., Schrimpf, R.D.: Band-to-band tunneling (BBT) induced leakage current enhancement in irradiated fully depleted SOl devices. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 54(6), 2174 (2007)
Joshi, T., Singh, Y., Singh, B.: Dual-channel trench-gate tunnel FET for improved ON-current and subthreshold swing. Electron. Lett. 55(21), 1152 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2019.2219
Jastrzebski, L., Corboy, J.F., McGinn, J.T., Pagliaro, R.: Growth process of silicon over SiO2 by CVD: epitaxial lateral overgrowth technique. J. Electrochem. Soc. 130(7), 1571 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2120037
Devi, W.V., Bhowmick, B.: Optimisation of pocket doped junctionless TFET and its application in digital inverter. Micro Nano Lett. 14(1), 69 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2018.5086
Strangio, S., Palestri, P., Esseni, D., Selmi, L., Crupi, F., Richter, S., Zhao, Q.T., Mantl, S.: Impact of TFET unidirectionality and ambipolarity on the performance of 6T SRAM cells. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 3(3), 223 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/JEDS.2015.2392793
Atan, N.B., Ahmad, I.B., Majlis, B.B.Y.: Effects of high-K dielectrics with metal gate for electrical characteristics of 18 nm NMOS device. In: 2014 IEEE international conference on semiconductor electronics (ICSE2014), pp. 56–59 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/SMELEC.2014.6920794
Kumar, S., Goel, E., Singh, K., Singh, B., Kumar, M., Jit, S.: A compact 2-D analytical model for electrical characteristics of double-gate tunnel field-effect transistors with a SiO2/high-k stacked gate-oxide structure. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 63(8), 3291 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2016.2572610
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, T., Singh, B. & Singh, Y. Controlling the ambipolar current in ultrathin SOI tunnel FETs using the back-bias effect. J Comput Electron 19, 658–667 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-020-01484-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-020-01484-8