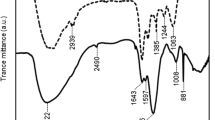
Abstract
The terrestrial cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. HK-01 was more tolerant to NaCl stress than the aquatic cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 (also called Nostoc sp. PCC 7120) which is similar to Nostoc sp. HK-01 in phylogeny. We determined the amount of extracellular polysaccharides (capsular and released polysaccharides) from the cells of both strains cultured with or without 200 mM NaCl. The amount of capsular polysaccharides from Nostoc HK-01 reached approximately 65% of the dry weight whereas that from Anabaena PCC 7120 only occupied approximately 18% of the dry weight under NaCl stress. Anabaena PCC 7120 grew well under NaCl stress when both polysaccharides from Nostoc HK-01 were added to the culture. However, Anabaena PCC 7120 barely grew under NaCl stress when both of its polysaccharides were added. Extracellular polysaccharides from Nostoc HK-01 contained abundant fucose and glucuronic acid in comparison with those from Anabaena PCC 7120. Under NaCl stress, the composition ratios of sugars in the extracellular polysaccharides from Anabaena PCC 7120 hardly changed in comparison with those in ordinary culture conditions. By contrast, the composition ratios of sugars in the extracellular polysaccharides from Nostoc HK-01 changed under NaCl stress. These results suggest that the effect of extracellular polysaccharides from Nostoc HK-01 on NaCl tolerance comes from the increased amount of capsular polysaccharides, the sugar composition, and the change of the sugar composition ratio under NaCl stress.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellezza S, Paradossi G, De Philippis R, Albertano P (2003) Leptolyngbya strains from Roman hypogea: cytochemical and physico-chemical characterisation of exopolysaccharides. J Appl Phycol 15:193–200
Bender J, Phillips P (2004) Microbial mats for multiple applications in aquaculture and bioremediation. Bioresour Technol 94:229–238
Bertocchi C, Nabarini L, Cesaro A, Anastasio M (1990) Polysaccharide from cyanobacteria. Cabohydrate Polym 12:127–153
Chauhan VS, Singh B, Singh S, Bisen PS (2001) Regulation of sodium influx in the NaCl-resistant (NaCl(r)) mutant strain of the cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis. Curr Microbiol 42:100–105
Chen J, Lee SM, Mao Y (2004) Protective effect of exopolysaccharide colanic acid of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to osmotic and oxidative stress. Int J Food Microbiol 93:281–286
Cuthbertson L, Mainprize IL, Naismith JH, Whitfield C (2009) Pivotal roles of the outer membrane polysaccharide export and polysaccharide copolymerase protein families in export of extracellular polysaccharides in gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 73:155–177
De Philippis R, Vincenzini M (1998) Exocellular polysaccharides from cyanobacteria and their possible applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:151–175
De Philippis R, Paperi R, Sili C (2007) Heavy metal sorption by released polysaccharides and whole cultures of two exopolysaccharide-producing cyanobacteria. Biodegradation 18:181–187
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Elanskaya IV, Karandashova IV, Bogachev AV, Hagemann M (2002) Functional analysis of the Na+/H+ antiporter encoding genes of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803. Biochemistry 67:432–440
Galambos JT (1967) The reaction of carbazole with carbohydrates. I. Effect of borate and sulfamate on the carbazole color of sugars. Anal Biochem 19:119–143
Grant WD, Sutherland IW, Wilkinson JF (1969) Exopolysaccharide colanic acid and its occurrence in the Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol 100:1187–1193
Hagemann M (2011) Molecular biology of cyanobacterial salt acclimation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35:87–123
Hill DR, Keenan TW, Helm RF, Potts M, Crowe ML, Crowe JH (1997) Extracellular polysaccharide of Nostoc commune (Cyanobacteria) inhibits fusion of membrane vesicles during desiccation. J Appl Phycol 9:237–248
Hincha DK, Hagemann M (2004) Stabilization of model membranes during drying by compatible solutes involved in the stress tolerance of plants and microorganisms. Biochem J 383:277–283
Ishikawa M, Kuroyama H, Takeuchi Y, Tsumuraya Y (2000) Characterization of pectin methyltransferase from soybean hypocotyls. Planta 210:782–791
Kaneko T, Nakamura Y, Wolk CP et al (2001) Complete genomic sequence of the filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. DNA Res 8(205–213):227–253
Katoh H, Shiga Y, Nakahira Y, Ohmori M (2003) Isolation and characterization of a drought-tolerant cyanobacterium, Nostoc sp. HK-01. Microb Environ 18:82–88
Knowles EJ, Castenholz RW (2008) Effect of exogenous extracellular polysaccharides on the desiccation and freezing tolerance of rock-inhabiting phototrophic microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66:261–270
Kumar AS, Mody K, Jha B (2007) Bacterial exopolysaccharides—a perception. J Basic Microbiol 47:103–117
Li P, Harding SE, Liu Z (2001) Cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides: their nature and potential biotechnological applications. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 18:375–404
Mackinney G (1941) Absorption of light by chlorophyll solutions. J Biol Chem 140:315–322
Mäki M, Renkonen R (2004) Biosynthesis of 6-deoxyhexose glycans in bacteria. Glycobiology 14:1R–15R
Marin K, Zuther E, Kerstan T, Kunert A, Hagemann M (1998) The ggpS gene from Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 encoding glucosyl-glycerol-phosphate synthase is involved in osmolyte synthesis. J Bacteriol 180:4843–4849
Mikkat S, Hagemann M, Schoor A (1996) Active transport of glucosylglycerol is involved in salt adaptation of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Microbiology 142:1725–1732
Potts M (1994) Desiccation tolerance of prokaryotes. Microbiol Rev 58:755–805
Potts M (2001) Dessication tolerance: a simple process? Trends Microbiol 9:553–559
Prosperi CH (1994) A cyanophyte capable of fixing nitrogen under high levels oxygen. J Phycol 30:222–224
Rai AK, Sharma NK (2006) Phosphate metabolism in the cyanobacterium Anabaena doliolum under salt stress. Curr Microbiol 52:6–12
Raungsomboon S, Chidthaisong A, Bunnag B, Inthorn D, Harvey NW (2006) Production, composition and Pb2+ adsorption characteristics of capsular polysaccharides extracted from a cyanobacterium Gloeocapsa gelatinosa. Water Res 40:3759–3766
Sakamoto T, Yoshida T, Arima H, Hatanaka Y, Takani Y, Tamaru Y (2009) Accumulation of trehalose in response to desiccation and salt stress in the terrestrial cyanobacterium Nostoc commune. Phycol Res 57:66–73
Stanier RY, Kunisawa R, Mandel M, Cohen-Bazire G (1971) Purification and properties of unicellular blue–green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev 35:171–205
Sutherland IW (1998) Novel and established applications of microbial polysaccharides. Trends Biotechnol 16:41–46
Tamaru Y, Takani Y, Yoshida T, Sakamoto T (2005) Crucial role of extracellular polysaccharides in desiccation and freezing tolerance in the terrestrial cyanobacterium Nostoc commune. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7327–7333
Welsh DT (2000) Ecological significance of compatible solute accumulation by micro-organisms: from single cells to global climate. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:263–290
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (18651013) and the Japan Space Forum.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshimura, H., Kotake, T., Aohara, T. et al. The role of extracellular polysaccharides produced by the terrestrial cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. strain HK-01 in NaCl tolerance. J Appl Phycol 24, 237–243 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9672-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9672-5