Abstract
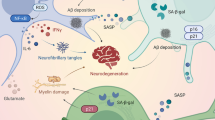
Neurodegenerative diseases are part of the central nervous system (CNS) disorders that indicate their presence with neuronal loss, neuroinflammation, and increased oxidative stress. Several pathophysiological factors and biomarkers are involved in this inflammatory process causing these neurological disorders. The nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is an inflammation element, which induced transcription and appears to be one of the important players in physiological procedures, especially nervous disorders. NF-κB can impact upon series of intracellular actions and induce or inhibit many inflammation-related pathways. Multiple reports have focused on the modification of NF-κB activity, controlling its expression, translocation, and signaling pathway in neurodegenerative disorders and injuries like Alzheimer’s disease (AD), spinal cord injuries (SCI), and Parkinson’s disease (PD). Curcumin has been noted to be a popular anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory substance and is the foremost natural compound produced by turmeric. According to various studies, when playing an anti-inflammatory role, it interacts with several modulating proteins of long-standing disease signaling pathways and has an unprovocative consequence on pro-inflammatory cytokines. This review article determined to figure out curcumin’s role in limiting the promotion of neurodegenerative disease via influencing the NF-κB signaling route. Preclinical studies were gathered from plenty of scientific platforms including PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane, and Google Scholar to evaluate this hypothesis. Extracted findings from the literature review explained the repressing impact of Curcumin on the NF-κB signaling pathway and, occasionally down-regulating the cytokine expression. Yet, there is an essential need for further analysis and specific clinical experiments to fully understand this subject.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- MPP+:
-
1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion
- SNCA:
-
A-Synuclein
- AD:
-
Alzheimer disease
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- ApoE4-Tg:
-
ApoE4 transgenic
- APOE4:
-
Apolipoprotein E4
- BMS:
-
Basso mouse scale
- BACE1:
-
Beta-Secretase 1
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- CAMKII:
-
Calcium–calmodulin (CaM)-dependent protein kinase II
- CREB:
-
CAMP response element-binding protein
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- ChAT:
-
Choline acetyltransferase
- CSPG:
-
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan
- Co-Q10:
-
Coenzyme Q10
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- CXCL10:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase 2
- DAMP:
-
Damage-associated molecular patterns
- DCM:
-
Diabetic cardiomyopathy
- DR:
-
Diabetic retinopathy
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- EMSA:
-
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase 1
- HTT:
-
Huntingtin protein
- HD:
-
Huntington’s disease
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- IRF3:
-
Interferon regulatory factor 3
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- IP:
-
Intra-peritoneal
- IV:
-
Intravenous
- Iba1:
-
Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1
- IKKβ:
-
IκB Kinase β
- KM:
-
Kun-Ming
- LRRK2:
-
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2
- LBD:
-
Lewy body dementia
- LTP:
-
Like long-term potentiation
- LUBAC:
-
Linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex
- LPO:
-
Lipid peroxidation
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharides
- LOX:
-
Lipoxygenase
- LTD:
-
Long-term depression
- LUBAC:
-
Linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex
- MIP-1α:
-
Macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- MnSOD:
-
Manganese superoxide dismutase
- MEM:
-
Memantine
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- mEPSCs:
-
Miniature excitatory post-synaptic currents
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MKK6:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- MyD88:
-
Myeloid differentiation primary response 88
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- ND:
-
Neurodegenerative disease
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/antioxidant responsive element
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- OPTN:
-
Optineurin
- p38MAPK:
-
P38 mitogen-activated protein kinases
- PAMP:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- PO:
-
Per os
- Prdx6:
-
Peroxiredoxin6
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide-3-kinase
- PSD-95:
-
Postsynaptic density protein 95
- PFC:
-
Prefrontal cortex
- PSEN:
-
Presenilin
- PGE2:
-
Prostaglandin E2
- Akt:
-
Protein kinase B
- AP-1:
-
Activator protein 1
- PKC-δ:
-
Protein kinase C-delta
- PINK1:
-
PTEN-induced putative kinase 1
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RANTES:
-
Regulated upon Activation Normal T Cell Expressed, and Secreted
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- SCO:
-
Scopolamine hydrobromide
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms
- SCI:
-
Spinal cord injury
- SPAR:
-
Spine-associated Rap GTPase-activating protein
- SOX9:
-
SRY-Box Transcription Factor 9
- SN:
-
Substantia nigra
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TDP-43:
-
TAR DNA-binding protein 43
- TAK1:
-
TGF-b-activated kinase 1
- TJ:
-
Tight junction protein
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- TGF:
-
Transforming growth factor
- TIRF:
-
Transmucosal immediate-release fentanyl
- TBI:
-
Traumatic brain injury
- TREM2:
-
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2
- Tau:
-
Tubulin-associated unit
- TRAF6:
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factor 6
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
- ZO-1:
-
Zonula occludens 1
- α-SMA:
-
α-Smooth muscle actin
- Aβ:
-
β-Amyloid peptides
- APACHE:
-
Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation
- ADAS-Cog:
-
Alzheimer’s disease Assessment Scale–cognitive subscale
- ADCS-ADL:
-
Alzheimer’s disease Cooperative society Study-Activities of Daily Living
References
Aggarwal BB, Harikumar KB (2009) Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:40–59
Aggarwal BB, Sung B (2009) Pharmacological basis for the role of curcumin in chronic diseases: an age-old spice with modern targets. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:85–94
Ahmadi M, Agah E, Nafissi S, Jaafari MR, Harirchian MH, Sarraf P, Faghihi-Kashani S, Hosseini SJ, Ghoreishi A, Aghamollaii V, Hosseini M, Tafakhori A (2018) Safety and efficacy of nanocurcumin as add-on therapy to riluzole in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a pilot randomized clinical trial. Neurotherapeutics 15:430–438
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB (2007) Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm 4:807–818
Anand P, Sundaram C, Jhurani S, Kunnumakkara AB, Aggarwal BB (2008a) Curcumin and cancer: an “old-age” disease with an “age-old” solution. Cancer Lett 267:133–164
Anand P, Thomas SG, Kunnumakkara AB, Sundaram C, Harikumar KB, Sung B, Tharakan ST, Misra K, Priyadarsini IK, Rajasekharan KN, Aggarwal BB (2008b) Biological activities of curcumin and its analogues (Congeners) made by man and Mother Nature. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1590–1611
Ashrafizadeh M, Ahmadi Z, Mohammadinejad R, Farkhondeh T, Samarghandian S (2020) Curcumin activates the Nrf2 pathway and induces cellular protection against oxidative injury. Curr Mol Med 20:116–133
Basnet P, Skalko-Basnet N (2011) Curcumin: an anti-inflammatory molecule from a curry spice on the path to cancer treatment. Molecules 16:4567–4598
Bates GP, Dorsey R, Gusella JF, Hayden MR, Kay C, Leavitt BR, Nance M, Ross CA, Scahill RI, Wetzel R (2015) Huntington disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:1–21
Baum L, Lam CW, Cheung SK, Kwok T, Lui V, Tsoh J, Lam L, Leung V, Hui E, Ng C, Woo J, Chiu HF, Goggins WB, Zee BC, Cheng KF, Fong CY, Wong A, Mok H, Chow MS, Ho PC, Ip SP, Ho CS, Yu XW, Lai CY, Chan MH, Szeto S, Chan IH, Mok V (2008) Six-month randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, pilot clinical trial of curcumin in patients with Alzheimer disease. J Clin Psychopharmacol 28:110–113
Bečanović K, Nørremølle A, Neal SJ, Kay C, Collins JA, Arenillas D, Lilja T, Gaudenzi G, Manoharan S, Doty CN, Beck J, Lahiri N, Portales-Casamar E, Warby SC, Connolly C, de Souza RA, Tabrizi SJ, Hermanson O, Langbehn DR, Hayden MR, Wasserman WW, Leavitt BR (2015) A SNP in the HTT promoter alters NF-κB binding and is a bidirectional genetic modifier of Huntington disease. Nat Neurosci 18:807–816
Bender K, Göttlicher M, Whiteside S, Rahmsdorf HJ, Herrlich P (1998) Sequential DNA damage-independent and -dependent activation of NF-kappaB by UV. Embo j 17:5170–5181
Béraud D, Maguire-Zeiss KA (2012) Misfolded α-synuclein and Toll-like receptors: therapeutic targets for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(Suppl 1):S17-20
Bhat A, Mahalakshmi AM, Ray B, Tuladhar S, Hediyal TA, Manthiannem E, Padamati J, Chandra R, Chidambaram SB, Sakharkar MK (2019) Benefits of curcumin in brain disorders. BioFactors 45:666–689
Bland AR, Ashton JC, Kamal MA, Sahebkar A (2023) The current evidence for the therapeutic role of curcumin in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 22:318–320
Boersma MC, Dresselhaus EC, de Biase LM, Mihalas AB, Bergles DE, Meffert MK (2011) A requirement for nuclear factor-kappaB in developmental and plasticity-associated synaptogenesis. J Neurosci 31:5414–5425
Bonizzi G, Bebien M, Otero DC, Johnson-Vroom KE, Cao Y, Vu D, Jegga AG, Aronow BJ, Ghosh G, Rickert RC, Karin M (2004) Activation of IKKalpha target genes depends on recognition of specific kappaB binding sites by RelB:p52 dimers. Embo j 23:4202–4210
Braak H, Rüb U, Gai WP, del Tredici K (2003) Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: possible routes by which vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown pathogen. J Neural Transm (vienna) 110:517–536
Chahine LM, Merchant K, Siderowf A, Sherer T, Tanner C, Marek K, Simuni T (2023) Proposal for a biologic staging system of Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis 13:297–309
Chami L, Buggia-Prévot V, Duplan E, del Prete D, Chami M, Peyron JF, Checler F (2012) Nuclear factor-κB regulates βAPP and β- and γ-secretases differently at physiological and supraphysiological Aβ concentrations. J Biol Chem 287:24573–24584
Chhunchha B, Fatma N, Kubo E, Rai P, Singh SP, Singh DP (2013) Curcumin abates hypoxia-induced oxidative stress based-ER stress-mediated cell death in mouse hippocampal cells (HT22) by controlling Prdx6 and NF-κB regulation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 304:C636–C655
Chiarini A, Armato U, Hu P, Dal Prà I (2020) Danger-sensing/patten recognition receptors and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 21:9036
Cho IH, Hong J, Suh EC, Kim JH, Lee H, Lee JE, Lee S, Kim CH, Kim DW, Jo EK, Lee KE, Karin M, Lee SJ (2008) Role of microglial IKKbeta in kainic acid-induced hippocampal neuronal cell death. Brain 131:3019–3033
Daverey A, Agrawal SK (2020) Curcumin protects against white matter injury through NF-κB and Nrf2 cross talk. J Neurotrauma 37:1255–1265
de Strooper B, Karran E (2016) The cellular phase of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 164:603–615
Demaagd G, Philip A (2015) Parkinson’s disease and its management: part 1: disease entity, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and diagnosis. P t 40:504–532
Dolati S, Babaloo Z, Ayromlou H, Ahmadi M, Rikhtegar R, Rostamzadeh D, Roshangar L, Nouri M, Mehdizadeh A, Younesi V, Yousefi M (2019) Nanocurcumin improves regulatory T-cell frequency and function in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 327:15–21
Dolatshahi M, Ranjbar Hameghavandi MH, Sabahi M, Rostamkhani S (2021) Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) in pathophysiology of Parkinson disease: diverse patterns and mechanisms contributing to neurodegeneration. Eur J Neurosci 54:4101–4123
Dresselhaus EC, Meffert MK (2019) Cellular specificity of NF-κB function in the nervous system. Front Immunol 10:1043
Duckworth EA, Butler T, Collier L, Collier S, Pennypacker KR (2006) NF-kappaB protects neurons from ischemic injury after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res 1088:167–175
Farkhondeh T, Samarghandian S, Pourbagher-Shahri AM, Sedaghat M (2019) The impact of curcumin and its modified formulations on Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Physiol 234:16953–16965
Fridmacher V, Kaltschmidt B, Goudeau B, Ndiaye D, Rossi FM, Pfeiffer J, Kaltschmidt C, Israël A, Mémet S (2003) Forebrain-specific neuronal inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activity leads to loss of neuroprotection. J Neurosci 23:9403–9408
Fu ES, Zhang YP, Sagen J, Candiotti KA, Morton PD, Liebl DJ, Bethea JR, Brambilla R (2010) Transgenic inhibition of glial NF-kappa B reduces pain behavior and inflammation after peripheral nerve injury. Pain 148:509–518
Fu W, Zhuang W, Zhou S, Wang X (2015) Plant-derived neuroprotective agents in Parkinson’s disease. Am J Transl Res 7:1189–1202
Gao F, Shen J, Zhao L, Hao Q, Yang Y (2019) Curcumin alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated neuroinflammation via modulation of miR-199b-5p/IκB Kinase β (IKKβ)/Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) pathway in microglia. Med Sci Monit 25:9801–9810
Garcia-Alloza M, Borrelli LA, Rozkalne A, Hyman BT, Bacskai BJ (2007) Curcumin labels amyloid pathology in vivo, disrupts existing plaques, and partially restores distorted neurites in an Alzheimer mouse model. J Neurochem 102:1095–1104
Gatto EM, Rojas NG, Persi G, Etcheverry JL, Cesarini ME, Perandones C (2020) Huntington disease: advances in the understanding of its mechanisms. Clin Park Relat Disord 3:100056
Ghanaatian N, Lashgari NA, Abdolghaffari AH, Rajaee SM, Panahi Y, Barreto GE, Butler AE, Sahebkar A (2019) Curcumin as a therapeutic candidate for multiple sclerosis: molecular mechanisms and targets. J Cell Physiol 234:12237–12248
Giacomeli R, Izoton JC, dos Santos RB, Boeira SP, Jesse CR, Haas SE (2019) Neuroprotective effects of curcumin lipid-core nanocapsules in a model Alzheimer’s disease induced by β-amyloid 1–42 peptide in aged female mice. Brain Res 1721:146325
Green KL, Gatto GJ, Grant KA (1997) The nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-NAME (N omega-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester) does not produce discriminative stimulus effects similar to ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 21:483–488
Grynkiewicz G, Ślifirski P (2012) Curcumin and curcuminoids in quest for medicinal status. Acta Biochim Pol 59:201–212
Guerreiro R, Wojtas A, Bras J, Carrasquillo M, Rogaeva E, Majounie E, Cruchaga C, Sassi C, Kauwe JS, Younkin S, Hazrati L, Collinge J, Pocock J, Lashley T, Williams J, Lambert JC, Amouyel P, Goate A, Rademakers R, Morgan K, Powell J, St George-HyslopSingletonHardy PPJ (2013) TREM2 variants in Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 368:117–127
Heissmeyer V, Krappmann D, Wulczyn FG, Scheidereit C (1999) NF-kappaB p105 is a target of IkappaB kinases and controls signal induction of Bcl-3-p50 complexes. Embo j 18:4766–4778
Hsiao HY, Chen YC, Chen HM, Tu PH, Chern Y (2013) A critical role of astrocyte-mediated nuclear factor-κB-dependent inflammation in Huntington’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 22:1826–1842
Huang L, Chen C, Zhang X, Li X, Chen Z, Yang C, Liang X, Zhu G, Xu Z (2018) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via mediating autophagy and inflammation. J Mol Neurosci 64:129–139
Huang P, Zheng N, Zhou HB, Huang J (2020) Curcumin inhibits BACE1 expression through the interaction between ERβ and NFκB signaling pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Mol Cell Biochem 463:161–173
Jones SV, Kounatidis I (2017) Nuclear factor-kappa B and Alzheimer disease, unifying genetic and environmental risk factors from cell to humans. Front Immunol 8:1805
Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C (2015) NF-KappaB in long-term memory and structural plasticity in the adult mammalian brain. Front Mol Neurosci 8:69
Kaltschmidt B, Uherek M, Wellmann H, Volk B, Kaltschmidt C (1999) Inhibition of NF-kappaB potentiates amyloid beta-mediated neuronal apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:9409–9414
Kaltschmidt B, Widera D, Kaltschmidt C (2005) Signaling via NF-kappaB in the nervous system. Biochim Biophys Acta 1745:287–299
Kang G, Kong PJ, Yuh YJ, Lim SY, Yim SV, Chun W, Kim SS (2004) Curcumin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression by inhibiting activator protein 1 and nuclear factor kappab bindings in BV2 microglial cells. J Pharmacol Sci 94:325–328
Khayatan D, Razavi SM, Arab ZN, Niknejad AH, Nouri K, Momtaz S, Gumpricht E, Jamialahmadi T, Abdolghaffari AH, Barreto GE, Sahebkar A (2022) Protective effects of curcumin against traumatic brain injury. Biomed Pharmacother 154:113621
Khoshnan A, Ko J, Watkin EE, Paige LA, Reinhart PH, Patterson PH (2004) Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex and nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to mutant huntingtin neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 24:7999–8008
Kou J, Wang M, Shi J, Zhang H, Pu X, Song S, Yang C, Yan Y, Döring Y, **e X, Pang X (2021) Curcumin reduces cognitive deficits by inhibiting neuroinflammation through the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in apolipoprotein E4 transgenic mice. ACS Omega 6:6654–6662
Kumar A, Thakur MK (2016) Binding of transcription factors to Presenilin 1 and 2 promoter cis-acting elements varies during the development of mouse cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett 628:98–104
Kumar A, Chetia H, Sharma S, Kabiraj D, Talukdar NC, Bora U (2015a) Curcumin resource database. Database (oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bav070
Kumar A, Sharma S, Prashar A, Deshmukh R (2015b) Effect of licofelone–a dual COX/5-LOX inhibitor in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced behavioral and biochemical abnormalities in rats. J Mol Neurosci 55:749–759
Kumar P, Singh A, Kumar A, Kumar R, Pal R, Sachan AK, Dixit RK, Nath R (2023) Effect of curcumin and coenzyme Q10 alone and in combination on learning and memory in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicines 11:1422
Kyrargyri V, Vega-Flores G, Gruart A, Delgado-García JM, Probert L (2015) Differential contributions of microglial and neuronal IKKβ to synaptic plasticity and associative learning in alert behaving mice. Glia 63:549–566
Lahiri DK (2004) Apolipoprotein E as a target for develo** new therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease based on studies from protein, RNA, and regulatory region of the gene. J Mol Neurosci 23:225–233
Li Y, Niu M, Zhao A, Kang W, Chen Z, Luo N, Zhou L, Zhu X, Lu L, Liu J (2019) CXCL12 is involved in α-synuclein-triggered neuroinflammation of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 16:263
Liu ZJ, Li ZH, Liu L, Tang WX, Wang Y, Dong MR, **ao C (2016) Curcumin attenuates beta-amyloid-induced neuroinflammation via activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma function in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Pharmacol 7:261
Machova Urdzikova L, Karova K, Ruzicka J, Kloudova A, Shannon C, Dubisova J, Murali R, Kubinova S, Sykova E, Jhanwar-Uniyal M, Jendelova P (2015) The anti-inflammatory compound curcumin enhances locomotor and sensory recovery after spinal cord injury in rats by immunomodulation. Int J Mol Sci 17:49
Marcora E, Kennedy MB (2010) The Huntington’s disease mutation impairs Huntingtin’s role in the transport of NF-κB from the synapse to the nucleus. Hum Mol Genet 19:4373–4384
Masrori P, van Damme P (2020) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a clinical review. Eur J Neurol 27:1918–1929
Mattson MP, Camandola S (2001) NF-kappaB in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. J Clin Invest 107:247–254
Mead RJ, Shan N, Reiser HJ, Marshall F, Shaw PJ (2023) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a neurodegenerative disorder poised for successful therapeutic translation. Nat Rev Drug Discov 22:185–212
Menon VP, Sudheer AR (2007) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin. Adv Exp Med Biol 595:105–125
Meschede J, Šadić M, Furthmann N, Miedema T, Sehr DA, Müller-Rischart AK, Bader V, Berlemann LA, Pilsl A, Schlierf A, Barkovits K, Kachholz B, Rittinger K, Ikeda F, Marcus K, Schaefer L, Tatzelt J, Winklhofer KF (2020) The parkin-coregulated gene product PACRG promotes TNF signaling by stabilizing LUBAC. Sci Signal 13:1256
Meunier A, Latrémolière A, Dominguez E, Mauborgne A, Philippe S, Hamon M, Mallet J, Benoliel JJ, Pohl M (2007) Lentiviral-mediated targeted NF-κB blockade in dorsal spinal cord glia attenuates sciatic nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain in the rat. Mol Ther 15:687–697
Mincheva S, Garcera A, Gou-Fabregas M, Encinas M, Dolcet X, Soler RM (2011) The canonical nuclear factor-κB pathway regulates cell survival in a developmental model of spinal cord motoneurons. J Neurosci 31:6493–6503
Mincheva-Tasheva S, Soler RM (2013) NF-κB signaling pathways: role in nervous system physiology and pathology. Neuroscientist 19:175–194
Ni H, ** W, Zhu T, Wang J, Yuan B, Jiang J, Liang W, Ma Z (2015) Curcumin modulates TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway following traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. J Spinal Cord Med 38:199–206
Nocito MC, de Luca A, Prestia F, Avena P, la Padula D, Zavaglia L, Sirianni R, Casaburi I, Puoci F, Chimento A, Pezzi V (2021) Antitumoral activities of curcumin and recent advances to improve its oral bioavailability. Biomedicines 9:1476
Nurmi A, Lindsberg PJ, Koistinaho M, Zhang W, Juettler E, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Weih F, Frank N, Schwaninger M, Koistinaho J (2004) Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 35:987–991
O’Mahony A, Raber J, Montano M, Foehr E, Han V, Lu SM, Kwon H, Lefevour A, Chakraborty-Sett S, Greene WC (2006) NF-kappaB/Rel regulates inhibitory and excitatory neuronal function and synaptic plasticity. Mol Cell Biol 26:7283–7298
O’Riordan KJ, Huang IC, Pizzi M, Spano P, Boroni F, Egli R, Desai P, Fitch O, Malone L, Ahn HJ, Liou HC, Sweatt JD, Levenson JM (2006) Regulation of nuclear factor kappaB in the hippocampus by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors. J Neurosci 26:4870–4879
Ouali Alami N, Schurr C, Olde Heuvel F, Tang L, Li Q, Tasdogan A, Kimbara A, Nettekoven M, Ottaviani G, Raposo C, Röver S, Rogers-Evans M, Rothenhäusler B, Ullmer C, Fingerle J, Grether U, Knuesel I, Boeckers TM, Ludolph A, Wirth T, Roselli F, Baumann B (2018) NF-κB activation in astrocytes drives a stage-specific beneficial neuroimmunological response in ALS. EMBO J 37:e98697
Owens R, Grabert K, Davies CL, Alfieri A, Antel JP, Healy LM, McColl BW (2017) Divergent neuroinflammatory regulation of microglial TREM expression and involvement of NF-κB. Front Cell Neurosci 11:56
Panicker N, Sarkar S, Harischandra DS, Neal M, Kam TI, ** H, Saminathan H, Langley M, Charli A, Samidurai M, Rokad D, Ghaisas S, Pletnikova O, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy AG, Kanthasamy A (2019) Fyn kinase regulates misfolded α-synuclein uptake and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia. J Exp Med 216:1411–1430
Panicker N, Ge P, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2021) The cell biology of Parkinson’s disease. J Cell Biol 220:12095
Parkinson J (2002) An essay on the shaking palsy. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 14:223–236
Pivari F, Mingione A, Brasacchio C, Soldati L (2019) Curcumin and type 2 diabetes mellitus: prevention and treatment. Nutrients 11:1837
Prasad S, Katta MR, Abhishek S, Sridhar R, Valisekka SS, Hameed M, Kaur J, Walia N (2023) Recent advances in Lewy body dementia: a comprehensive review. Dis Mon 69:101441
Priyadarsini KI (2014) The chemistry of curcumin: from extraction to therapeutic agent. Molecules 19:20091–20112
Rachmawati H, Al Shaal L, Müller RH, Keck CM (2013) Development of curcumin nanocrystal: physical aspects. J Pharm Sci 102:204–214
Ransohoff RM (2016) How neuroinflammation contributes to neurodegeneration. Science 353:777–783
Reich N, Hölscher C (2022) The neuroprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: an in-depth review. Front Neurosci 16:970925
Ringman JM, Frautschy SA, Teng E, Begum AN, Bardens J, Beigi M, Gylys KH, Badmaev V, Heath DD, Apostolova LG, Porter V, Vanek Z, Marshall GA, Hellemann G, Sugar C, Masterman DL, Montine TJ, Cummings JL, Cole GM (2012) Oral curcumin for Alzheimer’s disease: tolerability and efficacy in a 24-week randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study. Alzheimers Res Ther 4:43
Rojo AI, Salinas M, Martín D, Perona R, Cuadrado A (2004) Regulation of Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase expression via the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/Akt pathway and nuclear factor-kappaB. J Neurosci 24:7324–7334
Ruiz-Perera LM, Schneider L, Windmöller BA, Müller J, Greiner JFW, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B (2018) NF-κB p65 directs sex-specific neuroprotection in human neurons. Sci Rep 8:16012
Schmidt-Ullrich R, Mémet S, Lilienbaum A, Feuillard J, Raphaël M, Israel A (1996) NF-kappaB activity in transgenic mice: developmental regulation and tissue specificity. Development 122:2117–2128
Schwaninger M, Inta I, Herrmann O (2006) NF-kappaB signalling in cerebral ischaemia. Biochem Soc Trans 34:1291–1294
Shadnoush M, Zahedi H, Norouzy A, Sahebkar A, Sadeghi O, Najafi A, Hosseini S, Qorbani M, Ahmadi A, Ardehali SH, Hosseinzadeh-Attar MJ (2020) Effects of supplementation with curcuminoids on serum adipokines in critically ill patients: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Phytother Res 34:3180–3188
Shanmugam MK, Rane G, Kanchi MM, Arfuso F, Chinnathambi A, Zayed ME, Alharbi SA, Tan BK, Kumar AP, Sethi G (2015) The multifaceted role of curcumin in cancer prevention and treatment. Molecules 20:2728–2769
Sharifi-Rad J, Rayess YE, Rizk AA, Sadaka C, Zgheib R, Zam W, Sestito S, Rapposelli S, Neffe-Skocińska K, Zielińska D, Salehi B, Setzer WN, Dosoky NS, Taheri Y, el Beyrouthy M, Martorell M, Ostrander EA, Suleria HAR, Cho WC, Maroyi A, Martins N (2020) Turmeric and Its Major Compound Curcumin on Health: Bioactive Effects and Safety Profiles for Food, Pharmaceutical. Biotechnol Med Appl Front Pharmacol 11:01021
Sharma N, Sharma S, Nehru B (2017) Curcumin protects dopaminergic neurons against inflammation-mediated damage and improves motor dysfunction induced by single intranigral lipopolysaccharide injection. Inflammopharmacology 25:351–368
Snow WM, Albensi BC (2016) Neuronal gene targets of NF-κB and their dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Mol Neurosci 9:118
Steiner JA, Quansah E, Brundin P (2018) The concept of alpha-synuclein as a prion-like protein: ten years after. Cell Tissue Res 373:161–173
Sun SC (2011) Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Res 21:71–85
Sun G, Miao Z, Ye Y, Zhao P, Fan L, Bao Z, Tu Y, Li C, Chao H, Xu X, Ji J (2020) Curcumin alleviates neuroinflammation, enhances hippocampal neurogenesis, and improves spatial memory after traumatic brain injury. Brain Res Bull 162:84–93
Sun E, Motolani A, Campos L, Lu T (2022) The pivotal role of NF-kB in the pathogenesis and therapeutics of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 23:8972
Swarup V, Phaneuf D, Dupré N, Petri S, Strong M, Kriz J, Julien JP (2011) Deregulation of TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis triggers nuclear factor κB-mediated pathogenic pathways. J Exp Med 208:2429–2447
Takano H, Gusella JF (2002) The predominantly HEAT-like motif structure of huntingtin and its association and coincident nuclear entry with dorsal, an NF-kB/Rel/dorsal family transcription factor. BMC Neurosci 3:15
Tanaka Y, Sabharwal L, Ota M, Nakagawa I, Jiang JJ, Arima Y, Ogura H, Okochi M, Ishii M, Kamimura D, Murakami M (2018) Presenilin 1 regulates NF-κB activation via association with breakpoint cluster region and casein kinase II. J Immunol 201:2256–2263
Thawkar BS, Kaur G (2019) Inhibitors of NF-κB and P2X7/NLRP3/Caspase 1 pathway in microglia: novel therapeutic opportunities in neuroinflammation induced early-stage Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 326:62–74
Thomsen MB, Foster E, Nguyen KH, Sosunov EA (2009) Transcriptional and electrophysiological consequences of KChIP2-mediated regulation of CaV1.2. Channels (austin) 3:308–310
Thota RN, Rosato JI, Dias CB, Burrows TL, Martins RN, Garg ML (2020) Dietary supplementation with curcumin reduce circulating levels of glycogen synthase kinase-3β and islet amyloid polypeptide in adults with high risk of type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients 12:1032
Wang Z, Zhang Q, Yuan L, Wang S, Liu L, Yang X, Li G, Liu D (2014) The effects of curcumin on depressive-like behavior in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration. Behav Brain Res 274:282–290
Wang M, Kou J, Wang C, Yu X, **e X, Pang X (2020) Curcumin inhibits APOE4-induced injury by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) in SH-SY5Y cells. Iran J Basic Med Sci 23:1576–1583
Wood-Kaczmar A, Gandhi S, Wood NW (2006) Understanding the molecular causes of Parkinson’s disease. Trends Mol Med 12:521–528
**e P, Deng M, Sun Q, Jiang B, Xu H, Liu J, Zhou Y, Ma Y, Chen Z (2020) Curcumin protects BV2 cells against lipopolysaccharide-induced injury via adjusting the miR-362-3p/TLR4 axis. Mol Biol Rep 47:4199–4208
Xu L, Hao LP, Yu J, Cheng SY, Li F, Ding SM, Zhang R (2023) Curcumin protects against rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease in mice by inhibiting microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation and alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction. Heliyon 9:e16195
Yang S, Zhang D, Yang Z, Hu X, Qian S, Liu J, Wilson B, Block M, Hong JS (2008) Curcumin protects dopaminergic neuron against LPS induced neurotoxicity in primary rat neuron/glia culture. Neurochem Res 33:2044–2053
Yang H, Huang S, Wei Y, Cao S, Pi C, Feng T, Liang J, Zhao L, Ren G (2017) Curcumin enhances the anticancer effect Of 5-fluorouracil against gastric cancer through down-regulation of COX-2 and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Cancer 8:3697–3706
Ying H, Yue BY (2012) Cellular and molecular biology of optineurin. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 294:223–258
Yu DS, Cao Y, Mei XF, Wang YF, Fan ZK, Wang YS, Lv G (2014) Curcumin improves the integrity of blood-spinal cord barrier after compressive spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurol Sci 346:51–59
Yu S, Wang X, He X, Wang Y, Gao S, Ren L, Shi Y (2016) Curcumin exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties in 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP(+))-stimulated mesencephalic astrocytes by interference with TLR4 and downstream signaling pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones 21:697–705
Yuan J, Zou M, **ang X, Zhu H, Chu W, Liu W, Chen F, Lin J (2015) Curcumin improves neural function after spinal cord injury by the joint inhibition of the intracellular and extracellular components of glial scar. J Surg Res 195:235–245
Yuan J, Liu W, Zhu H, Chen Y, Zhang X, Li L, Chu W, Wen Z, Feng H, Lin J (2017) Curcumin inhibits glial scar formation by suppressing astrocyte-induced inflammation and fibrosis in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res 1655:90–103
Zahedi H, Hosseinzadeh-Attar MJ, Shadnoush M, Sahebkar A, Barkhidarian B, Sadeghi O, Najafi A, Hosseini S, Qorbani M, Ahmadi A, Ardehali SH, Norouzy A (2021) Effects of curcuminoids on inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers and clinical outcomes in critically ill patients: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Phytother Res 35:4605–4615
Zhang N, Wei G, Ye J, Yang L, Hong Y, Liu G, Zhong H, Cai X (2017) Effect of curcumin on acute spinal cord injury in mice via inhibition of inflammation and TAK1 pathway. Pharmacol Rep 69:1001–1006
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Luo Y, Du Y, Zhang X, Fu J (2019) Curcumin inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation by promoting microglial M2 polarization via TREM2/ TLR4/ NF-κB pathways in BV2 cells. Mol Immunol 116:29–37
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support was received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Niusha Esmaealzadeh: data curation, writing- original draft preparation. Mahdis Sadat Miri: data curation, writing—original draft preparation. Helia Mavvadat: data curation, writing—original draft preparation. Amirreza Peyrovinasab: data curation, writing—original draft preparation. Sara Ghasemi Zargar: data curation, writing—original draft preparation. Shirin Sirous Kabiri: data curation, writing—original draft preparation. Seyed Mehrad Razavi: conceptualization, methodology, reviewing and editing, supervision. Amir Hossein Abdolghaffari: conceptualization, reviewing and editing, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Esmaealzadeh, N., Miri, M., Mavaddat, H. et al. The regulating effect of curcumin on NF-κB pathway in neurodegenerative diseases: a review of the underlying mechanisms. Inflammopharmacol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-024-01492-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-024-01492-1