Abstract
Background
Neuropathic pain results from lesions or diseases affecting the somatosensory system. The management of a patient with chronic neuropathic pain remains a challenge several studies report the analgesic effect of serotonin receptor antagonists in different models of experimental pain. The present study was designed to study the effect of systemic administration of risperidone, on behavioral scores of neuropathic pains in chronic constriction (CCI) model in rats.
Methods
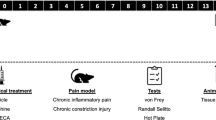
Inducing neuropathic pain with the CCI model which causes heat hyperalgesia, heat, and mechanical allodynia was performed on rats, and then, in two phases, risperidone effect was determined. In the acute phase, risperidone 1, 2, 4 mg was administered for three groups half an hour before behavioral tests on the 7th, 14th, and 21st day after surgery, and in the chronic phase, risperidone 1, 2, and 4 mg was administered for three different groups from the 1st to 14th days after surgery than on 14th-day behavioral scores were performed. For gene expression analysis, samples are taken from spinal cord tissues in lumbar segments.
Results
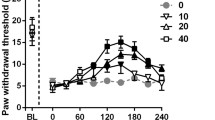
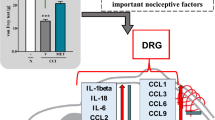
This study shows chronic administration of risperidone as an antipsychotic drug was effective on heat hyperalgesia and allodynia. However, only the max dosage (4 mg) of risperidone showed meaningful improvement in increasing mechanical allodynia. However, acute administering of risperidone did not show any meaningful changes in behavioral tests on neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rats. In addition, gene expression results showed an increase in IL-4 and IL-10 gene expression in the risperidone group compared to the sham group.
Conclusion
This study suggests the helpful preventive effects of risperidone in develo** and increasing neuropathic pain, but it does not have any instant effect.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The dataset used in this study is available with the authors and can be made available upon request.
References
Banafshe HR et al (2012) Lithium attenuates pain-related behavior in a rat model of neuropathic pain: possible involvement of opioid system. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100(3):425–430
Bardin L (2011) The complex role of serotonin and 5-HT receptors in chronic pain. Behav Pharmacol 22(5–6):390–404
Becker A et al (2009) Haloperidol and risperidone have specific effects on altered pain sensitivity in the ketamine model of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 202(4):579–587
Bennett GJ, **e YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33(1):87–107
Campbell JN, Meyer RA (2006) Mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Neuron 52(1):77–92
Chaplan SR et al (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53(1):55–63
Curatolo M, Sveticic G (2002) Drug combinations in pain treatment: a review of the published evidence and a method for finding the optimal combination. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol 16(4):507–519
DiPirro JM et al (2011) Low doses of risperidone and morphine interact to produce more analgesia and greater extrapyramidal effects in rats. Neurosci Lett 490(1):21–26
Dubin AE, Patapoutian A (2010) Nociceptors: the sensors of the pain pathway. J Clin Investig 120(11):3760–3772
Gao YJ, Ji RR (2010) Chemokines, neuronal-glial interactions, and central processing of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Ther 126(1):56–68
Hargreaves K et al (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32(1):77–88
Iwasa T et al (2019) IL-10 and CXCL2 in trigeminal ganglia in neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett 703:132–138
Kato T et al (2007a) Risperidone significantly inhibits interferon-γ-induced microglial activation in vitro. Schizophr Res 92(1–3):108–115
Kato T et al (2007b) Risperidone significantly inhibits interferon-gamma-induced microglial activation in vitro. Schizophr Res 92(1–3):108–115
Leucht S et al (2013) Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet 382(9896):951–962
Leung L, Cahill CM (2010) TNF-alpha and neuropathic pain–a review. J Neuroinflamm 7:27
MacDowell KS et al (2013) Risperidone normalizes increased inflammatory parameters and restores anti-inflammatory pathways in a model of neuroinflammation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16(1):121–135
Martinez V et al (2015) Clinical, histological, and biochemical predictors of postsurgical neuropathic pain. Pain 156(11):2390–2398
McNamara RK et al (2011) Chronic risperidone normalizes elevated pro-inflammatory cytokine and C-reactive protein production in omega-3 fatty acid deficient rats. Eur J Pharmacol 652(1–3):152–156
Noto C et al (2015) Effects of risperidone on cytokine profile in drug-naive first-episode psychosis. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18(4):pyu042
Nowacka A, Borczyk M (2019) Ketamine applications beyond anesthesia—a literature review. Eur J Pharmacol 860:172547
Reichling DB, Green PG, Levine JD (2013) The fundamental unit of pain is the cell. Pain 154:S2–S9
Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2007) The neuropathic pain triad: neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat Neurosci 10(11):1361–1368
Schreiber S et al (1997) Augmentation of opioid induced antinociception by the atypical antipsychotic drug risperidone in mice. Neurosci Lett 228(1):25–28
Smith ESJ, Lewin GR (2009) Nociceptors: a phylogenetic view. J Comp Physiol A 195:1089–1106
Sommer C, Schmidt C, George A (1998) Hyperalgesia in experimental neuropathy is dependent on the TNF receptor 1. Exp Neurol 151(1):138–142
Teng J, Mekhail N (2003) Neuropathic pain: mechanisms and treatment options. Pain Pract 3(1):8–21
Woolf CJ, Mannion RJ (1999) Neuropathic pain: aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet 353(9168):1959–1964
Yoon C et al (1994) Behavioral signs of ongoing pain and cold allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain 59(3):369–376
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all my colleagues for their assistance in laboratory techniques and our staff for their cooperation. This study supported by Kashan University of Medical Sciences.
Funding
The financial support for the current research was provided by Research Deputy of Kashan University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number: 98067), Kashan, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MMH, ESH, and HRB provided direction and guidance throughout the preparation of this manuscript. HHK, ESH, and MMH conducted the literature and drafted the manuscript. Other authors reviewed the manuscript and made significant revisions on the drafts. All authors read and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in the study involving human were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee of Kashan University of Medical Sciences. The protocol was approved by the research committee of Kashan University of Medical Sciences, Kashan, Iran.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Haghighat Lari, M., Banafshe, H., Seyed Hosseini, E. et al. The effect of risperidone on behavioral reactions and gene expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in neuropathic pain model induced by chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rat. Inflammopharmacol 31, 2641–2652 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01293-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01293-y