Abstract
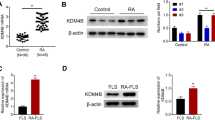
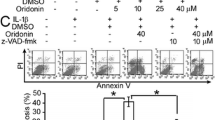
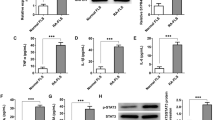
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs), the main pathological cells in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), display tumor-like phenotype, including hyper-proliferation, apoptosis resistance, and aggressive phenotype. Excessive proliferation and insufficient apoptosis of RA-FLSs can lead to hyperplastic synovial pannus tissue, excess production of inflammatory mediators, and destruction of joints. In this article, we investigate the effect of PRIMA-1MET on the apoptosis induction and inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines in RA-FLSs. Synovial tissue samples were obtained from 10 patients with RA. The FLSs were treated with different concentrations of PRIMA-1MET. The rate of apoptosis and cell survival was assessed by flow cytometry and MTT assay and Real-time quantitative PCR was performed to evaluate the transcription of p53, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, Noxa, p21, PUMA, Bax, Survivin, and XIAP in treated RA-FLSs. The protein level of p53, IκBα, and phospho-IκBα were measured using Western blotting. The results showed that PRIMA-1MET induced apoptosis in RA-FLSs and increased significantly the expression of Noxa, and decreased significantly IL-6, IL-1β, p53, and phospho-IκBα expression. PRIMA-1MET can induce apoptosis in RA-FLSs through induction of Noxa expression while p53 was downregulated. Furthermore, PRIMA-1MET treatment results in the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine production and NF-κB inhibition. Given the role of p53 and NF-κB in RA-FLSs, PRIMA-1MET can be considered as a new therapeutic strategy for rheumatoid arthritis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Applicable on requested.
References
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd et al (2010) 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American college of Rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27584
Bohuslav J, Chen LF, Kwon H, Mu Y, Greene WC (2004) p53 induces NF-kappaB activation by an IkappaB kinase-independent mechanism involving phosphorylation of p65 by ribosomal S6 kinase 1. J Biol Chem 279:26115–26125. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M313509200
Bottini N, Firestein GS (2013) Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nat Rev Rheumatol 9:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2012.190
Bykov VJ, Issaeva N, Selivanova G, Wiman KG (2002a) Mutant p53-dependent growth suppression distinguishes PRIMA-1 from known anticancer drugs: a statistical analysis of information in the National Cancer Institute database. Carcinogenesis 23:2011–2018. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/23.12.2011
Bykov VJ, Issaeva N, Shilov A, Hultcrantz M, Pugacheva E, Chumakov P et al (2002b) Restoration of the tumor suppressor function to mutant p53 by a low-molecular-weight compound. Nat Med 8:282–288. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0302-282
Bykov VJ, Selivanova G, Wiman KG (2003) Small molecules that reactivate mutant p53. Eur J Cancer 39:1828–1834. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-8049(03)00454-4
Bykov VJN, Eriksson SE, Bianchi J, Wiman KG (2018) Targeting mutant p53 for efficient cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 18:89–102. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.109
Colman MS, Afshari CA, Barrett JC (2000) Regulation of p53 stability and activity in response to genotoxic stress. Mutat Res 462:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1383-5742(00)00035-1
Cottier KE, Fogle EM, Fox DA, Ahmed S (2014) Noxa in rheumatic diseases: present understanding and future impact. Rheumatol (oxford) 53:1539–1546. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ket408
Farhadi E, Safa M, Sharifi AM, Bashash D (2017) PRIMA-1 induces caspase-mediated apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia NB4 cells by inhibition of nuclear factor-κB and downregulation of Bcl-2, XIAP, and c-Myc. Anticancer Drugs 28:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1097/cad.0000000000000426
Firestein GS (2003) Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 423:356–361. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01661
Firestein GS, Nguyen K, Aupperle KR, Yeo M, Boyle DL, Zvaifler NJ (1996) Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis: p53 overexpression in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Am J Pathol 149:2143–2151
Firestein GS, Echeverri F, Yeo M, Zvaifler NJ, Green DR (1997) Somatic mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:10895–10900. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.20.10895
Greenblatt MS, Bennett WP, Hollstein M, Harris CC (1994) Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: clues to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res 54:4855–4878
Güllülü Ö, Hehlgans S, Rödel C, Fokas E, Rödel F (2021) Tumor suppressor protein p53 and Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in colorectal cancer—a promising signaling network for therapeutic interventions. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040624
Han Z, Boyle DL, Shi Y, Green DR, Firestein GS (1999) Dominant-negative p53 mutations in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 42:1088–1092. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(199906)42:6%3c1088::aid-anr4%3e3.0.co;2-e
Hewagama A, Richardson B (2009) The genetics and epigenetics of autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun 33:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2009.03.007
Inazuka M, Tahira T, Horiuchi T, Harashima S, Sawabe T, Kondo M et al (2000) Analysis of p53 tumour suppressor gene somatic mutations in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Rheumatol (oxford) 39:262–266. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/39.3.262
Izetti P, Hautefeuille A, Abujamra AL, de Farias CB, Giacomazzi J, Alemar B et al (2014) PRIMA-1, a mutant p53 reactivator, induces apoptosis and enhances chemotherapeutic cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Invest New Drugs 32:783–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0090-9
Jänicke RU, Sohn D, Schulze-Osthoff K (2008) The dark side of a tumor suppressor: anti-apoptotic p53. Cell Death Differ 15:959–976. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.33
Khoo KH, Verma CS, Lane DP (2014) Drugging the p53 pathway: understanding the route to clinical efficacy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13:217–236. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4236
Kinne RW, Stuhlmüller B, Burmester GR (2007) Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Macrophages Arthritis Res Ther 9:224. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2333
Lambert JM, Gorzov P, Veprintsev DB, Söderqvist M, Segerbäck D, Bergman J et al (2009) PRIMA-1 reactivates mutant p53 by covalent binding to the core domain. Cancer Cell 15:376–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.03.003
Li XL, Zhou J, Chan ZL, Chooi JY, Chen ZR, Chng WJ (2015) PRIMA-1met (APR-246) inhibits growth of colorectal cancer cells with different p53 status through distinct mechanisms. Oncotarget 6:36689–36699. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5385
Liang Y, Besch-Williford C, Hyder SM (2009) PRIMA-1 inhibits growth of breast cancer cells by re-activating mutant p53 protein. Int J Oncol 35:1015–1023. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo_00000416
Makarov SS (2001) NF-kappa B in rheumatoid arthritis: a pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and tissue destruction. Arthritis Res 3:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar300
Messina RL, Sanfilippo M, Vella V, Pandini G, Vigneri P, Nicolosi ML et al (2012) Reactivation of p53 mutants by prima-1 [corrected] in thyroid cancer cells. Int J Cancer 130:2259–2270. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.26228
Mlakar V, Jurkovic Mlakar S, Lesne L, Marino D, Rathi KS, Maris JM et al (2019) PRIMA-1(MET)-induced neuroblastoma cell death is modulated by p53 and mycn through glutathione level. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1066-6
Murphy SH, Suzuki K, Downes M, Welch GL, De Jesus P, Miraglia LJ et al (2011) Tumor suppressor protein (p)53, is a regulator of NF-kappaB repression by the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:17117–17122. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1114420108
Rangel LP, Ferretti GDS, Costa CL, Andrade S, Carvalho RS, Costa DCF et al (2019) p53 reactivation with induction of massive apoptosis-1 (PRIMA-1) inhibits amyloid aggregation of mutant p53 in cancer cells. J Biol Chem 294:3670–3682. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.004671
Ruscitti P, Cipriani P, Liakouli V, Carubbi F, Berardicurti O, Di Benedetto P et al (2018) The emerging role of IL-1 inhibition in patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes. Rev Recent Clin Trials 13:210–214. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574887113666180314102651
Schett G, Gravallese E (2012) Bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8:656–664. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2012.153
Soans E, Evans SC, Cipolla C, Fernandes E (2014) Characterizing the sphingomyelinase pathway triggered by PRIMA-1 derivatives in lung cancer cells with differing p53 status. Anticancer Res 34:3271–3283
Synnott NC, Murray A, McGowan PM, Kiely M, Kiely PA, O’Donovan N et al (2017) Mutant p53: a novel target for the treatment of patients with triple-negative breast cancer? Int J Cancer 140:234–246. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30425
Vousden KH (2006) Outcomes of p53 activation–spoilt for choice. J Cell Sci 119:5015–5020. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.03293
Wang T, Lee K, Rehman A, Daoud SS (2007) PRIMA-1 induces apoptosis by inhibiting JNK signaling but promoting the activation of Bax. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.11.006
Webster GA, Perkins ND (1999) Transcriptional cross talk between NF-kappaB and p53. Mol Cell Biol 19:3485–3495. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.19.5.3485
Yamanishi Y, Boyle DL, Green DR, Keystone EC, Connor A, Zollman S et al (2005) p53 tumor suppressor gene mutations in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from erosion synovium and non-erosion synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R12-18. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar1448
Yoshida Y, Tanaka T (2014) Interleukin 6 and rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Res Int 2014:698313. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/698313
Zafari P, Rafiei A, Esmaeili SA, Moonesi M, Taghadosi M (2019) Survivin a pivotal antiapoptotic protein in rheumatoid arthritis. J Cell Physiol 234:21575–21587. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28784
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Grant No: 97-03-41-40374), and a grant from Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences (Grant No: 97887).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA: acquisition of data, drafting the article, analysis and interpretation of data, final approval of the article. MNT and AS: acquisition of clinical data and patient’s diagnosis and treatment, interpretation of data, drafting the article, and final approval of the article. MT, AJ, MM and EF: the conception and design of the study, revising the article critically, interpretation of data, final approval of the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was performed based on the Declaration of Helsinki guidelines and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Approval No: IR.TUMS.VCR.REC.1397.968).
Consent to participate
The written informed consent was signed by all participants before enrolling in the study.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Adib, M., Taghadosi, M., Tahmasebi, M.N. et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of PRIMA-1MET (mutant p53 reactivator) induced by inhibition of nuclear factor-κB on rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflammopharmacol 31, 385–394 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01094-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01094-9