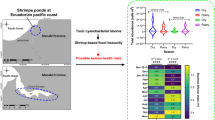
Abstract
Salinization of coastal freshwaters (FWs) due to sea-level rise is a significant stressor for FW biodiversity. However, the effect of changes in salinity on the bacterial microbiome of Neotropical FW insects is less known. We combined field collections and common garden experiments to assess how changes in salinity may affect the microbiome associated with fresh and brackish populations of the water strider Telmatometra withei in Panama. The brackish water (BW) population had higher bacterial diversity and the total communities associated with T. withei were different at each site. Common garden experiments showed that both β diversity and the relative abundance of key taxa varied significantly with changes in salinity, but α diversity remained constant. The BW treatments also showed increased diversity of taxa known to be pathogenic to both insects and humans, including Mycobacterium, Spiroplasma, and Vibrio. Our findings suggest that the host environment is an essential driver of host–microbiome interactions in T. withei. Given the expected increases in sea-level rise, salinity-driven changes in the microbiomes of aquatic insects could trigger important ecological, evolutionary, and pathogenic changes, with consequences for both natural and human populations.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Raw sequence data and metadata are available at: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/Salinity_effects_on_the_microbiome_of_a_Neotropical_water_strider/14676510. Raw sequence are available at: https://www.mg-rast.org/mgmain.html?mgpage=token&token=rxUJmwxaxo1J0pNV24Gw0VuP9JugUrnF1K.
References
Abbott, D. W. & A. B. Boraston, 2008. Structural biology of pectin degradation by Enterobacteriaceae. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 72: 301–316.
Abdelaziz, M., M. D. Ibrahem, M. A. Ibrahim, N. M. Abu-Elala & D. A. Abdel-Moneam, 2017. Monitoring of different Vibrio species affecting marine fishes in Lake Qarun and Gulf of Suez: phenotypic and molecular characterization. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research 43: 141–146.
Antwis, R. E., S. M. Griffiths, X. A. Harrison, P. Aranega-Bou, A. Arce, A. S. Bettridge, F. L. Brailsford, A. de Menezes, A. Devaynes, K. M. Forbes, E. L. Fry, I. Goodhead, E. Haskell, C. Heys, C. James, S. R. Johnston, G. R. Lewis, Z. Lewis, M. C. Macey, A. McCarthy, J. E. McDonald, N. L. Mejia-Florez, D. O’Brien, C. Orland, M. Pautasso, W. D. K. Reid, H. A. Robinson, K. Wilson & W. J. Sutherland, 2017. Fifty important research questions in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 93: 1–10.
Asmar, S., M. Sassi, M. Phelippeau & M. Drancourt, 2016. Inverse correlation between salt tolerance and host-adaptation in mycobacteria. BMC Research Notes 9: 1–9.
Baldwin, D. S., G. N. Rees, A. M. Mitchell, G. Watson & J. Williams, 2006. The short-term effects of salinization on anaerobic nutrient cycling and microbial community structure in sediment from a freshwater wetland. Wetlands 26: 455–464.
Berkey, C. D., N. Blow & P. I. Watnick, 2009. Genetic analysis of Drosophila melanogaster susceptibility to intestinal Vibrio cholerae infection. Cellular Microbiology 11: 461–474.
Blow, N. S., R. N. Salomon, K. Garrity, I. Reveillaud, A. Kopin, F. R. Jackson & P. I. Watnick, 2005. Vibrio cholerae infection of Drosophila melanogaster mimics the human disease cholera. PLoS Pathogens 1: 0092–0098.
Bokulich, N. A., B. D. Kaehler, J. R. Rideout, M. Dillon, E. Bolyen, R. Knight, G. A. Huttley & J. Gregory Caporaso, 2018. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 6: 1–17.
Callahan, B. J., P. J. McMurdie, M. J. Rosen, A. W. Han, A. A. Johnson & S. P. Holmes, 2016a. DADA2: high resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nature Methods 13: 4–5.
Callahan, B. J., K. Sankaran, J. A. Fukuyama, P. J. McMurdie & S. P. Holmes, 2016b. Bioconductor workflow for microbiome data analysis: from raw reads to community analyses [version 2; peer review: 3 approved]. F1000Research 5: 1492. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.8986.2.
Cañedo-Argüelles, M., 2020. A review of recent advances and future challenges in freshwater salinization. Limnetica 39: 185–211.
Cañedo-Argüelles, M., T. E. Grantham, I. Perrée, M. Rieradevall, R. Céspedes-Sánchez & N. Prat, 2012. Response of stream invertebrates to short-term salinization: a mesocosm approach. Environmental Pollution 166: 144–151.
Cañedo-Argüelles, M., B. J. Kefford, C. Piscart, N. Prat, R. B. Schäfer & C.-J. Schulz, 2013. Salinisation of rivers: an urgent ecological issue. Environmental Pollution 173: 157–167.
Caporaso, J. G., C. L. Lauber, W. A. Walters, D. Berg-lyons, C. A. Lozupone, P. J. Turnbaugh, N. Fierer & R. Knight, 2011. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA 108: 4516–4522.
Castillo, A. M. & L. F. De León, 2021. Evolutionary mismatch along salinity gradients in a Neotropical water strider. Ecology and Evolution 11(10): 1–14.
Castillo, A. M., K. Saltonstall, C. F. Arias, K. A. Chavarria, L. A. Ramírez-Camejo, L. C. Mejía & L. F. De León, 2020. The microbiome of Neotropical water striders and its potential role in codiversification. Insects 11: 1–15.
Castillo, A. M., M. T. Sharpe, C. K. Ghalambor & L. F. De León, 2017. Exploring the effects of salinization on trophic diversity in freshwater ecosystems: a quantitative review. Hydrobiologia 807: 1–17.
Chen, S. J., F. Lu, J. A. Cheng, M. X. Jiang & M. O. Way, 2012. Identification and biological role of the endosymbionts Wolbachia in rice water Weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environmental Entomology 41: 469–477.
Chong, J., P. Liu, G. Zhou & J. **a, 2020. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nature Protocols 15: 799–821.
Clarke, K. R., 1993. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Australian Journal of Ecology 18: 117–143.
Dhariwal, A., J. Chong, S. Habib, I. L. King, L. B. Agellon & J. **a, 2017. MicrobiomeAnalyst: a web-based tool for comprehensive statistical, visual and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nucleic Acids Research 45: W180–W188.
Edmonds, J. W., N. B. Weston, S. B. Joye, X. Mou, & M. A. Moran, 2009. Microbial community response to seawater amendment in low-salinity tidal sediments. Microbial Ecology 58: 558–568.
Engel, P. & N. A. Moran, 2013. The gut microbiota of insects – diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 37: 699–735.
Esemu, S. N., X. Dong, A. J. Kfusi, C. S. Hartley, R. N. Ndip, L. M. Ndip, A. C. Darby, R. J. Post & B. L. Makepeace, 2019. Aquatic Hemiptera in southwest Cameroon: biodiversity of potential reservoirs of Mycobacterium ulcerans and multiple Wolbachia sequence types revealed by metagenomics. Diversity 11: 1–28.
Gallardo, K., J. E. Candia, F. Remonsellez, L. V. Escudero & C. S. Demergasso, 2016. The ecological coherence of temperature and salinity tolerance interaction and pigmentation in a non-marine Vibrio isolated from Salar de Atacama. Frontiers in Microbiology 7: 1–10.
Gomez-Mestre, I. & M. Tejedo, 2003. Local adaptation of an Anuran Amphibian to osmotically stressful environments. Evolution 57: 1889–1899.
Hansen, J., M. Sato, P. Hearty, R. Ruedy, M. Kelley, V. Masson-Delmotte, G. Russell, G. Tselioudis, J. Cao, E. Rignot, I. Velicogna, B. Tormey, B. Donovan, E. Kandiano, K. Von Schuckmann, P. Kharecha, A. N. Legrande & M. Bauer, 2016. Ice melt, sea level rise and superstorms: evidence from paleoclimate data, climate modeling, and modern observations that 2 °C global warming could be dangerous. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 16: 3761–3812.
Hedges, L. M., J. C. Brownlie, S. L. O’Neill & K. N. Johnson, 2008. Wolbachia and virus protection in insects. Science 322: 702.
Heres, A., R. Redman & D. V. Lightner, 2011. Histopathology of Spiroplasma penaei systemic infection in experimentally infected Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. Israeli Journal of Aquaculture Bamidgeh 63: 589.
Hooper, L. V., T. Midtvedt & J. I. Gordon, 2002. How host–microbial interactions shape the nutrient environment of the mammalian intestine. Annual Review of Nutrition 22: 283–307.
Hughes, J. M., D. J. Schmidt, A. McLean & A. Wheatley, 2008. Population genetic structure in stream insects what have we learned. In Population Genetic Structure.
IPCC, 2007. Cambio climático 2007: Informe de síntesis. Informe del Grupo Intergubernamental de Expertos sobre el Cambio Climático.
Izabella, O., B. Pawel, J. Piotr & S. don Lee, 2007. Diet of water striders (Gerris lacustris L. 1758) in a rice field near Seoul, Korea. Journal of Asia–Pacific Entomology 10: 85–88.
Jackson, C. R., & S. C. Vallaire, 2009. Effects of salinity and nutrients on microbial assemblages in Louisiana Wetland Sediments. Wetlands 29: 277–287.
Kefford, B. J., G. L. Hickey, A. Gasith, E. Ben-David, J. E. Dunlop, C. G. Palmer, K. Allan, S. C. Choy & C. Piscart, 2012. Global scale variation in the salinity sensitivity of riverine macroinvertebrates: eastern Australia, France, Israel and South Africa. PLoS ONE 7: e35224.
Koch, H. & P. Schmid-Hempel, 2011. Socially transmitted gut microbiota protect bumble bees against an intestinal parasite. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA 108: 19288–19292.
Levermann, A., P. U. Clark, B. Marzeion, G. A. Milne, D. Pollard, V. Radic & A. Robinson, 2013. The multimillennial sea-level commitment of global warming. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA 110: 13745–13750.
Lozupone, C. A. & R. Knight, 2007. Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104: 11436–11440.
Merritt, R. W., K. W. Cummins & M. B. Berg, 2008. An Introduction to Aquatic Insects of North America, 4th ed. Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company, Dubuque:
Merritt, R. W., K. W. Cummins, M. B. Berg, J. A. Novak, M. J. Higgins, K. J. Wessell & J. L. Lessard, 2002. Development and application of a macroinvertebrate functional-group approach in the bioassessment of remnant river oxbows in southwest Florida. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 21: 290–310.
Merritt, R. W., J. R. Wallace, M. J. Higgins, M. K. Alexander, M. B. Berg, W. T. Morgan, K. W. Cummins & B. Vandeneeden, 1996. Procedures for the functional analysis of invertebrate communities in the Kissimmee River flood-plain ecosystem. Florida Scientist 59: 216–274.
Mizrahi-Man, O., E. R. Davenport & Y. Gilad, 2013. Taxonomic classification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes using short sequencing reads: evaluation of effective study designs. PLoS ONE 8: 18–23.
Molano, F., S. P. Mondragón-F & I. Morales, 2017. Nueva Especie y Nuevos Registros de Telmatometra (Hemiptera: Gerridae) en Colombia. Ciencia en Desarrollo 8: 93–98.
Moran, N. A., J. P. McCutcheon & A. Nakabachi, 2008. Genomics and evolution of heritable bacterial symbionts. Annual Review of Genetics 42: 165–190.
Morrissey, E. M., R. B. Franklin & A. Kent, 2015. Evolutionary history influences the salinity preference of bacterial taxa in wetland soils. Frontiers in Microbiology 6: 1–12.
Motta, E. V. S., K. Raymann & N. A. Moran, 2018. Glyphosate perturbs the gut microbiota of honey bees. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA 115: 10305–10310.
Neubauer, S. C. & C. B. Craft, 2009. Global change and tidal freshwater wetlands: scenarios and impacts. Tidal freshwater wetlands. Estuaries and Coasts 36: 491–507.
Nougue, O., R. Gallet, L.-M. Chevin & T. Lenormand, 2015. Niche limits of symbiotic gut microbiota constrain the salinity tolerance of brine shrimp. American Naturalist 186: 390–403.
Nowinski, B., C. B. Smith, C. M. Thomas, K. Esson, R. Marin, C. M. Preston, J. M. Birch, C. A. Scholin, M. Huntemann, A. Clum, B. Foster, B. Foster, S. Roux, K. Palaniappan, N. Varghese, S. Mukherjee, T. B. K. Reddy, C. Daum, A. Copeland, I.-M.A. Chen, N. N. Ivanova, N. C. Kyrpides, T. Glavina del Rio, W. B. Whitman, R. P. Kiene, E. A. Eloe-Fadrosh & M. A. Moran, 2019. Microbial metagenomes and metatranscriptomes during a coastal phytoplankton bloom. Scientific Data 6: 1–7.
Nummelin, M., 1988. Waterstriders (Het: Gerridae) as predators of hatching mosquitoes. Bicovas 1: 121–125.
Nunan, L. M., D. V. Lightner, M. A. Oduori & G. E. Gasparich, 2005. Spiroplasma penaei sp. nov., associated with mortalities in Penaeus vannamei, Pacific white shrimp. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 55: 2317–2322.
Oksanen, J., F. G. Blanchet, M. Friendly, R. Kindt, P. Legendre, D. Mcglinn, P. R. Minchin, R. B. O’Hara, G. L. Simpson, P. Solymos, M. Henry, H. Stevens, E. Szoecs & H. W. Maintainer, 2017. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.0-10. 2.
Pacheco, B., 2012. Diversidad taxonómica y distribución de los chinches patinadores (Hemiptera: Gerridae) en Costa Rica.
Padilla-Gil, D. N., 2012. Los Hemípteros Acuáticos del Municipio de Tumaco (Nariño, Colombia) Guía Ilustrada.
Panayidou, S., E. Ioannidou & Y. Apidianakis, 2014. Human pathogenic bacteria, fungi, and viruses in Drosophila. Virulence 5: 253–269.
Park, S. Y., Y. J. Heo, K. S. Kim & Y. H. Cho, 2005. Drosophila melanogaster is susceptible to Vibrio cholerae infection. Molecules and Cells 20: 409–415.
Pereira, C. S., I. Lopes, I. Abrantes, J. P. Sousa & S. Chelinho, 2019. Salinization effects on coastal ecosystems: a terrestrial model ecosystem approach. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2018.0251.
Philippot, L., S. G. E. Andersson, T. J. Battin, J. I. Prosser, J. P. Schimel, W. B. Whitman, & S. Hallin, 2010. The ecological coherence of high bacterial taxonomic ranks. Nature Reviews Microbiology 8: 523–529.
Poinsot, D., S. Charlat & H. Merçot, 2003. On the mechanism of Wolbachia-induced cytoplasmic incompatibility: confronting the models with the facts. BioEssays 25: 259–265.
Pruzzo, C., A. Huq, R. R. Colwell & G. Donelli, 2005. Pathogenic Vibrio species in the marine and estuarine environment. In Oceans and Health: Pathogens in the Marine Environment. Springer, Boston: 217–252.
R Development Core, 2008. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna:
Rahmstorf, S., 2007. A semi-empirical approach to projecting future sea-level rise. Science 315: 368–370.
Rath, K. M., N. Fierer, D. V. Murphy & J. Rousk, 2019. Linking bacterial community composition to soil salinity along environmental gradients. ISME Journal 13: 836–846.
Schuler, H., S. P. Egan, G. R. Hood, R. W. Busbee, A. L. Driscoe & J. R. Ott, 2018. Diversity and distribution of Wolbachia in relation to geography, host plant affiliation and life cycle of a heterogonic gall wasp. BMC Evolutionary Biology 18: 1–15.
Short, F. T., S. Kosten, P. A. Morgan, S. Malone & G. E. Moore, 2016. Impacts of climate change on submerged and emergent wetland plants. Aquatic Botany 135: 3–17.
Silverman, M. P. & E. F. Munoz, 1973. Effect of iron and salt on prodigiosin synthesis in Serratia marcescens. Journal of Bacteriology 114: 999–1006.
Spor, A., O. Koren & R. Ley, 2011. Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nature Reviews Microbiology 9: 279–290.
Suenami, S., M. Konishi Nobu & R. Miyazaki, 2019. Community analysis of gut microbiota in hornets, the largest eusocial wasps, Vespa mandarinia and V. simillima. Scientific Reports 9: 1–13.
Sullam, K. E., S. D. Essinger, C. A. Lozupone, M. P. O’Connor, G. L. Rosen, R. Knight, S. S. Kilham & J. A. Russell, 2012. Environmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: a meta-analysis. Molecular Ecology 21: 3363–3378.
Teixeira, L., Á. Ferreira & M. Ashburner, 2008. The bacterial symbiont Wolbachia induces resistance to RNA viral infections in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Biology 6: 2753–2763.
Thompson, F., T. Iida & J. Swings, 2004. Biodiversity of Vibrios. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 68: 403–431.
Truong, A., M. Sondossi & J. B. Clark, 2017. Genetic characterization of Wolbachia from Great Salt Lake brine flies. Symbiosis 72: 95–102.
Wetzel, F. T., W. D. Kissling, H. Beissmann & D. J. Penn, 2012. Future climate change driven sea-level rise: secondary consequences from human displacement for island biodiversity. Global Change Biology 18: 2707–2719.
Wickham, H., 2017. ggplot2 – Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis | Hadley Wickham. Springer [available on internet at https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9780387981413%0A, https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783319242750%0A, https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783319242750%0A].
Wilkinson, L., 2012. Exact and approximate area-proportional circular Venn and Euler diagrams. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 18: 321–331.
Wrange, A. L., C. André, T. Lundh, U. Lind, A. Blomberg, P. J. Jonsson & J. N. Havenhand, 2014. Importance of plasticity and local adaptation for co** with changing salinity in coastal areas: a test case with barnacles in the Baltic Sea. BMC Evolutionary Biology 14: 156.
Zchori-Fein, E., C. Borad & A. R. Harari, 2006. Oogenesis in the date stone beetle, Coccotrypes dactyliperda, depends on symbiotic bacteria. Physiological Entomology 31: 164–169.
Zhang, M., Y. Sun, Y. Liu, F. Qiao, L. Chen, W. Liu, Z. Du & E. Li, 2016. Response of gut microbiota to salinity change in two euryhaline aquatic animals with reverse salinity preference. Aquaculture 454: 72–80.
Acknowledgements
We thank Eyda Gómez and Marta Vargas Timchenko for logistical support in the STRI Ecological and Evolutionary Genomics Laboratory.
Funding
This work was supported by the Secretaría Nacional de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación (SENACYT, Panamá) in the form of a Doctoral Fellowship to A.M.C. (No. 270-2013-284) and a Research Grant (No. FID16-116) to L.F.D. Additional support was provided by Instituto para la Formación y Aprovechamiento de los Recursos Humanos in the form of a Doctoral Fellowship to A.M.C. A.M.C. and L.C.M. acknowledge support from the Sistema Nacional de Investigación (SNI, Panamá). L.F.D. is supported by the University of Massachusetts Boston and K.S. received support from the Simons Foundation (Grant 429440 to W. Wcislo, P.I.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization AMC and LFD; formal analysis AMC, KAC, and KS; methodology AMC; investigation AMC, LFD, KAC, KS, CFA, and LCM; writing—review and editing AMC, LFD, KAC, KS, CFA, and LCM; funding acquisition LFD. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Guest Editors: Isa Schön, Diego Fontaneto & Elena L. Peredo / Aquatic Microbiomes
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10750_2021_4732_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
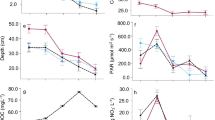
Supplementary file1 (PDF 42 kb) Fig. S1 Rarefaction curves of bacterial phylogenetic diversity (based on Faith’s PD, ± SE) associated with T. withei from two field sites (A) and common garden experiments (B)
10750_2021_4732_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file2 (PDF 90 kb) Fig. S2 Relative abundance of the most common bacteria taxa associated with T. withei in common garden experiments (salinity treatments 0 to 5 ppt). Abundance was estimated at the rank of bacterial class (A), as well as at the rank of genus (B). α Diversity was estimated based on Faith’s phylogenetic diversity for each site (C). FW and BW in upper part represent both FW and BW origin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castillo, A.M., Chavarria, K.A., Saltonstall, K. et al. Salinity effects on the microbiome of a Neotropical water strider. Hydrobiologia 850, 3705–3717 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04732-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04732-5