Abstract
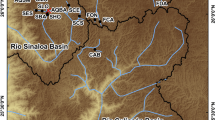
Many populations of Caspian Sea trout (Salmo caspius)—a nationally endangered species in Iran—have been extirpated or depleted due to anthropogenic impacts. The Lar National Park hosts large populations of Caspian Sea trout, which have not been subject to fisheries management programs before, but the population/s also face different human-related threats that may endanger their sustainability. A total of 357 Caspian Sea trout collected from different streams in Lar National Park were genotyped at 7978 filtered SNP using Genoty**-By-Sequencing to document population genetic structure and the contribution of each population/habitat to lake-run trout fisheries. Our results revealed a fine-scale population genetic structure, which is probably a product of factors including natural and artificial barriers to gene flow, geographic distance, and behavioral differences between resident and lake-run trout. Mixed-Stock Analyses revealed a high contribution from four panmictic populations of the national park to lake-run fish and almost no contribution from streams located in upper reaches or from streams with hydro-chemical or physical barriers. Our results highlighted the necessity for a more serious conservation plan for both the populations contributing greatly to lake fisheries and the highly diverged upstream populations due to their uniqueness.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
VCF files and other Data are available on request.
References
Abdoli, A., 2000. The Inland Water Fishes of Iran. Iranian Museum of Nature and Wildlife, Tehran.
Alexander, D. H., J. Novembre & K. Lange, 2009. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Research 19(9): 1655–1664.
Aljanabi, S. M. & I. Martinez, 1997. Universal and rapid salt-extraction of high quality genomic DNA for PCR-based techniques. Nucleic acids Research 25(22): 4692–4693.
Almodóvar, A., G. G. Nicola, D. Ayllón & B. Elvira, 2012. Global warming threatens the persistence of Mediterranean brown trout. Global Change Biology 18(5): 1549–1560.
Anderson, E. C., R. S. Waples & S. T. Kalinowski, 2008. An improved method for predicting the accuracy of genetic stock identification. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 65(7): 1475–1486.
Andrews, S., 2010. FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data.
Andrews, K. R., J. M. Good, M. R. Miller, G. Luikart & P. A. Hohenlohe, 2016. Harnessing the power of RADseq for ecological and evolutionary genomics. Nature Reviews Genetics 17(2): 81–92.
Antunes, A., R. Faria, W. E. Johnson, R. Guyomard & P. Alexandrino, 2006. Life on the edge: the long-term persistence and contrasting spatial genetic structure of distinct brown trout life histories at their ecological limits. Journal of Heredity 97(3): 193–205.
Benestan, L., T. Gosselin, C. Perrier, B. Sainte-Marie, R. Rochette & L. Bernatchez, 2015. RAD genoty** reveals fine-scale genetic structuring and provides powerful population assignment in a widely distributed marine species, the A merican lobster (Homarus americanus). Molecular Ecology 24(13): 3299–3315.
Bernatchez, S., M. Laporte, C. Perrier, P. Sirois & L. Bernatchez, 2016. Investigating genomic and phenotypic parallelism between piscivorous and planktivorous lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush) ecotypes by means of RAD seq and morphometrics analyses. Molecular Ecology 25(19): 4773–4792.
Bohlin, T., J. Pettersson & E. Degerman, 2001. Population density of migratory and resident brown trout (Salmo trutta) in relation to altitude: evidence for a migration cost. Journal of Animal Ecology 70(1): 112–121.
Breiman, L., 2006. randomForest: Breiman and Cutler’s random forests for classification and regression. http://stat-www.berkeley.edu/users/breiman/RandomForests, R package version.
Carlsson, J. & J. Nilsson, 2000. Population genetic structure of brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) within a northern boreal forest stream. Hereditas 132(3): 173–181.
Carlsson, J., K. Olsen, J. Nilsson, Ø. Øverli & O. Stabell, 1999. Microsatellites reveal fine-scale genetic structure in stream-living brown trout. Journal of Fish Biology 55(6): 1290–1303.
Catchen, J., P. A. Hohenlohe, S. Bassham, A. Amores & W. A. Cresko, 2013. Stacks: an analysis tool set for population genomics. Molecular Ecology 22(11): 3124–3140.
Chen, K. Y., E. A. Marschall, M. G. Sovic, A. C. Fries, H. L. Gibbs & S. A. Ludsin, 2018. assignPOP: an r package for population assignment using genetic, non-genetic, or integrated data in a machine-learning framework. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 9(2): 439–446.
Dionne, M., F. Caron, J. J. Dodson & L. Bernatchez, 2009. Comparative survey of within-river genetic structure in Atlantic salmon; relevance for management and conservation. Conservation Genetics 10(4): 869–879.
Esteve, M., A. Abdoli, I. H. Segherloo, K. Golzarianpour & A. A. Ahmadi, 2017. Observations of male choice in Brown Trout (Salmo trutta) from Lar National Park, Iran. Brown Trout: Biology, Ecology and Management 165: 178.
Hallerman, E. M., 2003. Population Genetics: Principles and Applications for Fisheries Scientists. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda.
Hansen, M. M., E. E. Nielsen & K. L. Mensberg, 1997. The problem of sampling families rather than populations: relatedness among individuals in samples of juvenile brown trout Salmo trutta L. Molecular Ecology 6(5): 469–474.
Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., H. Farahmand, A. Abdoli, L. Bernatchez, C. Primmer, A. Swatdipong, M. Karami & B. Khalili, 2012. Phylogenetic status of brown trout Salmo trutta populations in five rivers from the southern Caspian Sea and two inland lake basins, Iran: a morphogenetic approach. Journal of Fish Biology 81(5): 1479–1500.
Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I., E. Normandeau, L. Benestan, C. Rougeux, G. Coté, J.-S. Moore, N. Ghaedrahmati, A. Abdoli & L. Bernatchez, 2018. Genetic and morphological support for possible sympatric origin of fish from subterranean habitats. Scientific Reports 8(1): 2909.
Hébert, C., R. Danzman, M. Jones & L. Bernatchez, 2000. Hydrography and population genetic structure in brook charr (Salvelinus fontinalis, Mitchill) from eastern Canada. Molecular Ecology 9(7): 971–982.
I.R.G.O.A.F, 2005. Northern Iran Watershed. The Gazetteer of Rivers in the IR of Iran. Iranian Geographic Organization of the Armed Forces, Tehran.
Jombart, T. & C. Collins, 2015. A Tutorial for Discriminant Analysis of Principal Components (DAPC) Using Adegenet 2.0.0. Imperial College London, MRC Centre for Outbreak Analysis and Modelling, London.
Jones, M. R. & J. M. Good, 2016. Targeted capture in evolutionary and ecological genomics. Molecular Ecology 25(1): 185–202.
Jonnson, B. & N. Jonnson, 2011. Ecology of Atlantic Salmon and Brown Trout: Habitat as a Template for Life History. Springer, New York.
Keinan, A., J. C. Mullikin, N. Patterson & D. Reich, 2007. Measurement of the human allele frequency spectrum demonstrates greater genetic drift in East Asians than in Europeans. Nature Genetics 39(10): 1251.
Kelson, S. J., A. R. Kapuscinski, D. Timmins & W. R. Ardren, 2015. Fine-scale genetic structure of brook trout in a dendritic stream network. Conservation Genetics 16(1): 31–42.
Kiabi, B. H., A. Abdoli & M. Naderi, 1999. Status of the fish fauna in the South Caspian Basin of Iran. Zoology in the Middle East 18(1): 57–65.
Kitanishi, S., T. Yamamoto & S. Higashi, 2009. Microsatellite variation reveals fine-scale genetic structure of masu salmon, Oncorhynchus masou, within the Atsuta River. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 18(1): 65–71.
Kottelat, M. & J. R. Freyhof, 2007. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes. Publications Kottelat, Cornol.
Lien, S., B. F. Koop, S. R. Sandve, J. R. Miller, M. P. Kent, T. Nome, T. R. Hvidsten, J. S. Leong, D. R. Minkley & A. Zimin, 2016. The Atlantic salmon genome provides insights into rediploidization. Nature 533(7602): 200–205.
Mäkinen, H., T. Niva, M.-L. Koljonen, A. Swatdipong & C. R. Primmer, 2015. Temporal variation in lake-run brown trout (Salmo trutta) mixed-stock fishery catches in a large Fennoscandian lake. Boreal Environment Research 20: 661–665.
Martin, M., 2011. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet Journal 17(1): 10–12.
Mascher, M., S. Wu, P. S. Amand, N. Stein & J. Poland, 2013. Application of genoty**-by-sequencing on semiconductor sequencing platforms: a comparison of genetic and reference-based marker ordering in barley. PLoS ONE 8(10): e76925.
Niksirat, H. & A. Abdoli, 2009. On the status of the critically endangered Caspian brown trout, Salmo trutta caspius, during recent decades in the southern Caspian Sea basin (Osteichthyes: Salmonidae). Zoology in the Middle East 46(1): 55–60.
Olsson, I. & L. Greenberg, 2004. Partial migration in a landlocked brown trout population. Journal of Fish Biology 65(1): 106–121.
Ozerov, M. Y., A. J. Veselov, J. Lumme & C. R. Primmer, 2010. Genetic structure of freshwater Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) populations from the lakes Onega and Ladoga of northwest Russia and implications for conservation. Conservation Genetics 11(5): 1711–1724.
Patterson, N., P. Moorjani, Y. Luo, S. Mallick, N. Rohland, Y. Zhan, T. Genschoreck, T. Webster & D. Reich, 2012. Ancient admixture in human history. Genetics 192(3): 1065–1093.
Pembleton, L. W., N. O. Cogan & J. W. Forster, 2013. St AMPP: an R package for calculation of genetic differentiation and structure of mixed-ploidy level populations. Molecular ecology Resources 13(5): 946–952.
Pettersson, J., M. M. Hansen & T. Bohlin, 2001. Does dispersal from landlocked trout explain the coexistence of resident and migratory trout females in a small stream? Journal of Fish Biology 58(2): 487–495.
Pickrell, J. K. & J. K. Pritchard, 2012. Inference of population splits and mixtures from genome-wide allele frequency data. PLoS Genetics 8(11): e1002967.
Sedighkia, M., A. Abdoli, S. A. Ayyoubzadeh & A. Ahmadi, 2018. Modelling of thermal habitat loss of brown trout (Salmo trutta) due to the impact of climate warming. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology 19(1): 167–177.
Spidle, A. P., W. B. Schill, B. A. Lubinski & T. L. King, 2001. Fine-scale population structure in Atlantic salmon from Maine’s Penobscot River drainage. Conservation Genetics 2(1): 11–24.
Swatdipong, A., A. Vasemägi, T. Niva, M. L. Koljonen & C. Primmer, 2013. Genetic mixed-stock analysis of lake-run brown trout Salmo trutta fishery catches in the Inari Basin, northern Finland: implications for conservation and management. Journal of fish Biology 83(3): 598–617.
Tabatabaei, S. N., I. Hashemzadeh Segherloo, S. Eagderi & M. Z. Faradonbeh, 2015. Habitat use of two nemacheilid fish species, Oxynoemacheilus bergianus and Paracobitis sp. in the Kordan River, Iran. Hydrobiologia 762(1): 183–193.
Taugbøl, A., 2008. Fine-scale genetic structure of brown trout (Salmo trutta). Masters Thesis. University of Oslo
Vera, M., I. Sourinejad, C. Bouza, R. Vilas, A. Pino-Querido, M. R. Kalbassi & P. Martínez, 2011. Phylogeography, genetic structure, and conservation of the endangered Caspian brown trout, Salmo trutta caspius (Kessler, 1877), from Iran. Hydrobiologia 664(1): 51–67.
Vøllestad, L. A., D. Serbezov, A. Bass, L. Bernatchez, E. M. Olsen & A. Taugbøl, 2012. Small-scale dispersal and population structure in stream-living brown trout (Salmo trutta) inferred by mark–recapture, pedigree reconstruction, and population genetics. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 69(9): 1513–1524.
Weir, B. S. & C. C. Cockerham, 1984. Estimating F‐statistics for the analysis of population structure. evolution 38(6):1358-1370.
Wellband, K. W., D. Y. Atagi, R. A. Koehler & D. D. Heath, 2012. Fine-scale population genetic structure and dispersal of juvenile steelhead in the Bulkley-Morice river, British Columbia. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 141(2): 392–401.
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Perreault, C. Hernandez, and C. Babin of Laboratory of Bernatchez (Laval University) for their kind assistance during laboratory work and A. M. Elmi, A. Zamani, A. Alizadeh, A. Ahmadi, and M. Monemi of the Iranian Department of Environment for their assistance during field work in the Lar National Park. We also thank Brian Boyle and the staff from the IBIS genomic analyses platform (Laval University, Québec City, Canada), for their assistance in library preparation and genoty** (http://www.ibis.ulaval.ca). We are also grateful to Editor (Christian Sturmbauer) and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive inputs on a previous version of this manuscript. This work is supported by a NSERC (Canada) Discovery Grant (http://www.nserc-crsng.gc.ca) to Louis Bernatchez, the Iranian Ministry of Science, Research and Technology, Shahid Beheshti University, ShahreKord University (Grant No. 688MIGRD94), and the Fonds de Recherche du Québec – Nature et Technologies (FRQNT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SNT contributed in designing the study, did the field and laboratory work, data analysis, and drafted the manuscript; AA contributed in designing the study, field work, and drafting the manuscript, IHS contributed in designing the study, field work, data analysis, and drafting the manuscript; EN contributed in bioinformatics and drafting the manuscript; FA contributed in the design of the study and drafting the manuscript; FN contributed in field work; and LB contributed in designing the study, provided laboratory facilities necessary to perform all the laboratory work, next-generation sequencing, data processing, and contributed to drafting the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling editor: Christian Sturmbauer
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabatabaei, S.N., Abdoli, A., Hashemzadeh Segherloo, I. et al. Fine-scale population genetic structure of Endangered Caspian Sea trout, Salmo caspius: implications for conservation. Hydrobiologia 847, 3339–3353 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04334-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04334-7