Abstract
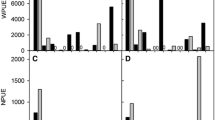
While the structuring role of fish in lakes is well studied for the summer season in North temperate lakes, little is known about their role in winter when fish activity and light irradiance potentially are lower. This is unfortunate as the progressing climate change may have strong effects on lake winter temperature and possibly on trophic dynamics too. We conducted an enclosure experiment with and without the presence of fish throughout winter in two shallow lakes with contrasting phosphorus concentrations. In hypertrophic Lake Søbygård, absence of fish led to higher biomass of zooplankton, higher grazing potential (zooplankton:phytoplankton ratio) and, accordingly, lower biomass of phytoplankton and chlorophyll a (Chl a), while the concentrations of total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), oxygen and pH decreased. The average size of egg-bearing Daphnia and Bosmina and the minimum size of egg-bearing specimens of the two genera rose. In the less eutrophic Lake Stigsholm, zooplankton and their grazing potential were also markedly affected by fish. However, the decrease in Chl a was slight, and phytoplankton biovolume, pH and the oxygen concentration were not affected. TN was higher when fish were absent. Our results indicate that: (i) there is a notable effect of fish on zooplankton community structure and size during winter in both eutrophic and hypertrophic North temperate lakes, (ii) Chl a can be high in winter in such lakes, despite low light irradiance, if fish are abundant, and (iii) the cascading effects on phytoplankton and nutrients in winter may be more pronounced in hypertrophic lakes. Climate warming supposedly leading to reduced winter mortality and dominance of small fish may enhance the risk of turbid state conditions in nutrient-enriched shallow lakes, not only during the summer season, but also during winter.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, R. & R. Deneke, 1996. Possible impact of mild winters on zooplankton succession in eutrophic lakes of the Atlantic European area. Freshwater Biology 36: 757–770.
Balayla, D., T. Lauridsen, M. Søndergaard & E. Jeppesen, 2010. Larger zooplankton in Danish lakes after cold winters: are winter fish kills of importance? Hydrobiologia 646: 159–172.
Bottrell, H. H., A. Duncan, Z. M. Gliwicz, E. Grygierek, A. Herzig, A. Hillbricht-Ilkowska, H. Kurasawa, P. Larsson & T. Weglenska, 1976. A review of some problems in zooplankton production studies. Norwegian Journal Zoology 24: 419–456.
Bramm, M. E., M. F. Lassen, L. Liboriussen, M. Ventura & E. Jeppesen, 2009. Fish-zooplankton-phytoplankton interactions in shallow lakes at contrasting irradiance levels with special focus on the winter season. Freshwater Biology 54: 1093–1109.
Brooks, J. L. & S. I. Dodson, 1965. Predation, body size, and composition of plankton. Science 150: 28–35.
Brönmark, C., J. Brodersen, B. B. Chapman, A. Nicolle, P. A. Nilsson, C. Skov & L.-A. Hansson, 2010. Regime shifts in shallow lakes: the importance of seasonal fish migration. Hydrobiologia 646: 91–100.
Brucet, S., D. Boix, X. D. Quintana, E. Jensen, L. W. Nathansen, C. Trochine, M. Meerhoff, S. Gascón & E. Jeppesen, 2010. Factors influencing zooplankton size structure at contrasting temperatures in coastal shallow lakes: implications for effects of climate change. Limnology and Oceanography 55: 1697–1711.
Burks, R. L., D. M. Lodge, E. Jeppesen & T. Lauridsen, 2002. Diel horizontal migration of zooplankton: costs and benefits of inhabiting littoral zones. Freshwater Biology 47: 343–365.
Carpenter, S. R. & J. F. Kitchell (eds), 1993. The Trophic Cascade in Lakes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Cox, E. J., 1996. Identification of Freshwater Diatoms from Live Material. Chapman & Hall, London.
Culver, D. A., M. M. Boucherle, D. J. Bean & J. W. Fletcher, 1985. Biomass of freshwater crustacean zooplankton from length-weight regressions. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 42: 1380–1390.
Dumont, H. J., I. Van de Velde & S. Dumont, 1975. The dry weight estimate of biomass in a selection of Cladocera, Copepoda and Rotifera from the plankton, periphyton and benthos of continental waters. Oecologia 19: 75–97.
Fowler, J., L. Cohen & P. Jarvis, 1998. Practical Statistics for Field Biology, 2nd ed. Wiley, New York.
George, D. G. & D. P. Hewitt, 1999. The influence of year-to-year variations in winter weather on the dynamics of Daphnia and Eudiaptomus in Esthwaite Water, Cumbria. Functional Ecology 13: 45–54.
Gliwicz, Z. M., 2003. Between hazards of starvation and risk of predation: ecology of offshore animals. In Kinne, O. (ed.), Excellence of Ecology, Book 12. International Ecology Institute, Oldendorf/Luhe: 379 pp.
Grafen, A. & R. Hails, 2002. Modern Statistics for the Life Sciences. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Hansen, A.-M., E. Jeppesen, S. Bosselmann & P. Andersen, 1992. Zooplankton i søer-metoder og artsliste. Miljøprojekt nr. 205. Miljøministeriet, Miljøstyrelsen. (in Danish).
Hansson, L.-A., A. Nicolle, J. Brodersen, P. Romare, P. A. Nilsson, C. Brönmark & C. Skov, 2007. Consequences of fish predation, migration, and juvenile ontogeny on zooplankton spring dynamics. Limnology and Oceanography 52: 696–706.
Havens, K. E., & J. B. Beaver, 2011. Composition, size, and biomass of zooplankton in large productive Florida lakes. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10750-010-0386-5.
Hessen, D. O., P. J. Færøvig & T. Andersen, 2002. Light, nutrients, and P:C ratios in algae grazers performance related to food quality and quantity. Ecology 83: 1886–1898.
IPCC, 2007. Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Jacobsen, L., S. Berg, M. Broberg, N. Jepsen & C. Skov, 2002. Activity and food choice of piscivorous perch (Perca fluviatilis) in a eutrophic shallow lake: a radio-telemetry study. Freshwater Biology 47: 2370–2379.
Jacobsen, L., S. Berg, N. Jepsen & C. Skov, 2004. Does roach behaviour differ between shallow lakes of different environmental state? Journal of Fish Biology 65: 135–147.
Jensen, H. S. & F. Ø. Andersen, 1992. Importance of temperature, nitrate and pH for phosphorus from aerobic sediments of four shallow, eutrophic lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 37: 577–589.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard, T. Lauridsen, L. J. Pedersen & L. Jensen, 1997. Top-down control in freshwater lakes: the role of nutrient state, submerged macrophytes and water depth. Hydrobiologia 242(343): 151–164.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, C. Jensen, B. Faafeng, D. O. Hessen, M. Søndergaard, T. L. Lauridsen, P. Brettum & K. Christoffersen, 2003. The impact of nutrient state and lake depth on top-down control in lakes: study of 466 lakes from the temperate zone to the Arctic. Ecosystems 6: 315–325.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard, M. Fenger-Grøn, K. Sandby, P. H. Møller & H. U. Rasmussen, 2004. Does fish predation influence zooplankton community structure and grazing during winter in north temperate lakes? Freshwater Biology 49: 432–447.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, A. R. Pedersen, K. Jürgens, A. Strzelczak, T. L. Lauridsen & L. S. Johansson, 2007. Salinity induced regime shift in shallow brackish lagoons. Ecosystems 10: 47–57.
Jeppesen, E., B. Kronvang, M. Meerhoff, M. Søndergaard, K. M. Hansen, H. E. Andersen, T. L. Lauridsen, M. Beklioglu, A. Özen & J. E. Olesen, 2009. Climate change effects on runoff, catchment phosphorus loading and lake ecological state, and potential adaptations. Journal of Environmental Quality 38: 1030–1041.
Jepsen, N. & S. Berg, 2002. The use of winter refuges by roach tagged with miniature radio transmitters. Hydrobiologia 483: 167–173.
Jespersen, A.-M. & K. Christoffersen, 1987. Measurements of chlorophyll a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 109: 445–454.
Jones, J. I. & S. Waldron, 2003. Combined stable isotope and gut contents analysis of food webs in plant-dominated, shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 48: 1396–1407.
Karlsson, J. & C. Sawström, 2009. Benthic algae support zooplankton growth during winter in a clear-water lake. Oikos 118: 539–544.
Keast, A., 1968. Feeding of some Great Lakes fishes at low temperatures. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada 25: 1199–1218.
Komárek, J. & B. Fott, 1983. Das Phytoplankton des Süßwassers 7, 1: Chlorophyceae (Grünalgen). Ordnung: Chlorococcales. Schweizerbart, Stuttgart.
Koroleff, F., 1976a. Determination of total phosphorus. In Grasshoff, K. (ed.), Methods of Seawater. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim: 168–172.
Koroleff, F., 1976b. Determination of total nitrogen. In Grasshoff, K. (ed.), Methods of Seawater. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim: 123–125.
Lampert, W., 1977. Studies on the carbon balance of Daphnia pulex de Geer as related to environmental conditions. IV. Determination of the “threshold” concentration as a factor controlling the abundance of zooplankton species. Archiv für Hydrobiologie—Supplement 3: 361–368.
Liboriussen, L. & E. Jeppesen, 2003. Temporal dynamics in epipelic, pelagic and epiphytic algal production in a clear and a turbid shallow lake. Freshwater Biology 48: 418–431.
McCauley, E., 1984. The estimation of the abundance and biomass of zooplankton in samples. In Downing, J. A. & F. H. Rigler (eds), A Manual on Methods for the Assessment of Secondary Productivityin Fresh Waters, 2nd ed. Blackwell Scientific Publishers, Oxford: 228–265.
Moss, B., 1998. The Ecology of Freshwaters, Man and Medium, Past to Future, 3rd ed. Blackwell Science, Oxford.
Olrik, K. 1991. Planteplanktonmetoder—prøvetagning, bearbejdning og rapportering ved undersøgelser af planteplankton i søer og marine områder. Miljøprojekt nr. 187. Miljøministeriet. Miljøstyrelsen. [Phytoplankton methods—sampling, analyses and reports when analysing phytoplankton in lake and marine waters. Environmental project no. 187. Ministry of the Environment. Danish Environment Protection Agency] (in Danish).
Pace, M. L., J. J. Cole, S. R. Carpenter & J. F. Kitchell, 1999. Trophic cascades revealed in diverse ecosystems. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 14: 483–488.
Pekcan-Hekim, Z. & J. Lappalainen, 2006. Effects of clay turbidity and density of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) larvae on predation by perch (Perca fluviatilis). Naturwissenschaften 93: 356–359.
Reynolds, C. F., 1984. The Ecology of Freshwater Phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Rudstam, L. G., R. C. Lathrop & S. R. Carpenter, 1993. The rise and fall of a dominant planktivore: direct and indirect effects on zooplankton. Ecology 74: 303–319.
Ruuhijärvi, J., M. Rask, S. Vesala, A. Westermark, M. Olin, J. Keskitalo & A. Lehtovaara, 2010. Recovery of the fish community and changes in the lower trophic levels in a eutrophic lake after a winter kill of fish. Hydrobiologia 646: 145–158.
Sokal, R. R. & F. J. Rohlf, 1995. Biometry—The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, 3rd ed. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York.
Sommer, U., Z. M. Gliwicz, W. Lambert & A. Duncan, 1986. The PEG-model for seasonal succession of planktonic events in fresh waters. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 106: 433–471.
Sterner, R. W., & J. J. Elser, 2002. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ.
Sterner, R. W., J. J. Elser, E. J. Fee, S. J. Guildford & T. H. Chrzanowski, 1997. The light:nutrient ratio in lakes: the balance of energy and materials affects ecosystem structure and process. American Naturalist 150: 663–684.
Søndergaard, M., T. L. Lauridsen, E. Jeppesen & L. Bruun, 1997. Macrophyte-waterfowl interactions: tracking a variable resource and the impact of herbivory on plant growth. In Jeppesen, E., Ma. Søndergaard, Mo. Søndergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes. Ecological Studies, Vol. 131. Springer Verlag, New York: 298–307.
Tikkanen, T. & T. Willén, 1992. Växtplanktonflora. Naturvårdsverket, Eskilstuna (in Swedish).
Urabe, J., M. Kyle, W. Makino, T. Yoshida, T. Andersen & J. J. Elser, 2002. Reduced light increases herbivore production due to stoichiometric effects of light:nutrient balance. Ecology 83: 619–627.
Vanni, M. J. & D. L. Findley, 1990. Trophic cascades and phytoplankton community structure. Ecology 71: 921–937.
Vijverberg, J., 1980. Effect of temperature in laboratory studies on development and growth of Cladocera and Copepoda from Tjeukemeer, the Netherlands. Freshwater Biology 10: 317–340.
Winberg, G. G., 1971. Methods for the Estimation of Production of Aquatic Animals (trans. by A. Duncan). Academic Press, London.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the owners of the lakes, Kirsten and Ove Henriksen (Stigsholm) and Wefri a/s Frijsenborg and Wedellsborg (Søbygård), for permission to set up the experiments. The technical staff at the National Environmental Research Institute, Silkeborg, is gratefully acknowledged for their assistance. We are also grateful to Anne Mette Poulsen for skilful editorial assistance. The study was supported by the projects EU WISER and EU REFRESH, CRES and CLEAR (a Villum Kann Rasmussen Centre of Excellence project).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handing editor: Luigi Naselli-Flores
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sørensen, T., Mulderij, G., Søndergaard, M. et al. Winter ecology of shallow lakes: strongest effect of fish on water clarity at high nutrient levels. Hydrobiologia 664, 147–162 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0595-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0595-y