Abstract
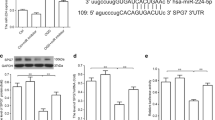
This study aims to investigate the role of miR-495 in neuronal cell apoptosis after acute spinal cord injury (ASCI). The ASCI rat model was established and the Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan (BBB) score was assessed. miR-495, PR domain containing 5 (PRDM5), and Bcl-2 expressions were measured by qRT-PCR or western blotting. Neuronal cell line PC-12 was subjected to hypoxia condition to simulate the in vitro ASCI model. PC-12 cell apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry, and the interaction between miR-495 and PRDM5 was confirmed by dual luciferase reporter assay. Results showed that BBB score was significantly decreased in ASCI rats compared with sham rats. miR-495 expression was down-regulated in spinal cord tissue of ASCI rats and hypoxia-induced PC-12 cells, and PRDM5 protein level was up-regulated in spinal cord tissue of ASCI rats and hypoxia-induced PC-12 cells. miR-495 overexpression could reduce apoptosis of PC-12 cells, and up-regulated anti-apoptosis protein Bcl-2 protein level. Moreover, PRDM5 was a target of miR-495, and mRNA and protein levels of PRDM5 were negatively regulated by miR-495. miR-495 overexpression could reduce the hypoxia-induced PC-12 cell apoptosis, while PRDM5 overexpression abolished this inhibiting effect. The agomir-495 was injected into ASCI rats, and Bcl-2 protein level and BBB score were increased, but the PRDM5 overexpression reversed these results. Overall, we concluded that miR-495 could inhibit neuronal cell apoptosis and relieve acute spinal cord injury through inhibiting PRDM5.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Z, Wang J, Wang T, Li Y, Zhao X, Wu G, Yang Y, Deng W, Zhang Z (2017) The MiR-495/annexin A3/P53 axis inhibits the invasion and EMT of colorectal cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 44(5):1882–1895
Bowes A, Yip P (2014) Modulating inflammatory cell responses to spinal cord injury: all in good time. J Neurotrauma 31(21):1753–1766
Chen G, **e Y (2018) miR-495 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion and induces apoptosis via inhibiting PBX3 in melanoma cells. Onco Targets Ther 11:1909–1920
Chen Q, Xu J, Li L, Li H, Mao S, Zhang F, Zen K, Zhang C, Zhang Q (2014) MicroRNA-23a/b and microRNA-27a/b suppress Apaf-1 protein and alleviate hypoxia-induced neuronal apoptosis. Cell Death Dis 5:e1132
Chen X, Cui J, Zhai X, Zhang J, Gu Z, Zhi X, Weng W, Pan P, Cao L, Ji F et al (2018) Inhalation of hydrogen of different concentrations ameliorates spinal cord injury in mice by protecting spinal cord neurons from apoptosis, oxidative injury and mitochondrial structure damages. Cell Physiol Biochem 47(1):176–190
Dai J, Xu L, Han G, Sun H, Zhu G, Jiang H, Yu G, Tang X (2018) MiR-137 attenuates spinal cord injury by modulating NEUROD4 through reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(7):1884–1890
Gao K, Shen Z, Yuan Y, Han D, Song C, Guo Y, Mei X (2016) Simvastatin inhibits neural cell apoptosis and promotes locomotor recovery via activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway after spinal cord injury. J Neurochem 138(1):139–149
Gao L, Dai C, Feng Z, Zhang L, Zhang Z (2018) MiR-137 inhibited inflammatory response and apoptosis after spinal cord injury via targeting of MK2. J Cell Biochem 119(4):3280–3292
Geng J, Liu X, Zhao H, Fan W, Geng J, Liu X (2018) LncRNA UCA1 inhibits epilepsy and seizure-induced brain injury by regulating miR-495/Nrf2-ARE signal pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 99:133–139
Gong Z, Tang Z, Sun X (2018) miR-411 suppresses acute spinal cord injury via downregulation of Fas ligand in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 501(2):501–506
Li S, Liu L, Zhuang X, Yu Y, Liu X, Cui X, Ji L, Pan Z, Cao X, Mo B et al (2013) MicroRNAs inhibit the translation of target mRNAs on the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis. Cell 153(3):562–574
Ling W, Xu X, Liu J (2017) A causal relationship between the neurotherapeutic effects of miR182/7a and decreased expression of PRDM5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490(1):1–7
Liu J, Wu Y (2017) Electro-acupuncture-modulated miR-214 prevents neuronal apoptosis by targeting Bax and inhibits sodium channel Nav1.3 expression in rats after spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother 89:1125–1135
Liu J, Wu W, Hao J, Yu M, Liu J, Chen X, Qian R, Zhang F (2016) PRDM5 expression and essential role after acute spinal cord injury in adult rat. Neurochem Res 41(12):3333–3343
Luan Y, Chen M, Zhou L (2017) MiR-17 targets PTEN and facilitates glial scar formation after spinal cord injuries via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Brain Res Bull 128:68–75
McDonald J, Sadowsky C (2002) Spinal-cord injury. Lancet 359(9304):417–425
Meister G (2007) miRNAs get an early start on translational silencing. Cell 131(1):25–28
Nakanishi K, Nakasa T, Tanaka N, Ishikawa M, Yamada K, Yamasaki K, Kamei N, Izumi B, Adachi N, Miyaki S et al (2010) Responses of microRNAs 124a and 223 following spinal cord injury in mice. Spinal Cord 48(3):192–196
Orre M, Kamphuis W, Osborn LM, Melief J, Kooijman L, Huitinga I, Klooster J, Bossers K, Hol EM (2014) Acute isolation and transcriptome characterization of cortical astrocytes and microglia from young and aged mice. Neurobiol Aging 35(1):1–14
Rodrigues L, Moura-Neto V (2018) Biomarkers in spinal cord injury: from prognosis to treatment. Mol Neurobiol 55(8):6436–6448
Sun W, Dep** R, Jelkmann W (2014) Interleukin-1β promotes hypoxia-induced apoptosis of glioblastoma cells by inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediated adrenomedullin production. Cell Death Dis 5:e1020
Wang X, ** H, Jiang S, Xu Y (2018) MicroRNA-495 inhibits the high glucose-induced inflammation, differentiation and extracellular matrix accumulation of cardiac fibroblasts through downregulation of NOD1. Cell Mol Biol Lett 23:23
**a L, Ke C, Lu J (2018) NEAT1 contributes to neuropathic pain development through targeting miR-381/HMGB1 axis in CCI rat models. J Cell Physiol 233(9):7103–7111
Xu Y, An B, ** X, Li Z, Li F (2016) MicroRNA-9 controls apoptosis of neurons by targeting monocyte chemotactic protein-induced protein 1 expression in rat acute spinal cord injury model. Brain Res Bull 121:233–240
Zhang Y, Liu X, Xue H, Liu X, Dai A, Song Y, Ke K, Cao M (2016) Upregulation of PRDM5 is associated with astrocyte proliferation and neuronal apoptosis caused by lipopolysaccharide. J Mol Neurosci 59(1):146–157
Zhang D, Xuan J, Zheng B, Zhou Y, Lin Y, Wu Y, Zhou Y, Huang Y, Wang Q, Shen L et al (2017) Metformin improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury via autophagy flux stimulation. Mol Neurobiol 54(5):3327–3341
Zhang H, Li D, Zhang Y, Li J, Ma S, Zhang J, **ong Y, Wang W, Li N, **a L (2018) Knockdown of lncRNA BDNF-AS suppresses neuronal cell apoptosis via downregulating miR-130b-5p target gene PRDM5 in acute spinal cord injury. RNA Biol 15(8):1071–1080
Zhu H, **e R, Liu X, Shou J, Gu W, Gu S, Che X (2017) MicroRNA-494 improves functional recovery and inhibits apoptosis by modulating PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in rats after spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother 92:879–887
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10735_2021_9959_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
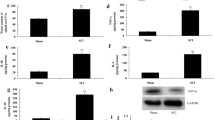
Supplementary file1 Supplemental Figure 1. a Rat spinal cord tissue was collected, and primary rat neuronal cells, microglia and astrocytes were isolated in sham and ASCI group followed by the protocol of previous study Orre et al. (2014), and the expression of miR-495 was detected by qRT-PCR (n = 7). Rat neuronal cell line PC-12 was cultured without hypoxia, and miR-495 inhibitor was transfected into PC-12 cells. Cells were divided into NC and miR-495 inhibitor group. b The percentage of PC-12 cell apoptosis was determined by Flow cytometry. c Bcl-2 protein level in PC-12 cells was measured by western blotting. The independent experiments were performed for 3 times. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001vs NC or sham. (JPG 841 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Wang, S., Li, H. et al. miR-495 reduces neuronal cell apoptosis and relieves acute spinal cord injury through inhibiting PRDM5. J Mol Histol 52, 385–396 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-09959-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-09959-z