Abstract
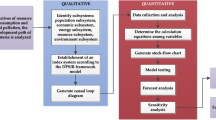
China has numerous declining coal cities, and their sustainable development is lagging due to resource exhaustion, economic recession, and environmental destruction. In order to overcome these problems associated with scientifically selecting the development mode, this study designed the evaluation system including four subsystems (resource, environment, society and economy). Then the system dynamics (SD) model of sustainable development was built by analyzing the interaction between factors of four subsystems. Huaibei city was chosen as a case study to evaluate and simulate the variation trend of its sustainable development level via the SD model. Four alternative scenarios: current scenario, society and economy scenario, environment scenario and coordinated scenario were presented. The simulation results demonstrated that: (1). Sustainable development level improved in all scenarios. (2). The society and economy scenario played a more significant role in promoting sustainable development. Based on the results and analysis, we recommend that Huaibei City should implement water resources conservation, and concentrate on promoting economic transformation to achieve socio-economic stability and rapid development. This study integrates the quantitative evaluation of sustainable development with SD model based on the comprehensive perspective. The research results provide theoretical reference for the systematic and comprehensive evaluation of the sustainable development level, as well as the scientific selection of a development mode for declining coal cities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Changjun, W., Yangyang, Q., & **angli, W. (2019). A study on economic-population contraction governance in resource-exhausted cities: A realistic analysis based on resource-exhausted cities in Heilongjiang Province. Macroeconomics, 08(1), 156–169.
Das, D. K. (2019). Exploring perspectives of the information technology industry in a South African city. Sustainability, 11(22), 6520.
Dongmei, J., **aoshun, L., & Yuexiang, W. (2021). Coordinating urban construction and coal resource mining based on equilibrium value between coal reserve and land resource in coal cities. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 12(1), 2865–2879.
Fang, H. (2015). Carbon emission in coal-oriented city: A case study of **dingshan city. China Mining Magazine, 24(10), 93.
Fuxi, W., Aihua, M., & Helong, L. (2013). Quality measurement and regional difference of urbanization in Shandong Province based on the entropy method. Scientia Geographica Sinica., 33(11), 1323–1329.
Gang, L., Dong, J., & **gying, F. (2020). Spatial relationships of water resources with energy consumption at coal mining operations in China. Mine Water and the Environment, 39(2), 407–415.
Gross, M. (2008). Population decline and the new nature: Towards experimental “refactoring” in landscape development of post-industrial regions. Futures, 40(5), 451–459.
Kai, W., & Zhenghai, Y. (2021). Research on the evaluation and driving factors of high-quality development under the five development concepts taking Xuzhou city as an example. Resource Development & Market, 37(05), 566–573.
Keliang, W., Huibing, Y., & **angrui, M. (2013). Study on China’s coal resource-based cities’ sustainable development capacity evaluation-Based on the factor analysis and entropy weight method. Journal of Industrial Technological Economics, 43(12), 108–117.
Marschalko, M., Yilmaz, I., & Lamich, D. (2014). Unique documentation, analysis of origin and development of an undrained depression in a subsidence basin caused by underground coal mining (Kozinec, Czech Republic). Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(1), 11–20.
Martinat, S., Dvorak, P., & Frantal, B. (2016). Sustainable urban development in a city affected by heavy industry and mining? Case Study of Brownfields in Karvina, Czech Republic, Journal of Cleaner Production, 118(1), 78–87.
Ming, Z., **, L., & Meng, Z. (2020). Water quality in worldwide coal mining city: A scenario in water chemistry and health risks exploration. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 213(4), 106513.
Qiwen, C., Chaolin, G., & Weihua, G. (2021). China’s urbanization SD modeling and simulation based on land use. Journal of Natural Resources., 36(04), 1062–1084.
Ruiyin, D., Shengling, Z., & Xuemin, L. (2019). Study on transformation model of resource-based cities based on SD: A case of Ordos. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment., 33(8), 18–25.
Santos, M. D., Júlia, O. P., & Baisch, P. R. M. (2021). Selenium dietary intake, urinary excretion, and toxicity symptoms among children from a coal mining area in Brazil. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(1), 65–75.
Tozan, Y., & Ompad, D. C. (2015). Complexity and dynamism from an urban health perspective: A rationale for a system dynamics approach. Journal of Urban Health, 92(3), 490–501.
Tsolakis, N., & Anthopoulos, L. (2015). Eco-cities: An integrated system dynamics framework and a concise research taxonomy. Sustainable Cities and Society, 17(1), 1–14.
**angang, Z., & Cunru, D. (2018). Performance evaluation and differential analysis on green transformation of coal resource-exhausted cities in China. China Population, Resources and Environment., 28(07), 127–135.
**anming, Y., Huafu, J., & Jili, X. (2014). Research on the evolution and optimization of spatial structure in Huaibei city. World Regional Studies, 23(04), 127–135.
**aofan, L., & Liwen, L. (2021). Linkage effect of industrial structure adjustment and environmental pollution in resource-declining cities. Journal of Central China Normal University (natural Sciences)., 55(05), 900–907.
**aoli, T., **ao, W., & Yuxuan, T. (2020). A quantitative assessment of vulnerability using social-economic-natural compound ecosystem framework in coal mining cities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 258(1), 1–11.
**aoshuang, F., Yanlan, W., Zihan, L., & Jie, W. (2017). Analysis of the landscape pattern and driving force of the spatio-temporal dynamic change in a typical plain coal mining subsidence area: A case study of Linhuan mining area. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 44(01), 94–101.
**aowen, L., Wanfang, S., Peixin, D., & **aolan, C. (2020). Evaluation on sustainable development transformation of coal resource-exhausted cities in the new era. China Mining Magazine, 29(12), 75–82.
**, Y., Gangmin, W., & Yujun, H. (2018). Modeling and simulation of urban tourism environment carrying potential based on the SD model under multiple scenarios: Taking Lanzhou city as an example. Economic Geography., 38(3), 208–216.
Xue, L., Chunyou, D., Zhiguo, C., & **aoli, Y. (2012). Evaluation model of coal cities’ sustainable development based on uncertain theory. China Mining Magazine, 21(04), 37–40.
Yang, X., Lina, H., Haibin, L., & Donghai, L. (2021). System dynamics simulation model construction of urbanization quality improvement in Bei**g-Tian**-Hebei Urban agglomeration. Statistics & Decision, 37(24), 185–188.
Yifeng, S., Na, L., & **, W. (2020). Regional coordination of resource-exhausted cities based on symbiosis theory: The case of Tongchuan. Planners, 36(10), 26–31.
Zhiyun Z., Hui L., & Yiwei Y. (2018). Urban spatial-temporal expansion process of resource-exhausted cities: A case study of Huaibei City. Geographical Research., 37(01), 183–198.
Zhaoqing, Y., Zhaohua, L., Dan, L., Mingyang, Y., et al. (2021). Ecological security evaluation on the coal resource-based city: A case of **linhot city. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(01), 280–289.
Zhen, C., Zhe, Z., Kanghui, Z., & Shuwei, J. (2022). Simulation of urban traffic sources pollution and health benefits for residents. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 39(04), 91–96.
Zhenhua, W., Shaogang, L., & Baojie, H. (2019). Assessment of landscape ecological health: A case study of a mining city in a semi-arid steppe. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(5), 1–21.
Funding
This work is supported by the following programs: 1. Scientific Research Project of Universities of Anhui Province in 2022 (Philosophy and Social Science) with the tiele "Dynamic evaluation and spatial effect analysis of eco-environmental quality of resource-based cities of Anhui Province from the perspective of regional integration". 2. Talent introduction scientific research start-up fund of Anhui University of Science and Technology (No.2022yjrc16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Ethical approval
The paper complies with the ethical standards as put forward by GeoJournal.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, K., He, G. & Zhu, Y. Research on the evolution of sustainable development of declining coal city using system dynamics model. GeoJournal 88, 2691–2703 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-022-10770-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-022-10770-w