Abstract
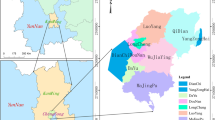
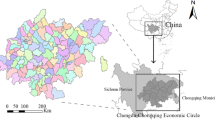
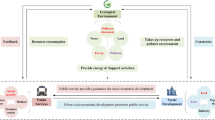
The carrying capacity of urban resources and environment is an important yardstick to measure the sustainable development of a city, and it is also an important indicator to measure the degree of synergy between urban economic development and the environment. The main objective of this paper is to evaluate the economic, social, resource and environmental system carrying capacity of the cities in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) Economic Belt by building a state space model, so as to lay a theoretical foundation for promoting the green and sustainable development of the urban agglomeration in the GBA. The following conclusions were reached: (1) The resource and environmental carrying capacity of the 11 cities in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area is generally overloaded and shows an "N" distribution pattern. (2) The level of the city's opening to the outside world, the government's management ability, the investment of science and technology funds, and the industrial development are the main factors that affect the resource and environmental carrying capacity of the urban agglomeration. (3) The regression analysis results of the economic and social subsystems and resource subsystems of the 11 cities in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area are consistent with the results of the overall system of resource and environmental carrying capacity. The spatial differentiation characteristics are weakened, but the spatial differentiation characteristics of the resource and environmental carrying capacity of the environmental subsystem are gradually obvious. The innovation of this paper is that we can see the state of the resource and environment carrying capacity of the urban agglomeration in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area by building a state space model. Using GIS geographic map** technology, we can clearly see the dynamic changes of urban agglomeration during the 10-year period and realize the unification of space–time evolution.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao, C., & Fang, C. L. (2012). Water resources flows related to urbanization in China: Challenges and perspectives for water management and urban development. Water Resources Management, 26(2), 531–552.
Cao, X., Ouyang, S., Yang, W., Luo, Y., Baochao, L. I., & Liu, D. (2019). Transport accessibility and spatial connections of cities in the guangdong-hong kong-macao greater bay area. Chinese Geographical Science, 29, 820–833.
Chang, Y. C., & Leu, L. Y. (1998). A state space model for software reliability. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 50(4), 789–799.
Chen, H., & Meng, J. (2017). Emissions inventory and scenario analyses of air pollutants in Guangdong Province. China. Frontiers of Earth Science, 11(1), 46–62.
Chen, J., & Wang, J. (2021). How Can the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Expedite a New System of Opening-Up?. In Studies on China’s Special Economic Zones 4 (pp. 209–224). Springer, Singapore.
Deng, H., & Li, H. (2021). Characteristics of the spatiotemporal changes in urban agglomeration in the Guangdong-Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 147(4), 04021042.
Diao, S., Yuan, J., & Wu, Y. (2019). Performance evaluation of urban comprehensive carrying capacity of Harbin, Heilongjiang Province in China. Chinese Geographical Science, 29(4), 579–590.
El-Shinnawy, N. A., Heikal, S., & Fahmy, Y. (1983). Saccharification of cotton bolls by Concentrated sulphuric acid. Research and Industry, 28(2), 123–126.
Fahmy, T. Y. A., Fahmy, Y., Mobarak, F., et al. (2020). Biomass pyrolysis: Past, present, and future. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22, 17–32.
Fahmy, Y., Fadl, M. H., & El-Shinnawy, N. A. (1975). Saccharification of cotton stalks. Research and Industry, 20(1), 7–10.
Fahmy, Y., Fahmy, T. Y. A., Mobarak, F., et al. (2017). Agricultural residues (wastes) For manufacture of paper, board, and miscellaneous products: Background overview And future prospects. International Journal of ChemTech Research, 10, 424–448.
Fahmy, Y., Mobarak, F., & Schweers, W. (1982). Pyrolysis of agricultural residues. II. Yield and chemical composition of tars and oils produced from cotton stalks, and Assessment of lignin structure. Cellulose Chemistry and Technology, 16, 453–459.
Huang, S. L., & Chen, C. S. (1990). A system model to analyse environmental carrying capacity for managing urban growth of the taipei metropolitan region. Journal of Environmental Management, 31(1), 47–60.
Hui, E. C., Li, X., Chen, T., & Lang, W. (2020). Deciphering the spatial structure of China’s megacity region: A new bay area—The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in the making. Cities, 105, 102168.
Hu, S., & Kim, H. H. (2022). Research on urban innovation efficiency of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area based on DEA-Malmquist model. Annals of Operations Research, 326, 1–14.
Kornoushenko, E. K. (2016). Goal-oriented state control of a cognitive linear model with a bounded state space. Automation and Remote Control, 77(1), 133–143.
Kurek, J. E. (1985). The general state-space model for a two-dimensional linear digital system. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 30(6), 600–602.
Lau, S. K. (2019). China’s Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao greater bay area: a new development opportunity for Hong Kong. Public Administration and Policy.
Lin, G. C., & Ma, L. J. (1994). The role of towns in Chinese regional development: The case of Guangdong Province. International Regional Science Review, 17(1), 75–97.
Lu, W. M., & Lo, S. F. (2007). A closer look at the economic-environmental disparities for regional development in China. European Journal of Operational Research, 183(2), 882–894.
Mobarak, F. (1983). Rapid continuous pyrolysis of cotton stalks for charcoal Production. Holzforschung, 37(5), 251–254.
Mobarak, F., Fahmy, Y., & Schweers, W. (1982). Production of phenols and charcoal From bagasse by a rapid continuous pyrolysis process. Wood Science and Technology, 16, 59–66.
Patankar, R., & Qu, R. (2005). Validation of the state-space model of fatigue crack growth in ductile alloys under variable-amplitude load via comparison of the crack-opening stress data. International Journal of Fracture, 131(4), 337–349.
Peters, G. W., Hosack, G. R., & Hayes, K. R. (2010). Ecological non-linear state space model selection via adaptive particle markov chain monte carlo (adpmcmc). statistics.
Weng, H., Kou, J., & Shao, Q. (2020). Evaluation of urban comprehensive carrying capacity in the Guangdong-Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area based on regional collaboration. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(16), 20025–20036.
**e, H., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Peng, Q., Liao, Z., & Zhu, J. (2021). A case study of development and utilization of urban underground space in Shenzhen and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 107, 103651.
You, X., Li, Q., Monahan, K. M., Fan, F., Ke, H., & Hong, N. (2022). Can collaborative innovation constrain ecological footprint? Empirical Evidence From Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 1–16.
Ye, L. (2019). Evaluation of urban development quality based on the connotation of high-quality development: A case study of guangdong province. Journal of Landscape Research, 11(2), 83–94.
Zhang, X. (2021). Create a Strategic System for Ecological Civilization Development in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. In Beautiful China: 70 Years Since 1949 and 70 People’s Views on Eco-civilization Construction (pp. 379–389). Springer, Singapore.
Zhao, L., Li, J., & Shao, Q. (2020). Evaluation of urban comprehensive carrying capacity: Case study of the Bei**g–Tian**–Hebei urban agglomeration. China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(16), 19774–19782.
Zhou, Y., Shan, Y., Liu, G., & Guan, D. (2018). Emissions and low-carbon development in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area cities and their surroundings. Applied Energy, 228, 1683–1692.
Funding
This research was funded by Shandong Provincial Federation of Social Science Humanities and Social Sciences Project “Research on the social impact and governance system of the commercialization of new generation artificial intelligence”, Award number:2023-zkzd-055; National Social Science Foundation Youth Project “Research on the Construction Mechanism and Social Support System Optimization of Families of Disabled Children”, Award number:23CSH095; Shandong Provincial Social Science Planning Research Project “Construction of the Social Work System for Disabled Persons in Shandong Province Based on the Bio-Psycho-Social Model and optimization research”, Award number:23DSHJ04.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Our research data is publicly available.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Zhang, G. Evaluation and influencing factors of resources and environment carrying capacity of Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area Economic Belt. Environ Dev Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04428-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04428-x