Abstract
This study empirically analyzes the impacts of e-commerce adoption by Chinese agri-food companies on their financial performance, with a nationwide dataset of Chinese agri-food companies. Results show that, on average, the adoption of e-commerce can significantly improve the financial performance of Chinese agri-food companies by 20%. The impacts of e-commerce adoption on financial performance are heterogeneous regarding enterprise scale, industry type, enterprise ownership, enterprise location, and enterprise maturity. In light of these findings, this study discusses the suggestions to encourage e-commerce adoption and improve the financial performance of companies from the perspectives of business operators and policymakers.

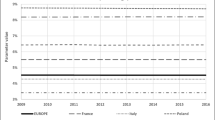
(Source: Ministry of Commerce of China)

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Our focus is not on establishing causal differences in the impact of e-commerce adoption across different enterprises. Instead, we explored correlations to illuminate how enterprises, based on size, ownership, location, industry type and maturity, responded differently to e-commerce adoption.
References
Behzadi, G., O’Sullivan, M. J., Olsen, T. L., & Zhang, A. (2018). Agribusiness supply chain risk management: A review of quantitative decision models. Omega, 79(01), 21–42.
Chae, H., Koh, C., & Park, K. (2018). Information technology capability and firm performance: Role of industry. Information & Management, 55(05), 525–546.
Dong, X., & Yuan, Y. (2014). Firm innovation, life cycle and agglomeration economies. China Economic Quarterly, 13(02), 767–792.
He, S., Huang, X., & Chen, Q. (2016). Does manager’s environmental cognitive improve firms performance? The mediating role of proactive environmental strategy and the moderating role of business environmental uncertainty. Nankai Business Review, 19(06), 49–57.
Hu, H., Zhu, S., Li, S., Ye, Y., Hu, H., Chen, Y., & Shu, N. (2015). Research on the development strategy of online merchants in Taobao Village: Taking China’s “First Village of Online Stores” as an example in Qingyan Liucun, Yiwu. Zhejiang. China Market, 45, 93–94.
Kartiwi, M., & MacGregor, R. C. (2007). Electronic commerce adoption barriers in small to medium-sized companies (SMEs) in developed and develo** countries: A cross-country comparison. Journal of Electronic Commerce in Organizations (JECO), 5(03), 35–51.
Kurnia, S., Karnali, R. J., & Rahim, M. (2015). A qualitative study of business-to-business electronic commerce adoption within the Indonesian grocery industry: A multi-theory perspective. Information & Management, 52(04), 518–536.
Li, H. (2015). Research on the relationship between institutional environment, green entrepreneurship orientation and performance. Social Science Journal, 02, 92–99.
Li, L., Lin, J., Turel, O., Liu, P., & Luo, X. R. (2020). The impact of e-commerce capabilities on agricultural firms’ performance gains: The mediating role of organizational agility. Industrial Management & Data Systems.
Li, X., Guo, H., **, S., Ma, W., & Zeng, Y. (2021). Do farmers gain internet dividends from e-commerce adoption? Evidence from China. Food Policy, 101, 102024.
Lin, J., Li, L., Luo, X., & Benitez, J. (2020a). How do agribusinesses thrive through complexity? The pivotal role of e-commerce capability and business agility. Decision Support Systems, 135.
Lin, J., Lu, X. Y., Zhang, J. S., & Zheng, Y. (2020b). State-owned enterprises in China: A review of 40 years of research and practice. China Journal of Accounting Research, 13(1), 31–35.
Lin, T. (2003). Vigorously develop agri-food companies and promote agricultural industrialization. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 02, 8–9.
Liu, D., & Zhang, B. (2018). Ownership structure and dual performance of rural commercial banks: Impact mechanism and empirical test. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 02, 60–70.
Luo, Z. (2015). E-commerce talent training mode for building home textile industry cluster. Contemporary Economics, 14, 53–55.
Ma, W., Grafton, R. Q., & Renwick, A. (2020). Smartphone use and income growth in rural China: Empirical results and policy implications. Electronic Commerce Research, 20(4), 713–736.
Montealegre, F., Thompson, S., & Eales, J. S. (2007). An empirical analysis of the determinants of success of food and agribusiness e-commerce firms. International Food and Agribusiness Management Review, 10(01), 61–81.
Moschini, G., & Hennessy, D. A. (2001). Uncertainty, risk aversion, and risk management for agricultural producers. Handbook of agricultural economics, 1, 87–153.
Nto, P. O. O., Mbanasor, J. A., & Nwaru, J. C. (2011). Analysis of risk among agribusiness companies investment in Abia State, Nigeria. Journal of Economics and International Finance, 3(03), 187–197.
Pool, B. (2001). How will agricultural E-Markets evolve?. Agricultural Outlook Forum 2001.
Qi, J., Zheng, X., Cao, P., et al. (2019). The effect of e-commerce agribusiness clusters on farmers’ migration decisions in China. Agribusiness, 35(1), 20–35.
Qiu, Y., & Wei, W. (2016). The impact of R&D investment on enterprise performance: A research based on propensity score matching method. Contemporary Finance & Economics, 03, 96–106.
Solaymani, S., Sohaili, K., & Yazdinejad, E. A. (2012). Adoption and use of e-commerce in SMEs: A case study. Electronic Commerce Research, 12, 249–263.
Song, Y., Wu, W., & Miocevic, D. (2022). Farmers’ choice between endogenous vs. exogenous e-commerce: alignment with resources and performance goals. British Food Journal, 124(01), 61–77.
Tang, G., Chen, L., Chen, Y., & Liu, S. (2019). Commitment to human resource management of top management team, green human resource management and firm performance: The moderating effect of firm size. Nankai Business Review, 22(04), 212–224.
Wang, D. (2017). E-commerce industrial spatial agglomeration and regional talent training of cluster reconstruction: A case study of Yiwu business circle of “E-Commerce Industrial Park” and “Taobao Village.” Business & Economy, 02, 19–21.
Wang, Y., & **e, W. (2015). Research on the influence of managerial ties on firm performance in transitonal environments. Journal of Management Science, 28(06), 39–49.
Wang, Y., Liu, J., & Wu, H. (2019). The empirical study on the impact of replacing business tax to value-added tax on financial performance of real estate industry. Journal of Technical Economics & Management, 02, 9–13.
Wu, Z., & Liu, Y. (2021). Could regional integration promote enterprise performance?: An empirical study based on quasi-natural experiment of the Yangtze River delta urban economic coordination commission. West Forum, 31(02), 61–76.
**e, J., & Hu, G. (2020b). An empirical study on influencing factors of e-commerce behavior adoption and e-commerce performance of agri-food companies—based on the experience data of agricultural industrialization leading companies. Soft Science, 34(08), 6–11+18.
Xu, Y., & Cai, Q. (2019). The influence of hi-tech companies recognition on enterprise’s innovation and financial performance—based on RDD. Fudan Journal (Social Sciences Edition), 61(06), 139–150.
Xu, N., **e, R., & Wu, S. (2019). Chinese-style family business management: Governance model, leadership model and firm performance. Economic Research Journal, 54(12), 165–181.
Ye, C., Qiu, L., & Zhang, L. (2016). Corporate governance structure, internal control quality and corporate financial performance. Auditing Research, 02, 104–112.
Zeng, Y., & Guo, H. (2016). The income-added effect of specialized village’s e-commercialization. Journal of South China Agricultural University (Social Science Edition), 15(06), 104–113.
Zhang, J., & Tian, L. (2019). An empirical study on the impact of capital structure of asset-light companies on financial performance. Commercial Accounting, (12), 47–49+112.
Zhu, B., Song, Y., Li, G., & Yu, T. (2016). Spatial aggregation pattern and influencing factors of “Taobao Village” in China under the C2C e-commerce model. Economic Geography, 36(04), 92–98.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72103180; 72161147001, 71861147002), National Office for Philosophy and Social Sciences (21&ZD091, 21&ZD092), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (S20230068), the Ministry of Education of China (22JJD790077), the Zhejiang Province Soft Science Research Program (“Research on the Mechanism, Effects, and Policy Optimization of Digitization Empowering Value Addition throughout the Agricultural Industry Chain”, No. 2024C35001), Zhejiang Province Philosophy and Social Science Planning Leading Talent Cultivation Project General Subproject (No. 24YJRC01ZD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, C., Dong, X. & Lin, W. The effects of e-commerce adoption on the financial performance of agri-food enterprises in China. Electron Commer Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-024-09810-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-024-09810-z